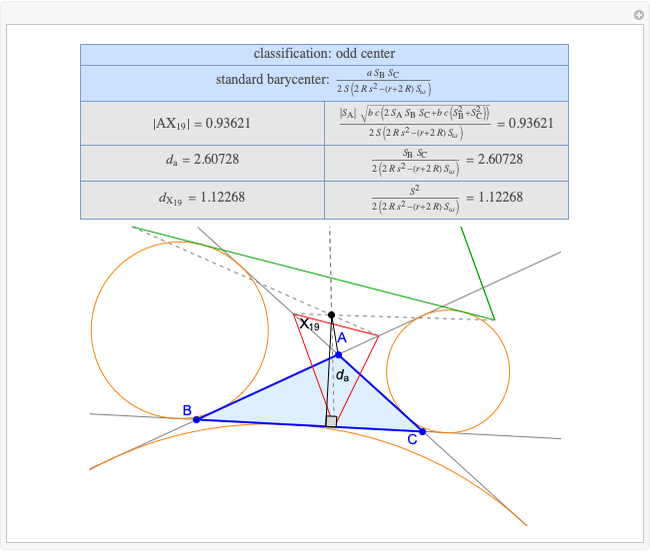
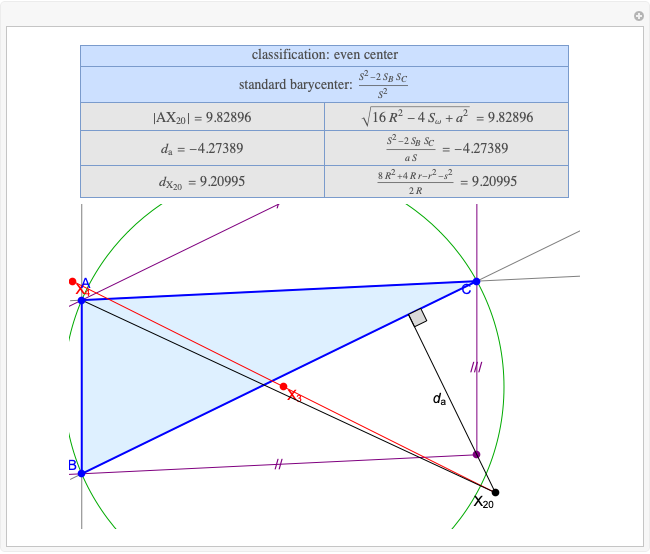
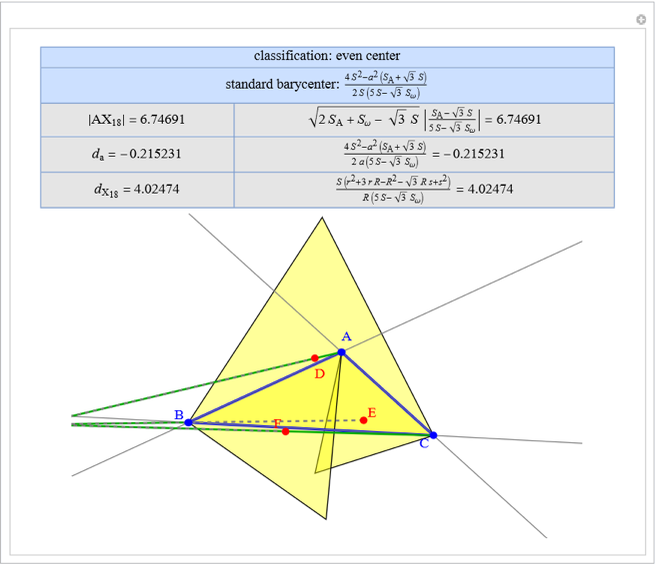
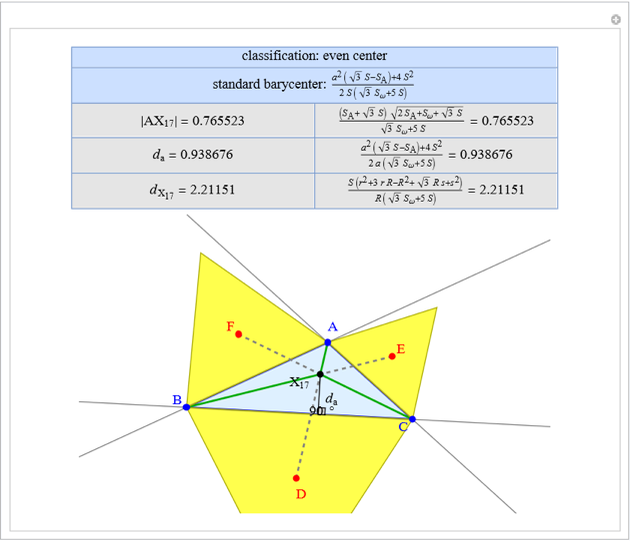
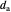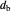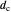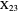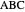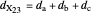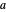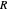