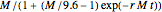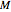Iterations of Some Algorithms for Nonlinear Fitting

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
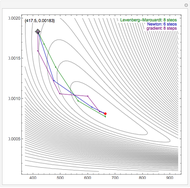
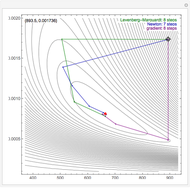
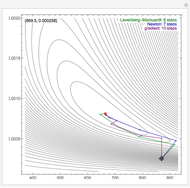
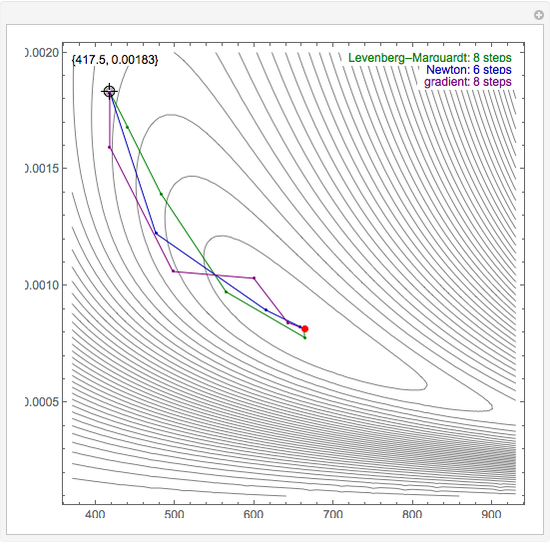
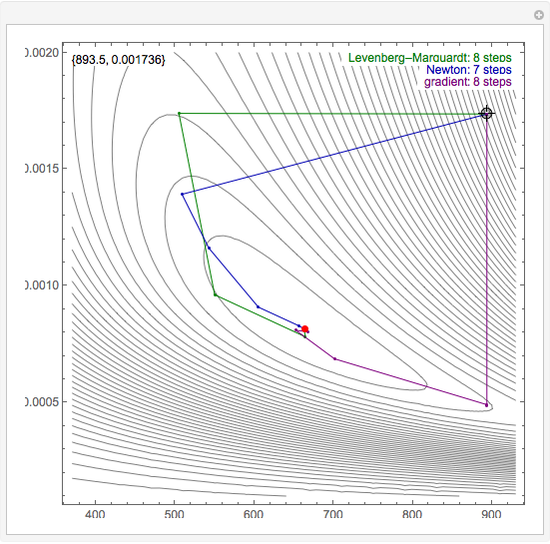
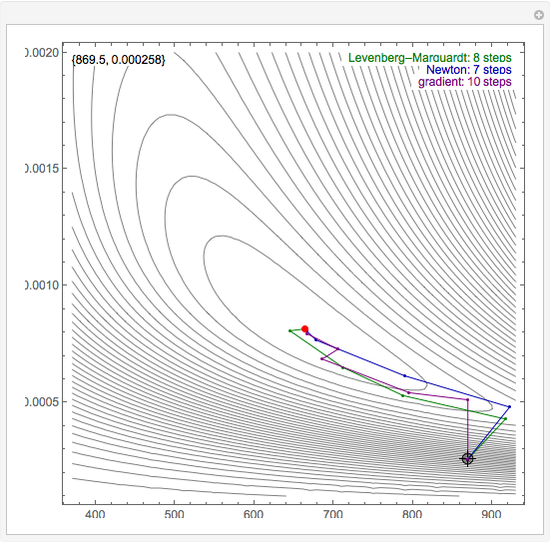
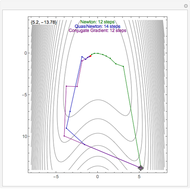
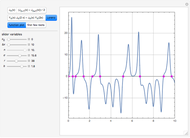
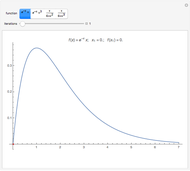
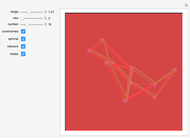
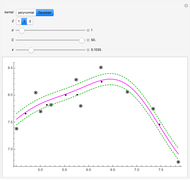
By dragging the starting point with the locator, you can see how three nonlinear fitting algorithms proceed and how many steps they need. The three algorithms considered are the Levenberg–Marquardt, Newton, and gradient methods.
[more]
Contributed by: Heikki Ruskeepää (February 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] R. Pearl, "The Growth of Populations," Quarterly Review of Biology, 2(4), 1927 pp. 532–548.
Permanent Citation
"Iterations of Some Algorithms for Nonlinear Fitting"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/IterationsOfSomeAlgorithmsForNonlinearFitting/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: February 21 2012