Constructing Vector Geometry Solutions

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
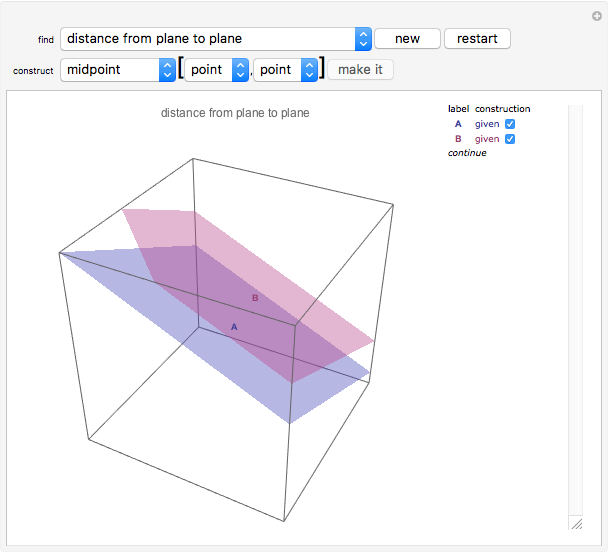
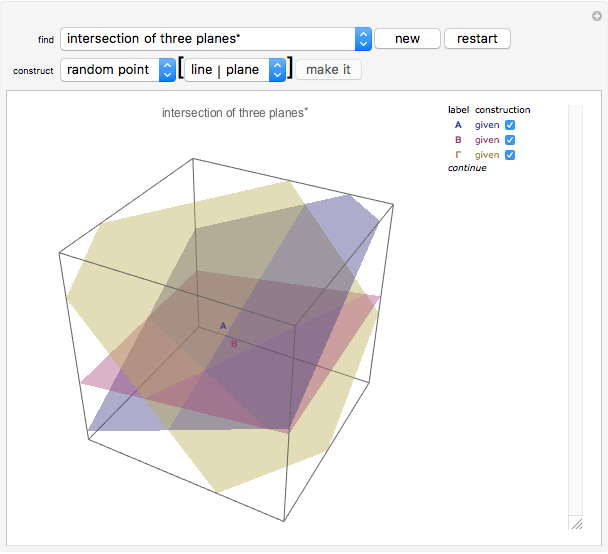
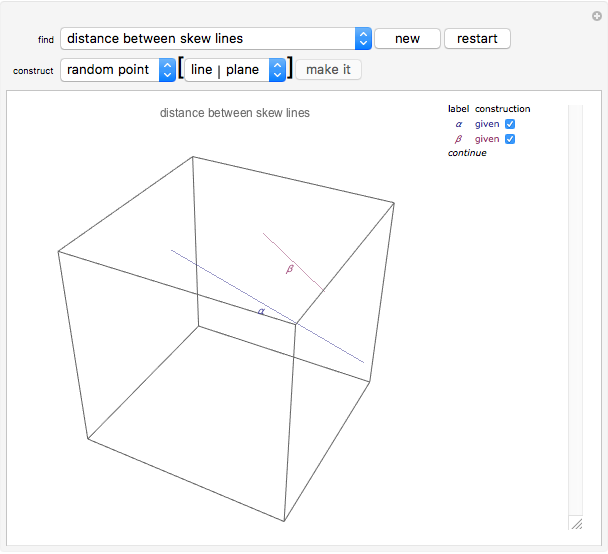
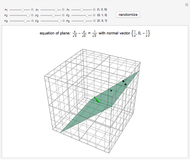
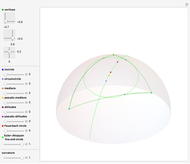
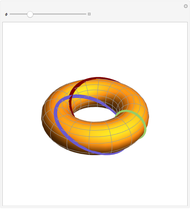
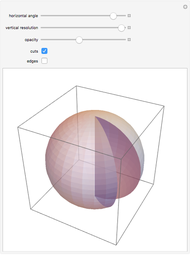
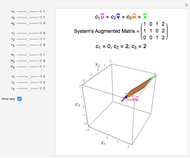
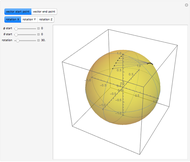
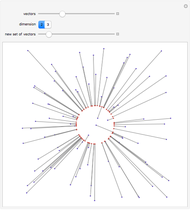
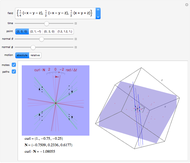
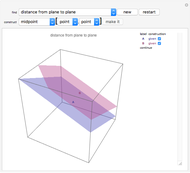
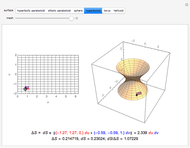
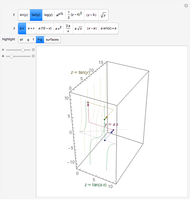
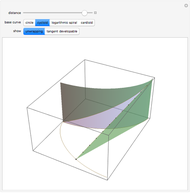
This Demonstration presents over twenty problems in three-dimensional geometry, whose solutions are to be constructed with standard vector methods from existing objects. The problems are stated succinctly, sometimes omitting necessary conditions. Construct each object needed to find the object sought from the given objects. Hide or delete objects with the checkbox or button, respectively; scalars are not displayed. This Demonstration will display "YOU FOUND IT!!!" when the object sought is constructed.
Contributed by: Michael Rogers (Oxford College of Emory University) (April 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Only vector methods are supported, except for picking a random point on a line or plane. Intersections, which are granted in ordinary geometry, must be constructed. The only way to construct a line is by a point on the line and a direction vector; a plane by a point on the plane and a normal vector. For convenience, constructing a projection and a midpoint are included. Also for convenience, direction and normal vectors for lines and planes are unit vectors. The spirit of this Demonstration is akin to synthetic geometry and not to analytic geometry. For this reason, analytic vector methods (that is, coordinate methods) are not provided.
Starred problems may require some pencil-and-paper work and the law of sines or the law of cosines might be helpful. Of course it may be easier to work out every problem with pencil and paper first.
All problems ask you to construct a point, line, plane, or scalar distance bearing a certain relation to given objects. Click "new" to get a new set of given objects. Click "restart" to start over with the same given objects.
