Direct Control for Hex Machine
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
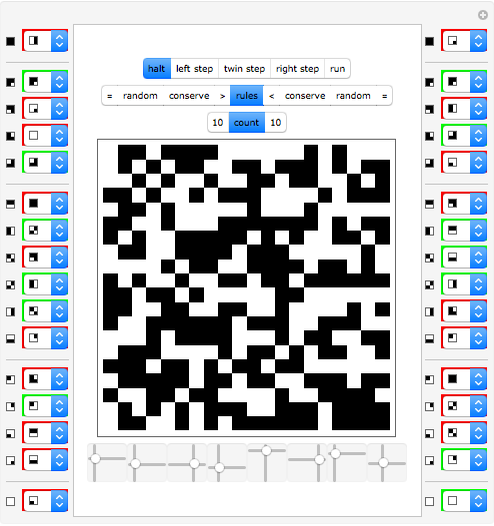
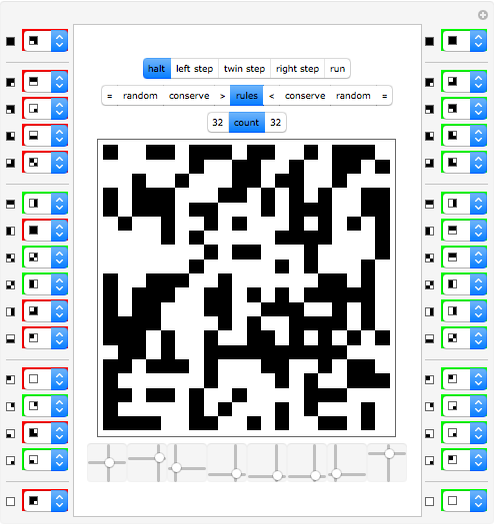
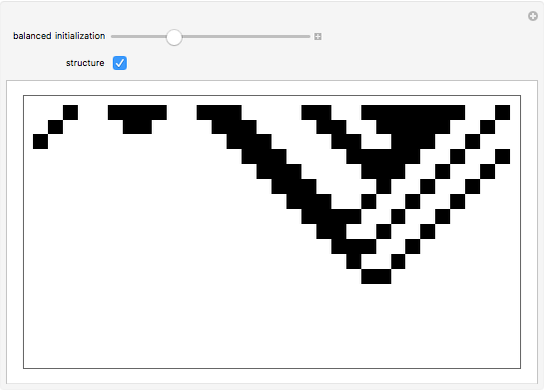
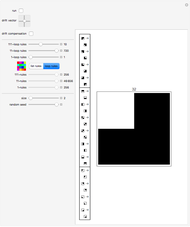
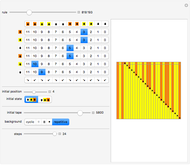
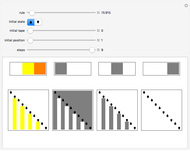
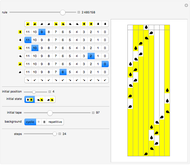
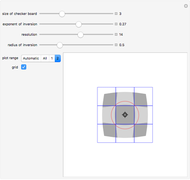
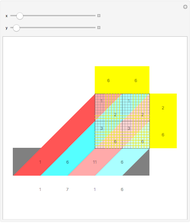
A machine that returns four bits for four bits is called a hex machine.
[more]
Contributed by: Michael Schreiber (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Direct Control for Hex Machine"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/DirectControlForHexMachine/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011