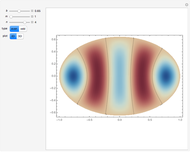
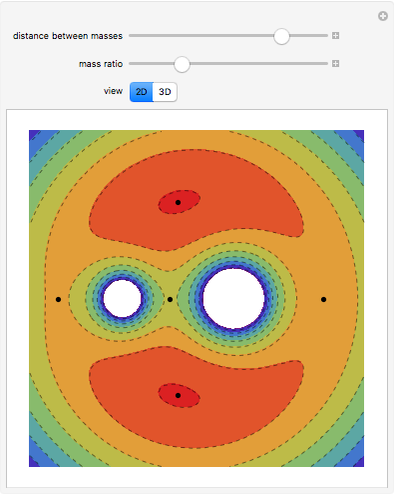
Acoustic Dipole in a Duct

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
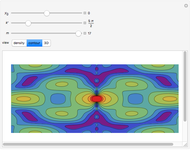
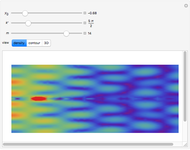
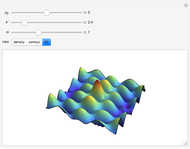
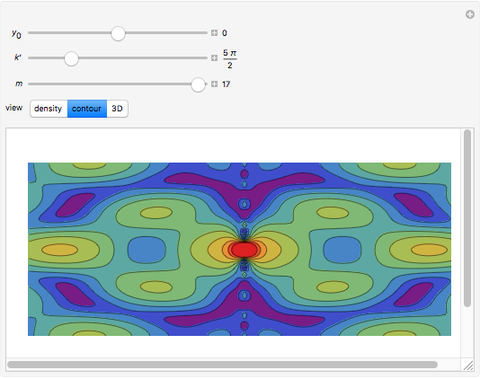
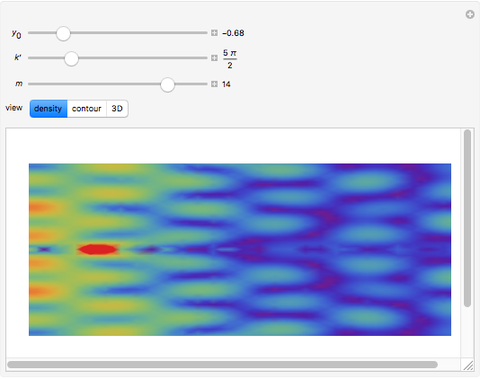
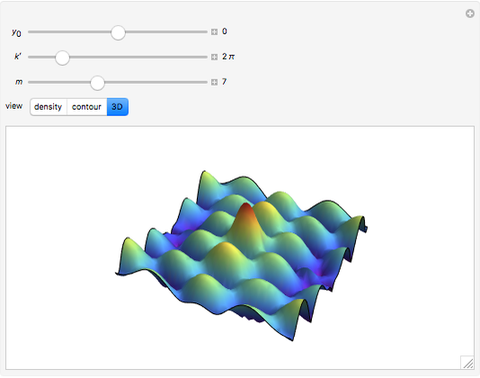
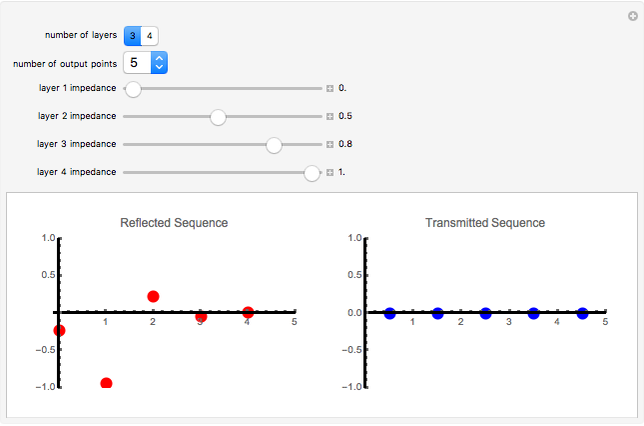
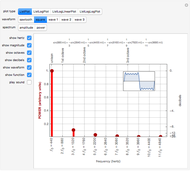
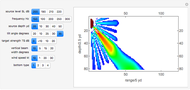
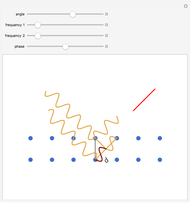
An acoustic dipole oriented along the  axis is placed in a duct. The dipole can be moved along the
axis is placed in a duct. The dipole can be moved along the 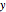 axis. The resulting sonic radiation can be approximated by an
axis. The resulting sonic radiation can be approximated by an 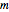 -term Fourier series, given in the Details section, with
-term Fourier series, given in the Details section, with 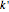 representing the Helmholtz number (the cut-off frequency of a duct, product of the wavenumber and the duct radius) in multiples of
representing the Helmholtz number (the cut-off frequency of a duct, product of the wavenumber and the duct radius) in multiples of 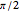 .
.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (January 2014)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The solution for the pressure is
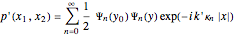 ,
,
with
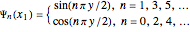
and
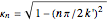 .
.
Reference
[1] M. Gupta, "Simulation and Visualization of Various Acoustic Sources in MATLAB." (2006) wenku.baidu.com/view/9ca5d912f18583d049645990.
Permanent Citation