Construction methods: Select the method and argument(s) from the pull-down menus. Click the "make it" button to create the object.
random point: Picks a random point on a selected line or plane; denoted 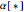 or
or 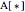 , respectively.
, respectively.
displacement: Create a vector representing the displacement between two selected points; denoted 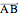 .
.
direction: Create a unit vector parallel to a selected line; denoted  .
.
normal: Create a unit vector normal to a selected plane; denoted 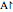 .
.
cross: Create the cross product of two selected vectors; denoted 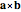 .
.
projection: Create the projection of the first selected vector onto the second; denoted 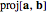 .
.
sum: (1) Create a point that is the result of applying a selected vector to a selected point; (2) create the sum of two selected vectors; denoted 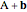 and
and 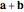 , respectively.
, respectively.
difference: (1) Create a point that is the result of applying the negative of a selected vector to a selected point; (2) create the difference of two selected vectors; denoted  and
and 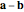 , respectively.
, respectively.
scale (×): Multiply a selected vector by a selected scalar; denoted 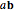 .
.
scale (÷): Divide a selected vector by a selected scalar; denoted 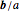 .
.
length: Create a scalar equal to the length (norm) of a selected vector; denoted 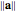 .
.
dot: Create a scalar equal to the length (norm) of a selected vector; denoted 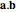 .
.
line: Create a line through a selected point parallel to a selected vector; denoted 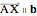 .
.
plane: Create a plane through a selected point normal to a selected vector; denoted 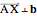 .
.
midpoint: Create the midpoint of two selected points; denoted 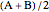 .
.
Permanent Citation