Gas Particle Attraction and Repulsion Using Lennard-Jones Potential

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
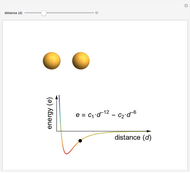
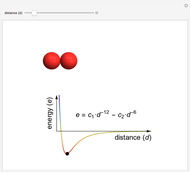
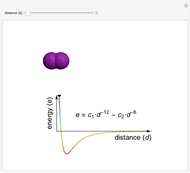
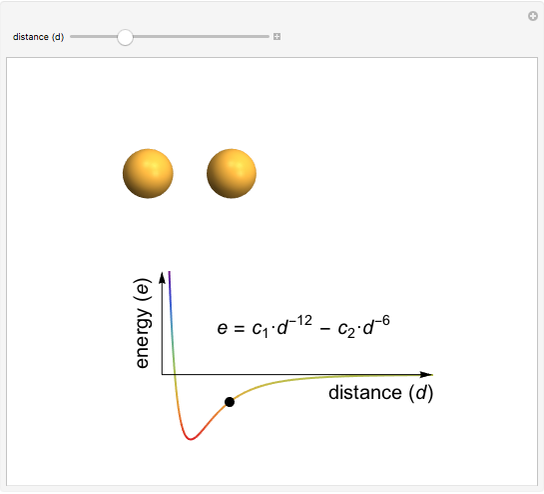
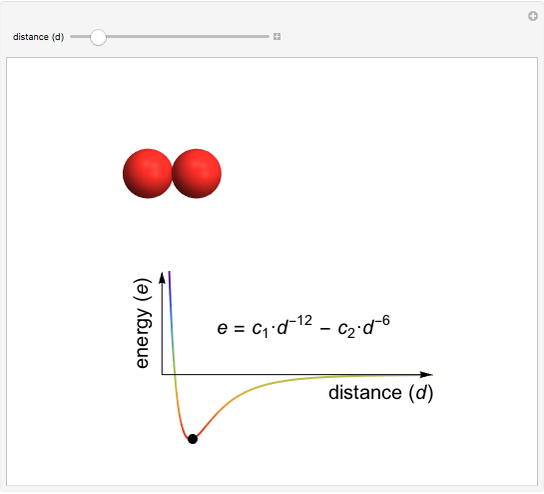
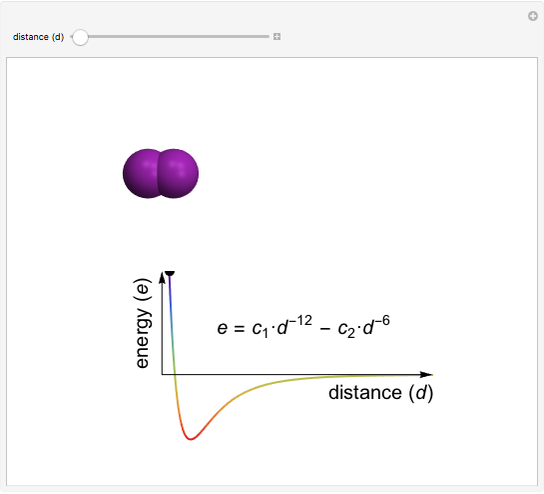
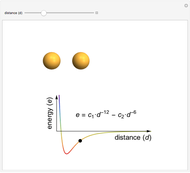
This Demonstration shows how the interactive potential energy of two gas particles varies as a function of separation. If the atoms are far apart, then the energy is effectively zero, represented by a neutral green coloring. Moving closer makes the energy decrease to more red values—this means the atoms are transitioning into a more favorable state and will likely continue to ease into that state. Eventually the atoms reach the mimimum of the curve, where the energy is the lowest (and reddest) it can be. If we keep pushing the atoms closer, however, repulsive interactions come into play, making this configuration energetically unfavorable. This region is shown in violet.
Contributed by: Christopher P. Muzzillo (July 2014)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA