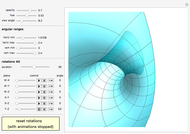
Geodesics of a Torus Solved with a Method of Lagrange

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
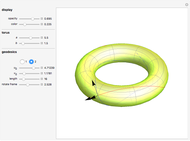
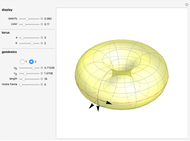
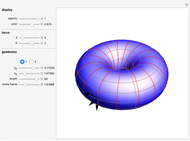
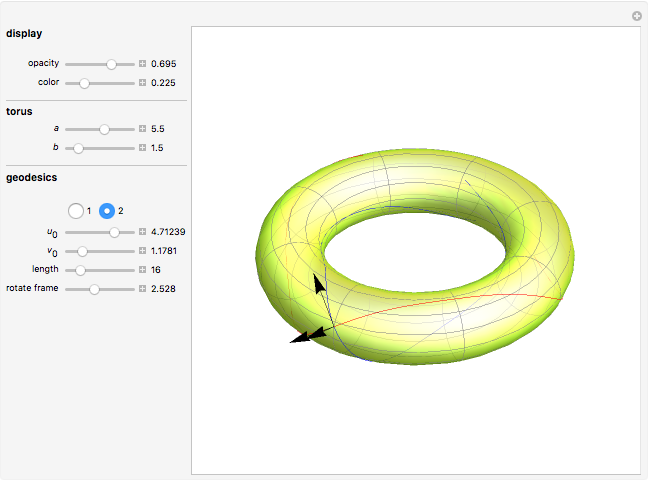
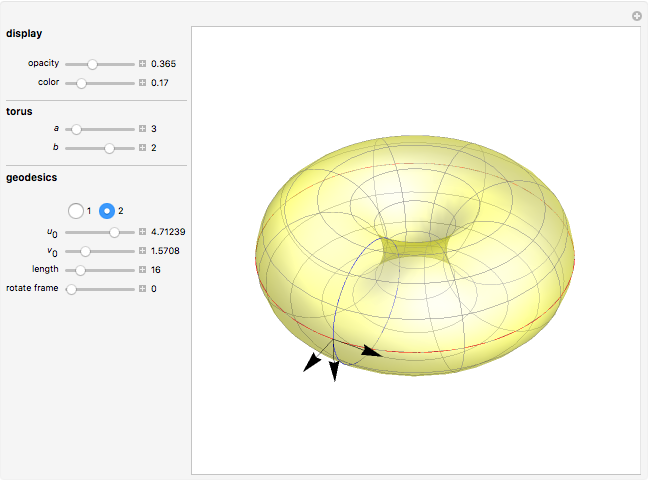
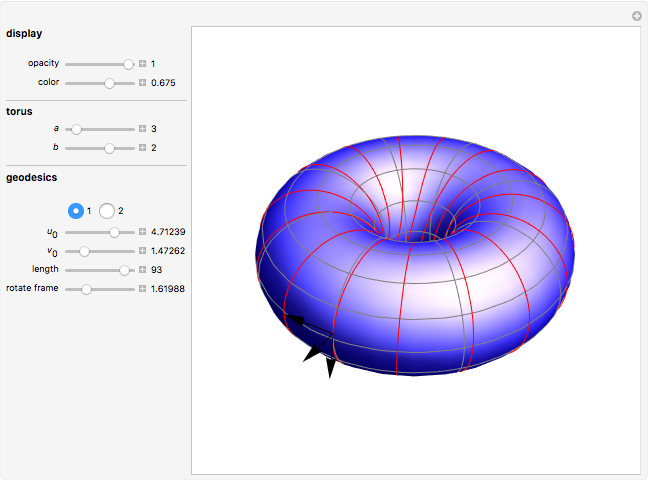
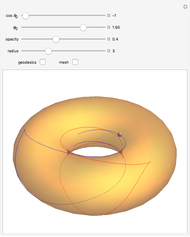
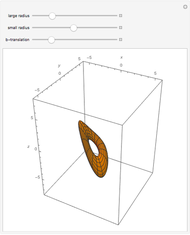
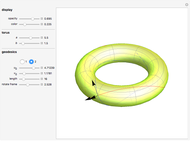
A geodesic is the equivalent of a straight line on a surface; locally a geodesic is the shortest path between two points. Lagrange's method can be used to find the differential equations describing the geodesic for a torus, which are then solved with Mathematica's built-in function NDSolve. You can place the frame anywhere on the torus and rotate it to set the initial position and directions of geodesics of a given length.
[more]
Contributed by: Gerard Balmens (November 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Geodesics of a Torus Solved with a Method of Lagrange"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/GeodesicsOfATorusSolvedWithAMethodOfLagrange/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: November 28 2012