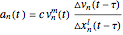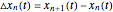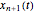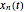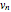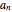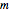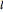Gazis-Herman-Rothery (GHR) Car-Following Model
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
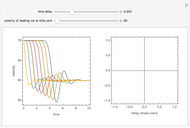
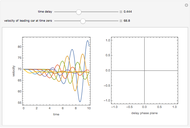
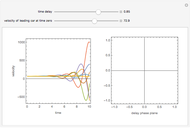
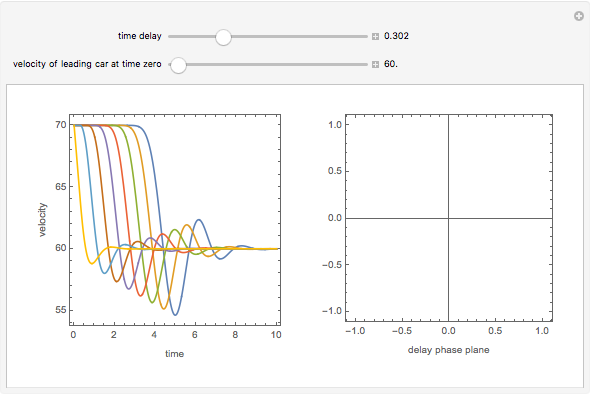
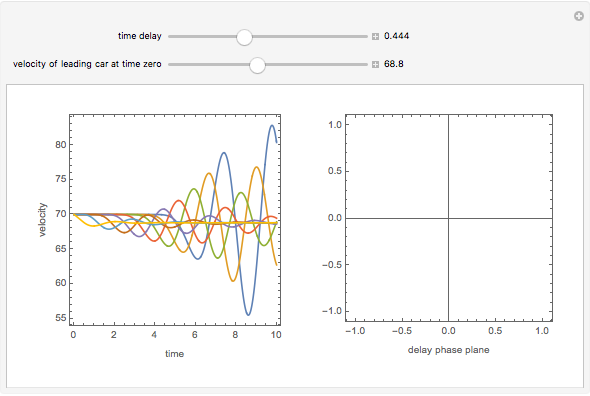
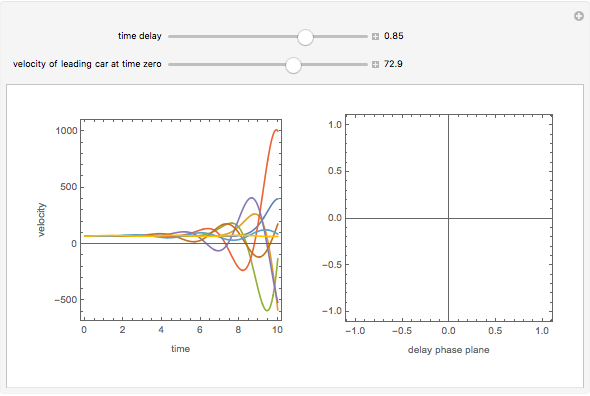
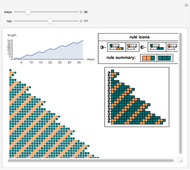
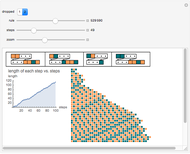
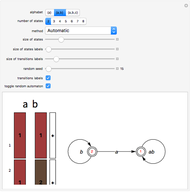
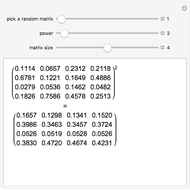
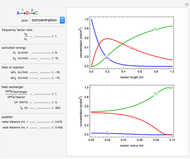
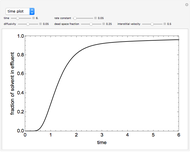
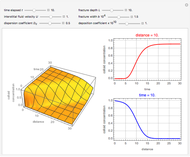
This Demonstration solves a Gazis–Herman–Rothery (GHR) car-following model. In this model a vehicle accelerates in response to the velocity and distance of the vehicle in front. The model in its most general form is:
[more]
Contributed by: Clay Gruesbeck (December 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] M. Brackstone and M. McDonald, "Car-Following: A Historical Review," Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2(4), 1999 pp. 181–196. doi:10.1016/S1369-8478(00)00005-X.
Permanent Citation