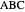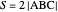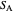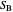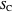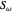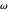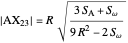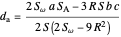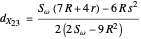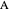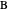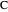Basic Parameters of the Far-Out Point

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
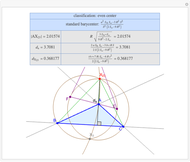
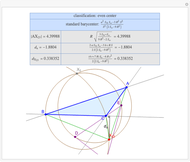
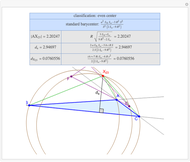
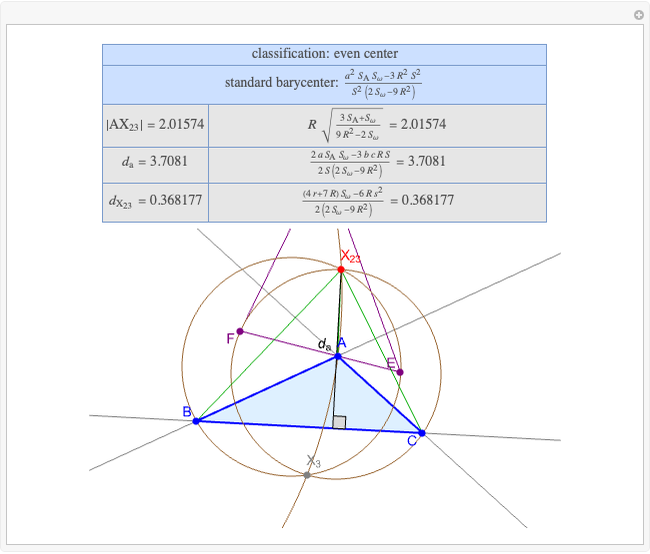
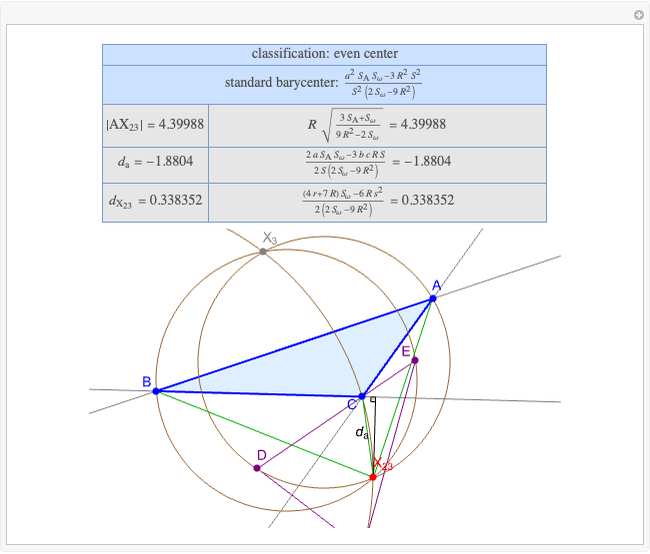
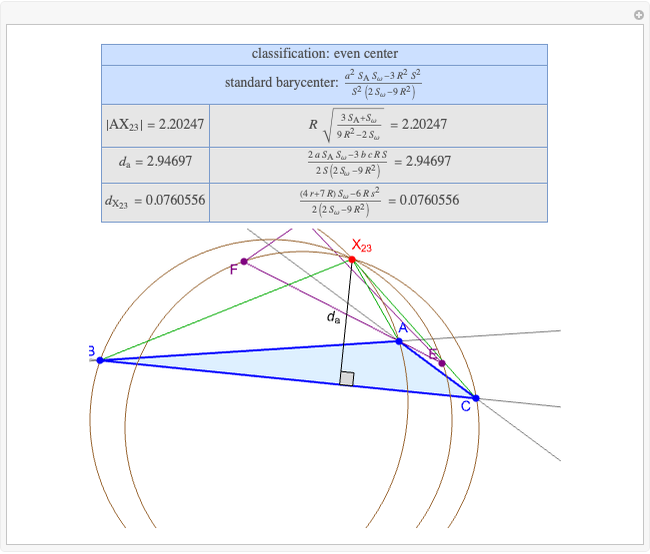
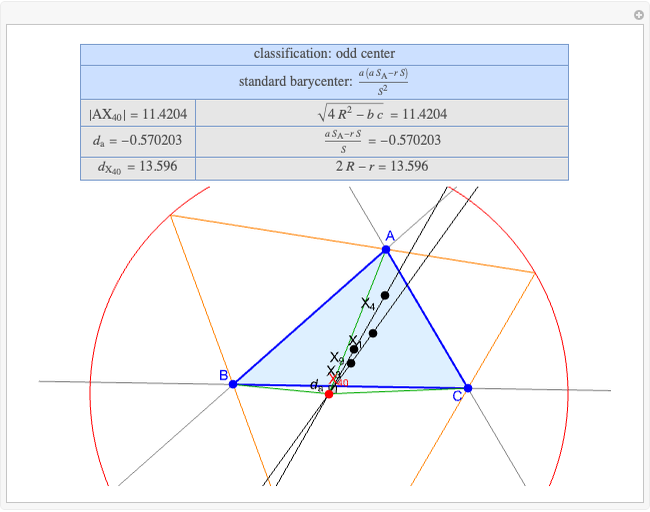
Given a triangle  , let
, let  be its circumcenter and
