Joule's Experiment

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
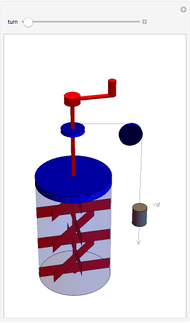
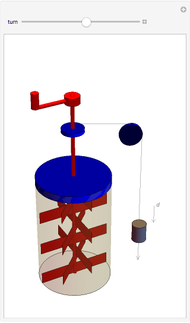
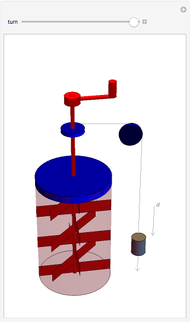
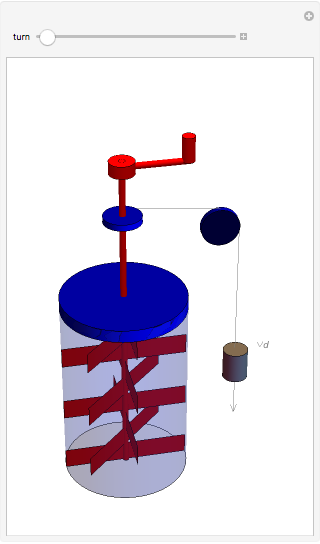
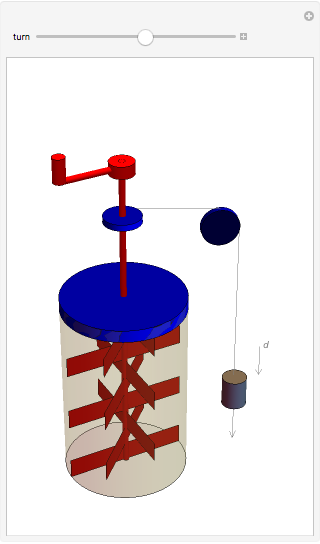
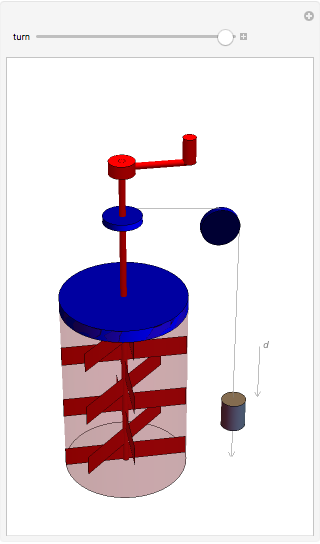
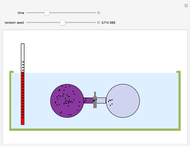
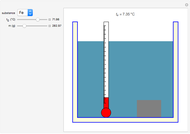
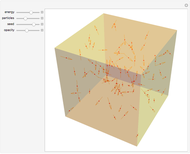
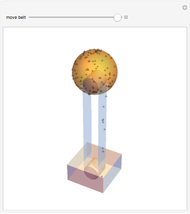
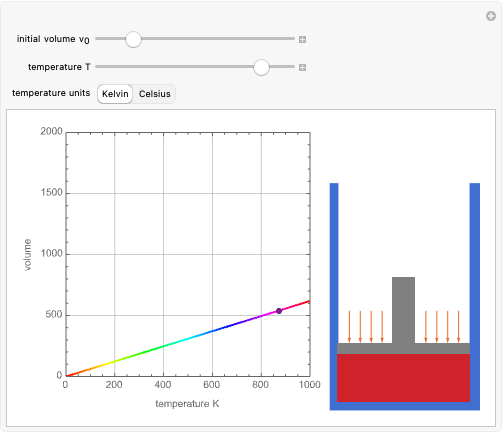
The original Joule experiment consists of a receptacle filled with water and a mechanism with spinning plates. The kinetic energy of the plates is transformed into heat, because the force of gravity performs work on the weight falling a distance  . This gave an experimental confirmation of the equivalence between heat and work, now defined to be exactly 1 calorie for every 4.184 joules and called a "thermochemical calorie".
. This gave an experimental confirmation of the equivalence between heat and work, now defined to be exactly 1 calorie for every 4.184 joules and called a "thermochemical calorie".
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Joule's Experiment"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/JoulesExperiment/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011