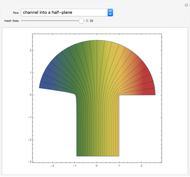
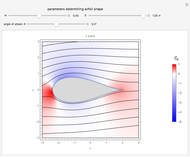
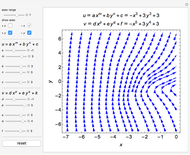
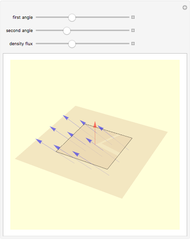
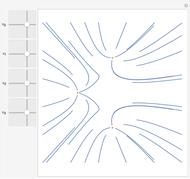
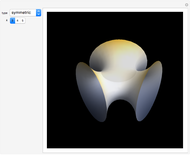
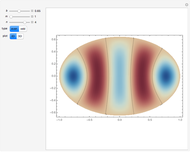
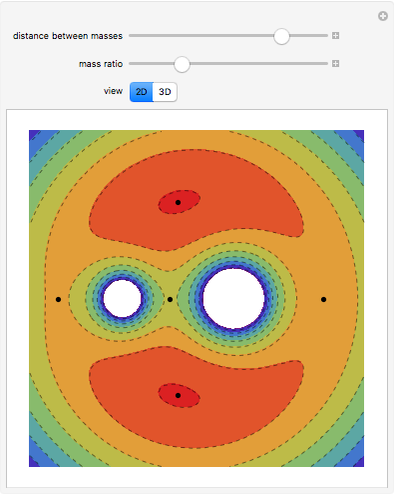
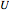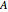Potential Flows

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
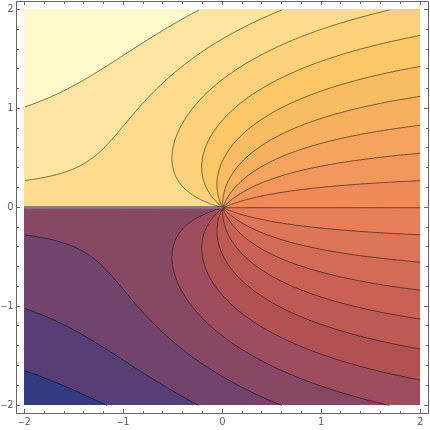
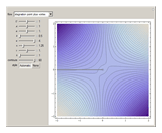
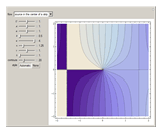
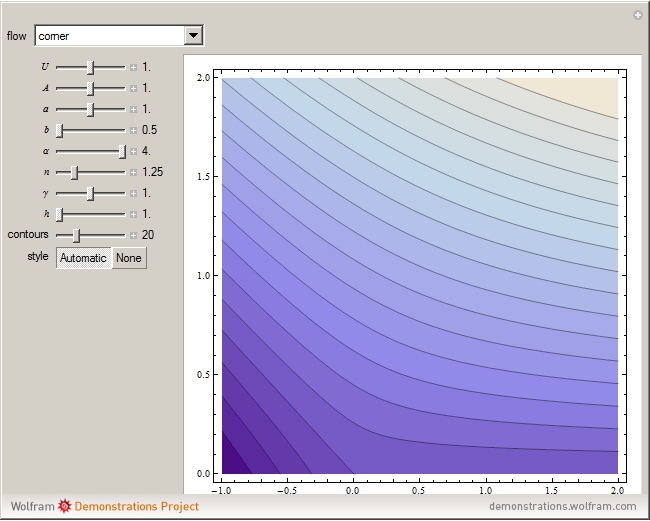
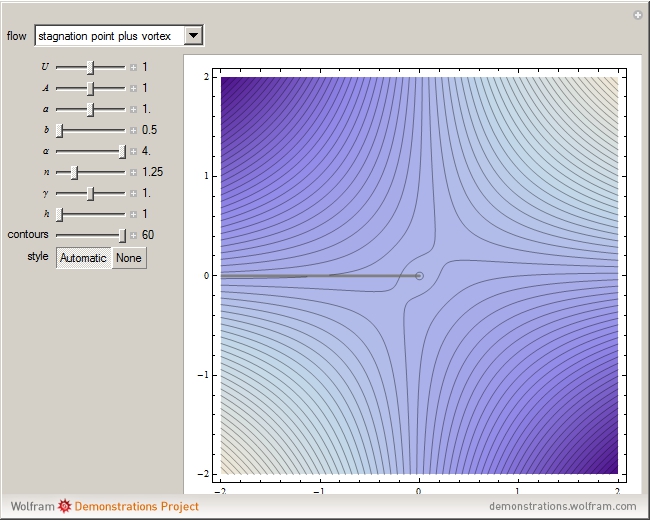
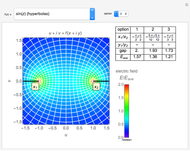
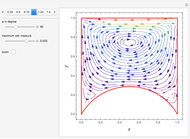
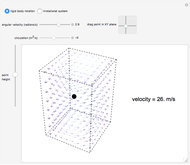
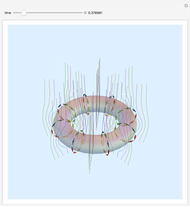
A potential flow is characterized by a velocity field that is the gradient of a scalar function, the velocity potential. This velocity field is irrotational, because the curl of a gradient is identically zero. Velocity potentials are obtained as solutions of Laplace's equation, most conveniently in the complex plane. Some applications include water-wave propagation, airfoils, electrostatics, and heat flow. The equations can be used for modeling both stationary and nonstationary flows.
[more]
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (August 2014)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
References
[1] B. J. Cantwell. "Elements of Potential Flow, Chapter 10, AA200: Applied Aerodynamics." (Apr 6, 2014) http://web.stanford.edu/~cantwell/AA200_Course_Material/AA200_Course_Notes/AA200_Ch_ 10_Elements _of _potential _flow _Cantwell.pdf.
[2] P. Nylander. "Potential Flow." (Aug 4, 2014) bugman123.com/GANNAA/index.html.
[3] J. H. Mathews. "Complex Analysis Project." (Aug 4, 2014) mathfaculty.fullerton.edu/mathews/complex.html.
Permanent Citation