be its circumcenter and  be its tangential triangle (shown in purple). Then the circumcircles of the three triangles
be its tangential triangle (shown in purple). Then the circumcircles of the three triangles 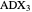 ,
, 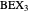 ,
, 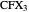 intersect at the "far-out point"
intersect at the "far-out point" 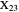 (Randy Hutson, October 13, 2015) [1].
(Randy Hutson, October 13, 2015) [1].
Contributed by: Minh Trinh Xuan (January 2023)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
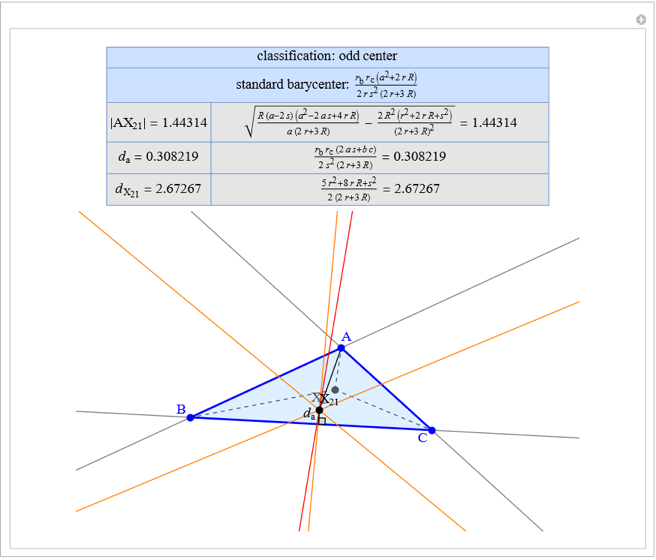
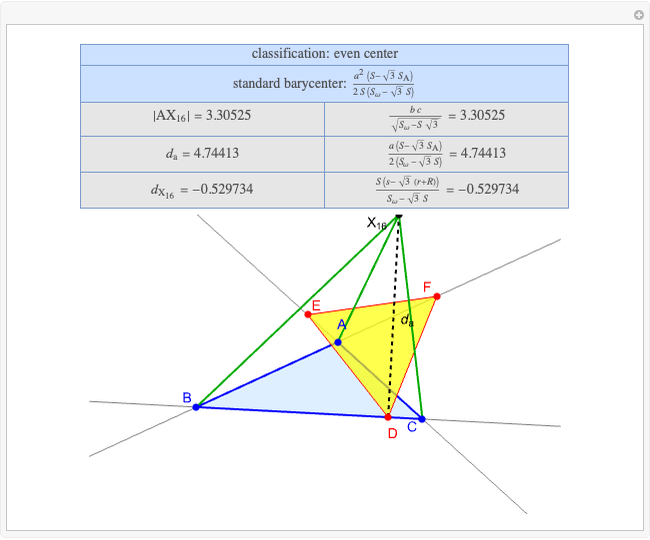
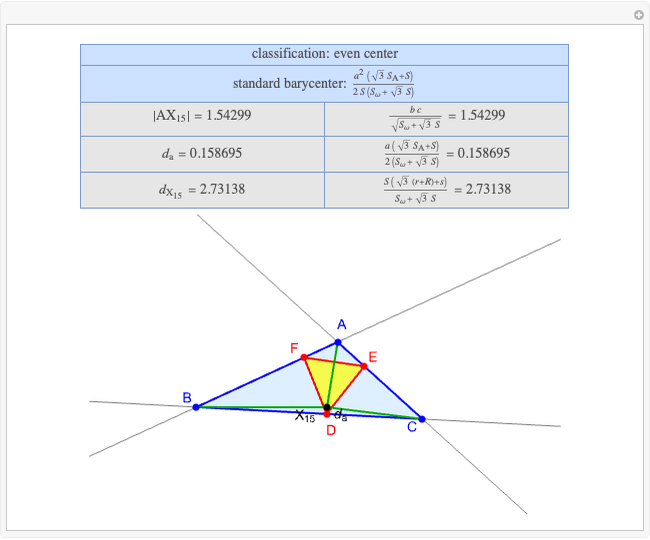
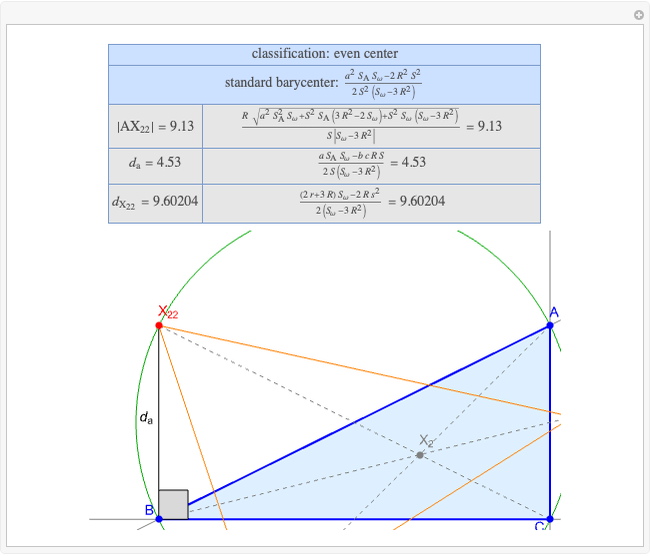
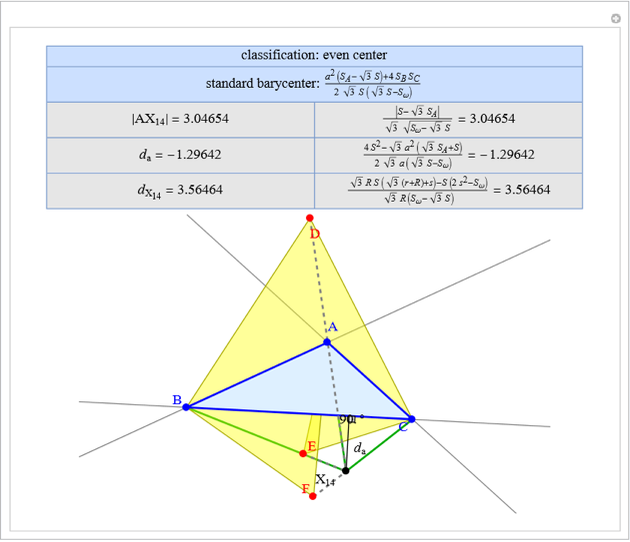
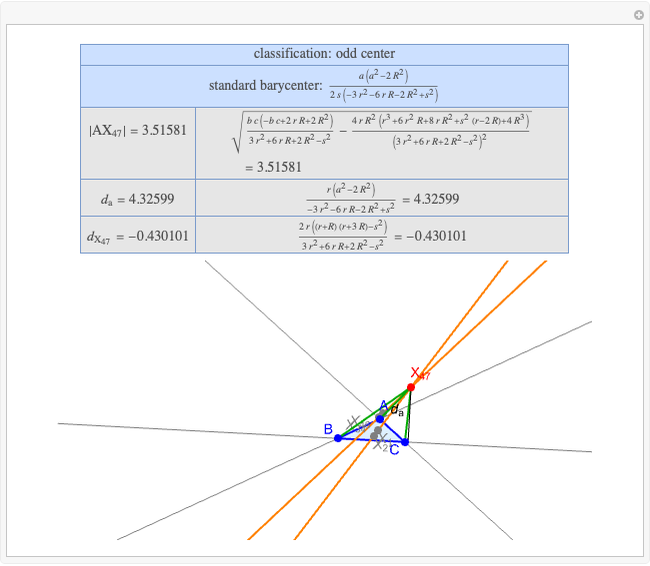
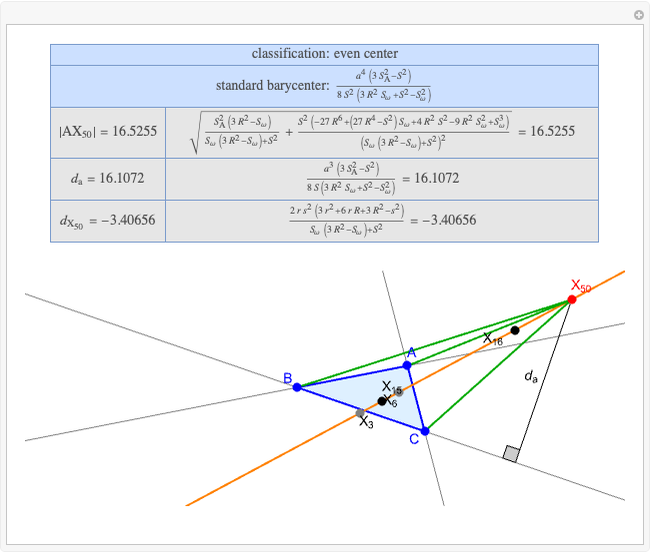
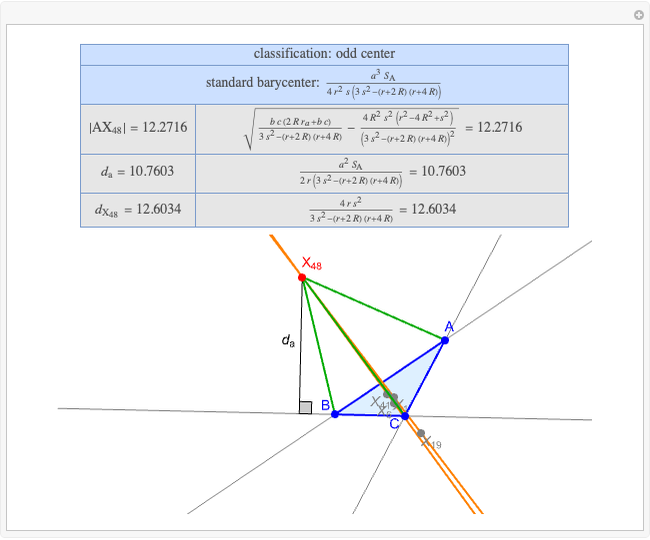
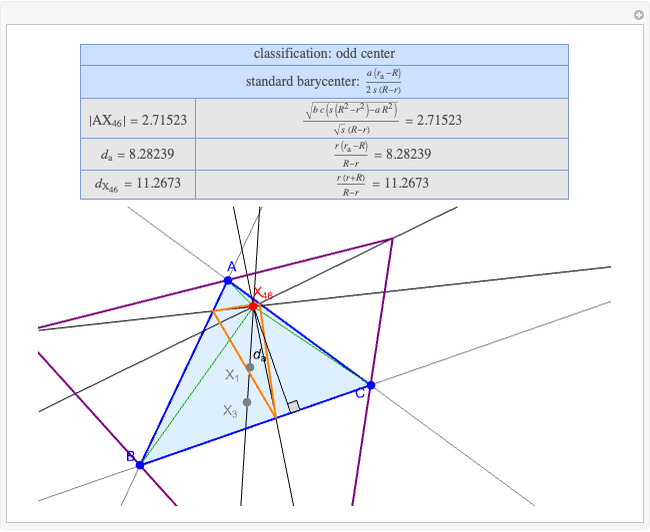
