Membrane Reactor to Improve Selectivity in Multiple Reactions

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
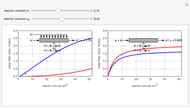
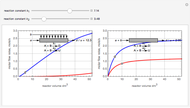
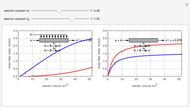
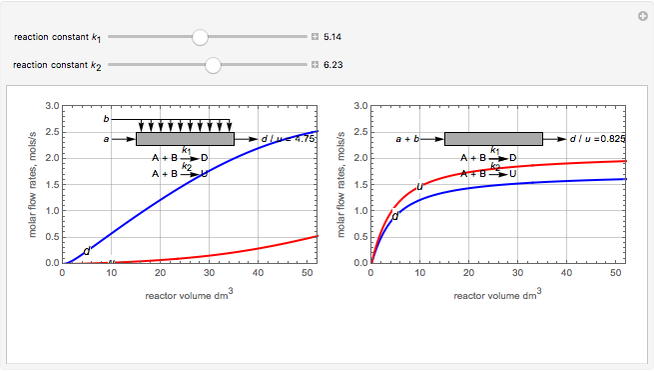
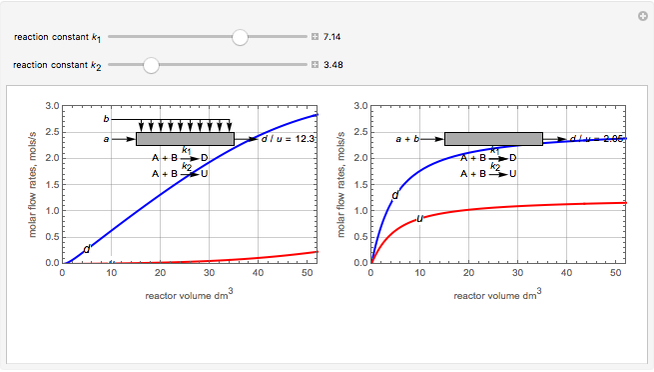
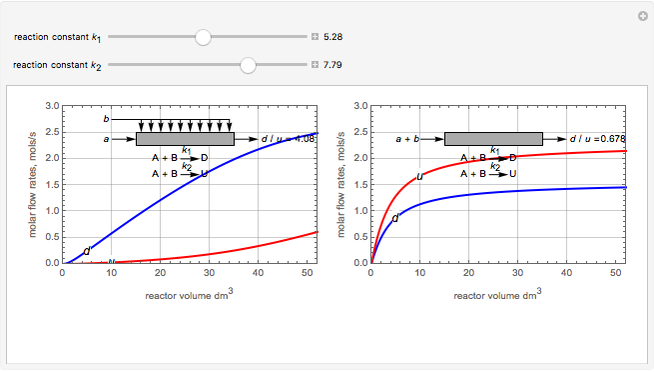
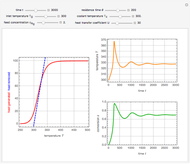
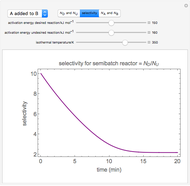
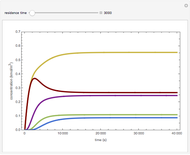
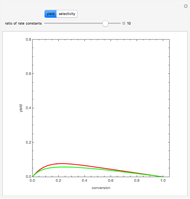
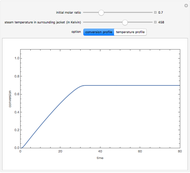
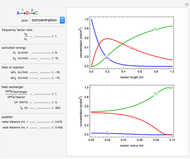
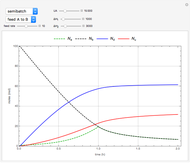
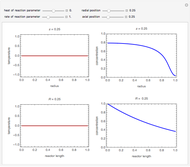
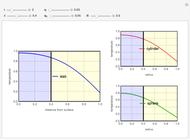
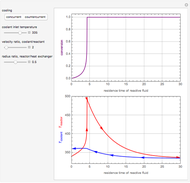
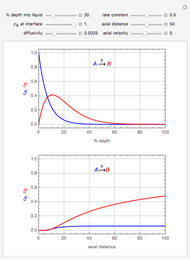
Membrane reactors have a semipermeable membrane that can be used to selectively add reactants or remove products and thus shift the equilibrium. This Demonstration compares multiple reactions taking place in a membrane reactor and a plug flow reactor (PFR). The membrane reactor shows a significant improvement in selectivity over the PFR.
Contributed by: Clay Gruesbeck (November 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Consider the following chemical reactions that take place in the gas phase
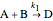 ,
,
 ,
where
,
where  is the desired product and the rates of reaction are
is the desired product and the rates of reaction are  and
and 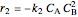 .
.
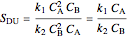 .
.
In order to maximize  , the concentration of
, the concentration of  must be high and the concentration of
must be high and the concentration of 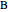 low; therefore we feed
low; therefore we feed 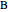 through the membrane. The molar rate of
through the membrane. The molar rate of  entering the reactor is equal to that of
entering the reactor is equal to that of 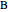 entering through the membrane, 4 mols/s;
entering through the membrane, 4 mols/s; 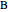 enters along with
enters along with  in the PFR. The reactor volume is 50
in the PFR. The reactor volume is 50  and the entering total concentration is 0.8 mols/
and the entering total concentration is 0.8 mols/ .
.
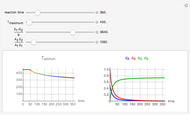
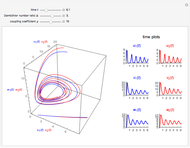
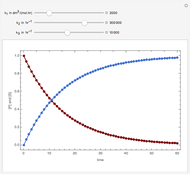
The molar flow rates of the reactants and products ( ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ) are calculated along the length of the reactors for selected values of
) are calculated along the length of the reactors for selected values of  and
and 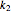 . The parameters used are given in equations E6.9 to E6.18 of Chapter 6 in [1].
. The parameters used are given in equations E6.9 to E6.18 of Chapter 6 in [1].
Reference
[1] H. S. Fogler, Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering, 4th ed., Upper Saddle River, NJ : Prentice Hall PTR, 2006 pp. 348–351.
Permanent Citation