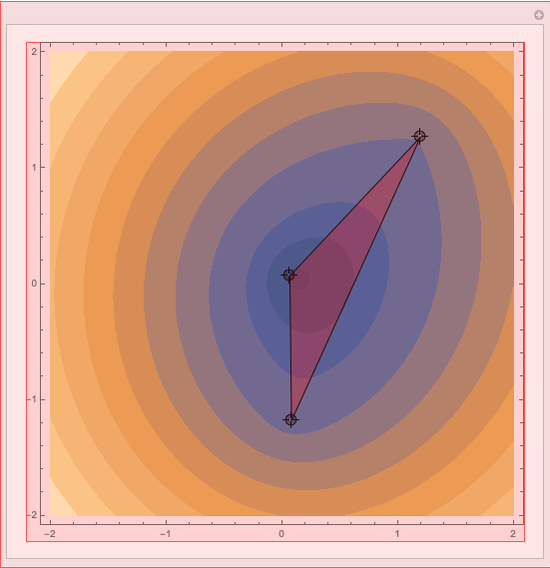
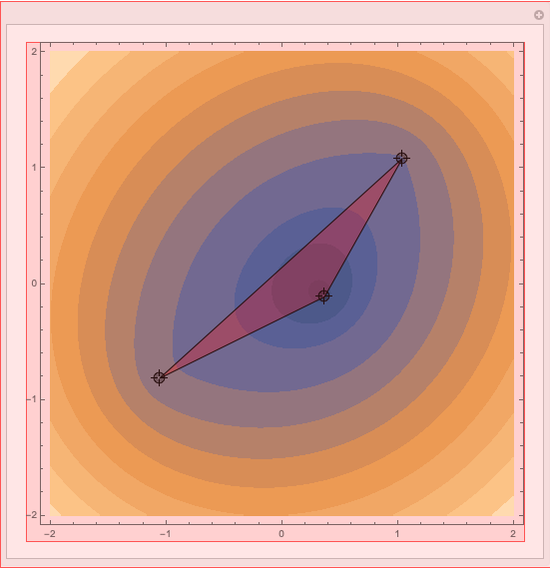
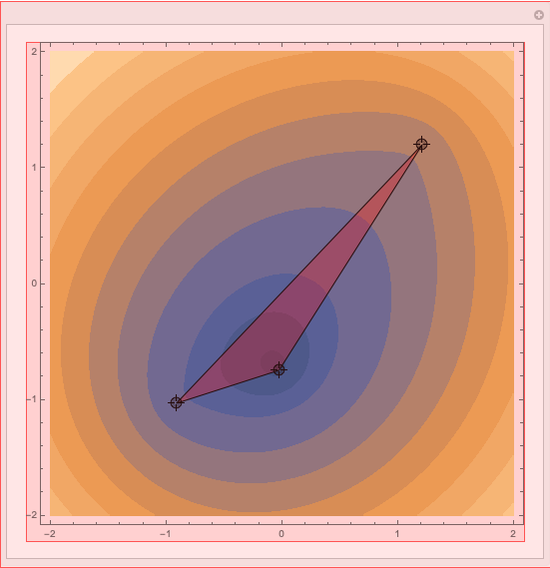
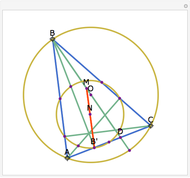
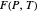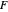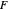First Fermat Point and Isogonic Center of a Triangle

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
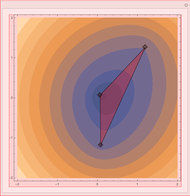
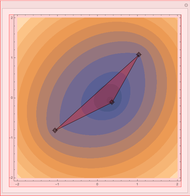
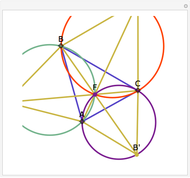
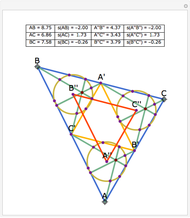
This Demonstration plots the first Fermat point 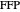 (red) and first isogonic center
(red) and first isogonic center 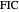 (yellow) of a triangle
(yellow) of a triangle 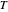 . You can drag the triangle vertices. When
. You can drag the triangle vertices. When 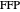 and
and 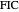 are both inside the triangle, they coincide.
are both inside the triangle, they coincide.
Contributed by: E. Coiras (July 2020)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
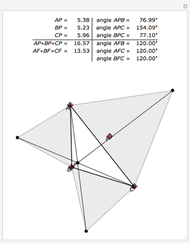
If all the vertex angles are less than 120º, 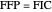 ; otherwise
; otherwise 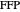 is the obtuse-angled vertex [2]. The use of a closed formula removes the need for such conditional checks.
is the obtuse-angled vertex [2]. The use of a closed formula removes the need for such conditional checks. 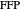 is also the 2D geometric median [3] of the triangle vertices, which as shown here can be calculated by computing two scalar (1D) medians on the corresponding barycentric coordinates [4]. A closed formula for the median of three scalars is also introduced to remove implicit conditional checks.
is also the 2D geometric median [3] of the triangle vertices, which as shown here can be calculated by computing two scalar (1D) medians on the corresponding barycentric coordinates [4]. A closed formula for the median of three scalars is also introduced to remove implicit conditional checks.
References
[1] Wikipedia. "Fermat Point." (Jul 13, 2020) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fermat_point.
[2] C. Kimberling. "X(13)." Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers. (Jul 13, 2020) faculty.evansville.edu/ck6/encyclopedia/ETC.html.
[3] Wikipedia. "Geometric Median." (Jul 13, 2020) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geometric_median.
[4] Wikipedia. "Barycentric Coordinates." (Jul 13, 2020) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barycentric_coordinate_system.
Permanent Citation