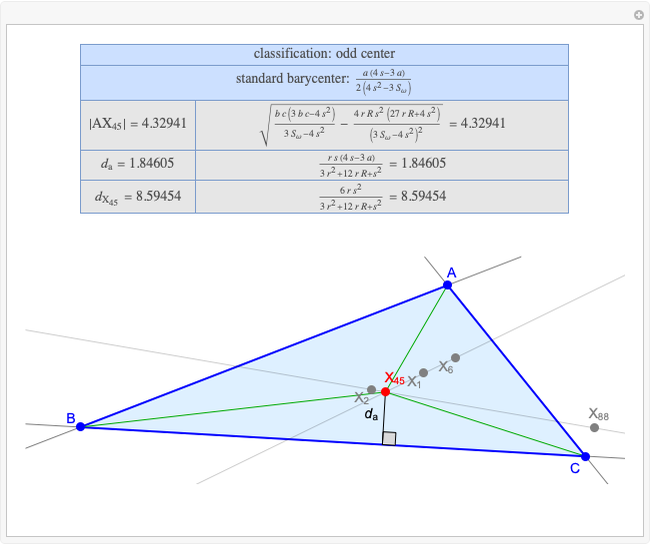
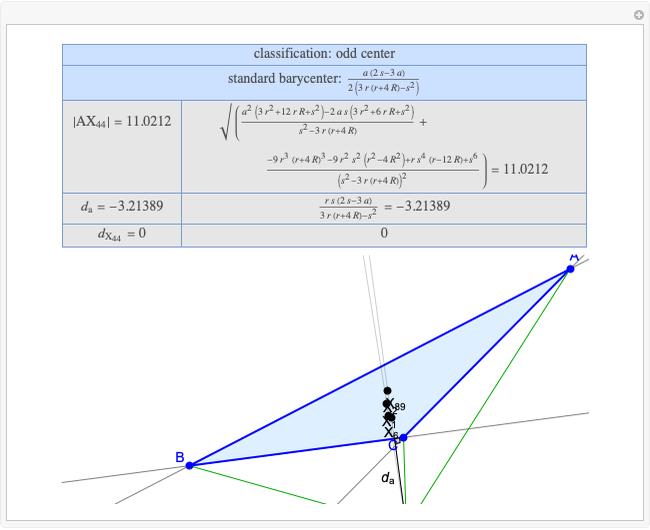
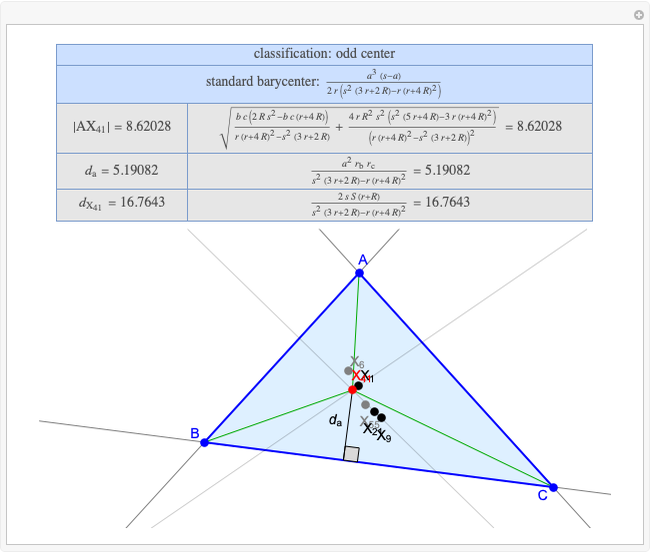
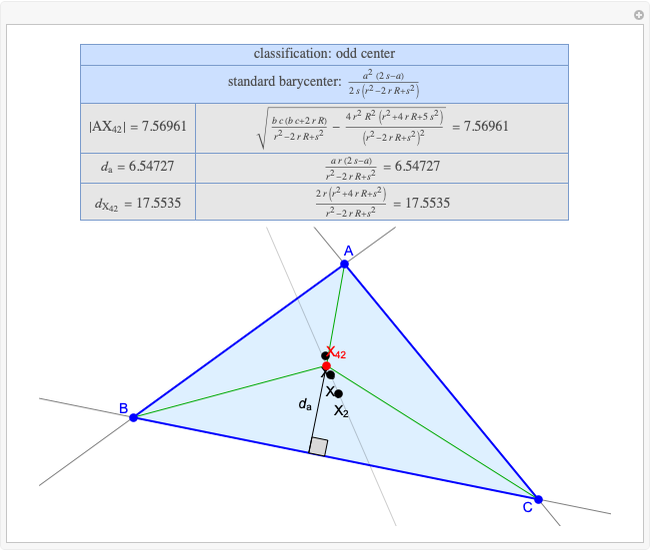
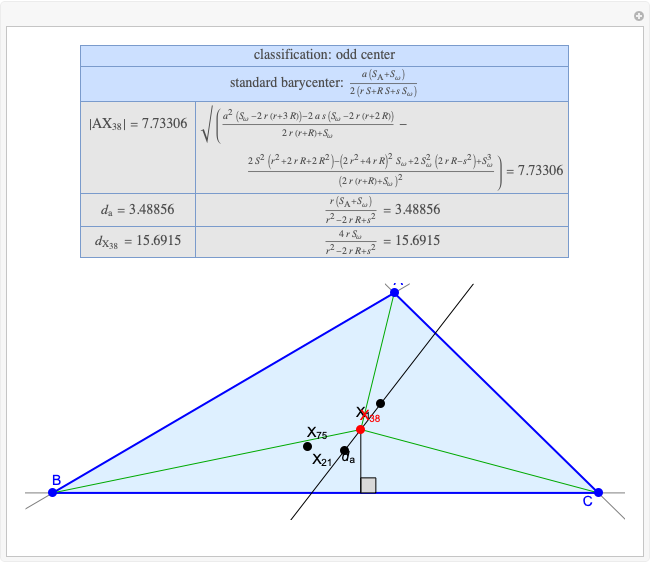
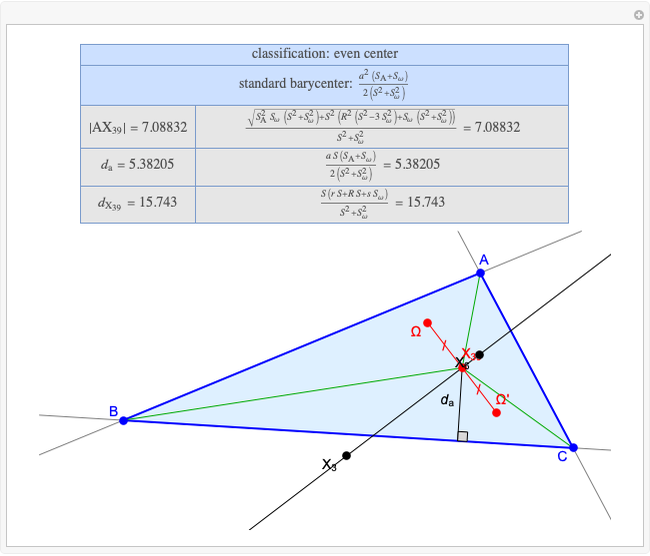
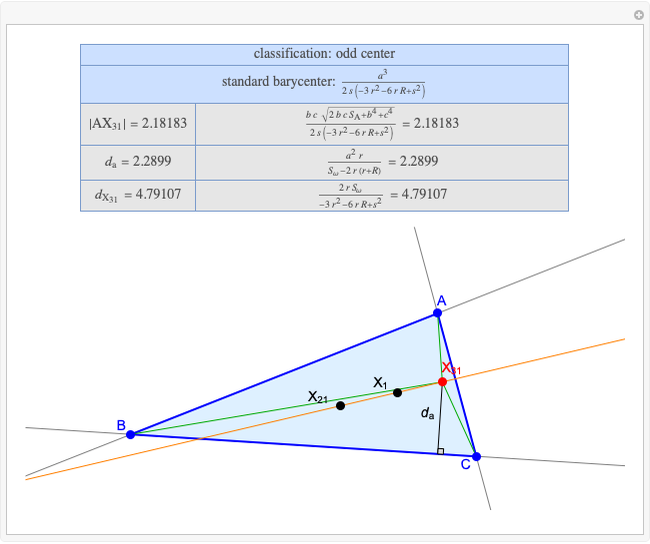
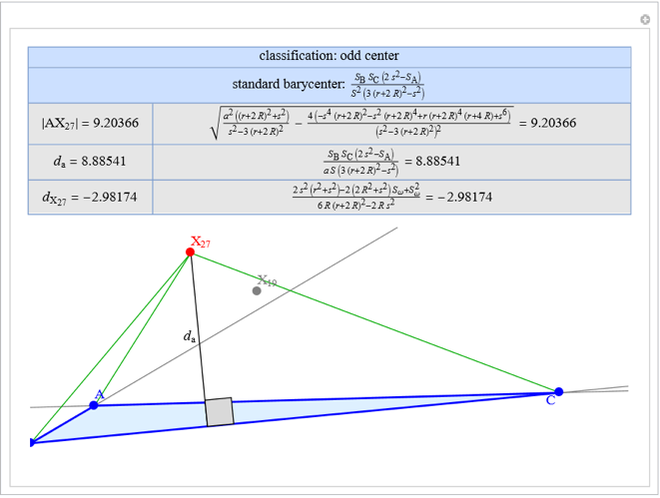
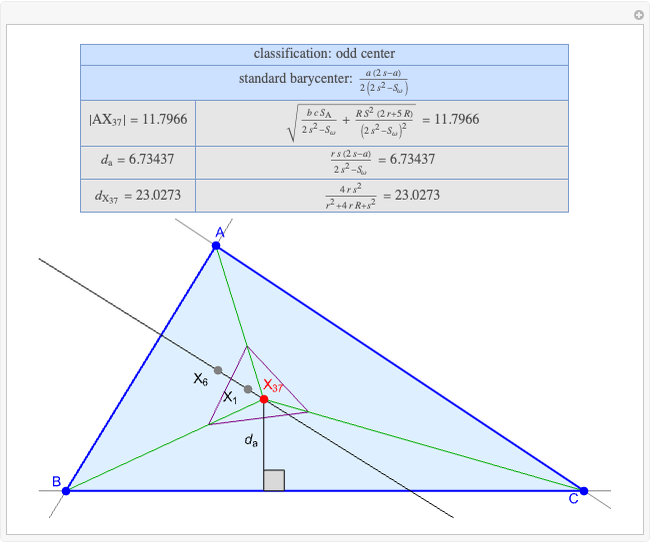
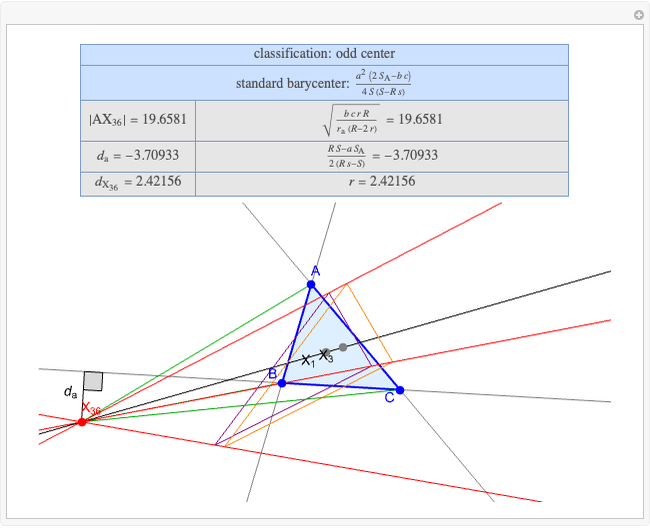
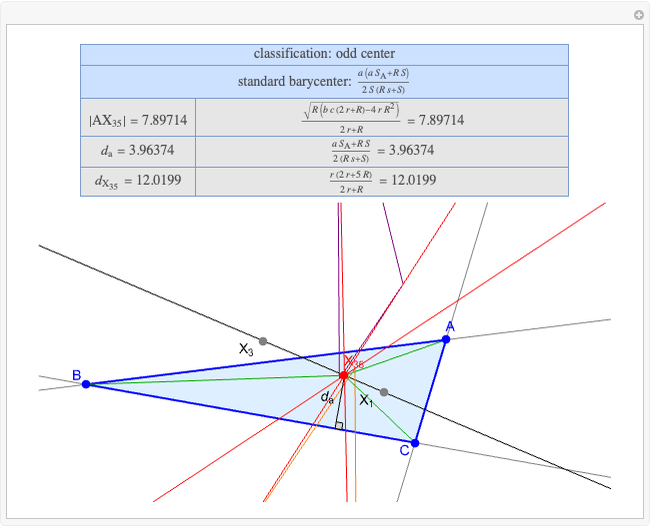
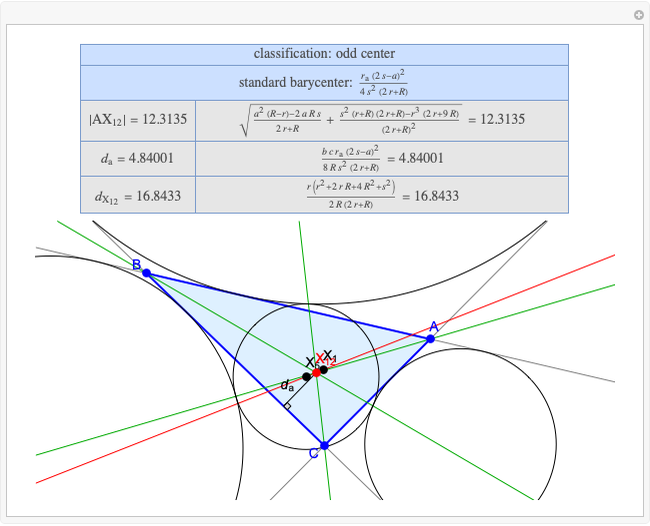
A triangle center is said to be even when its barycentric coordinates can be expressed as a function of three variables 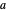 ,
,  ,
,  that all occur with even exponents. If the center of a triangle has constant barycentric coordinates, it is called a neutral center (the centroid
that all occur with even exponents. If the center of a triangle has constant barycentric coordinates, it is called a neutral center (the centroid 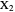 is the only neutral center). A triangle center is said to be odd if it is neither even nor neutral.
is the only neutral center). A triangle center is said to be odd if it is neither even nor neutral.
Standard barycentric coordinates of a point with respect to a reference triangle have a sum of 1.
Reference
[1] C. Kimberling. "Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers." (Sep 27, 2022) faculty.evansville.edu/ck6/encyclopedia.
Permanent Citation