Pressure Profile for Column of Multiple Fluids

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
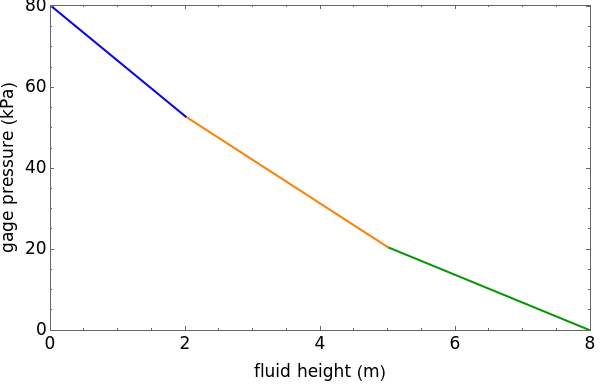
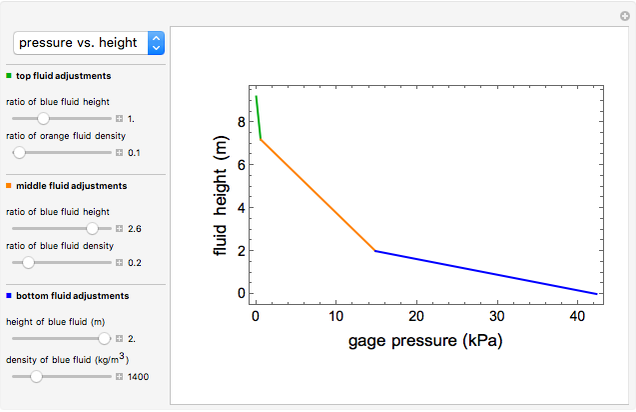
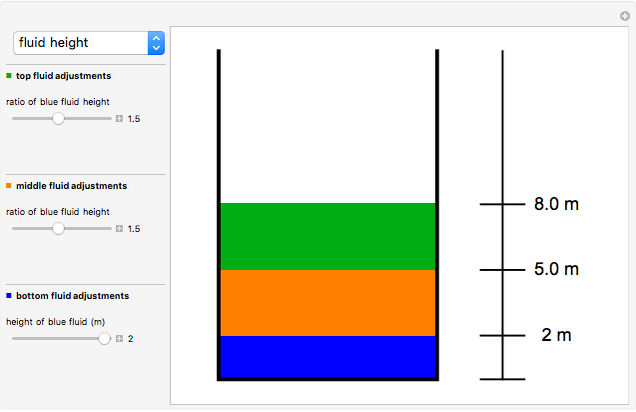
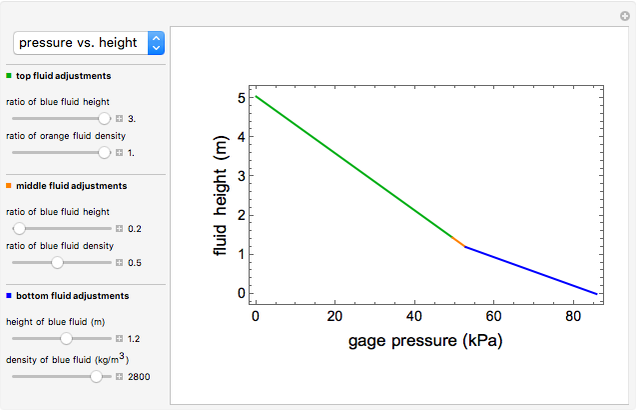
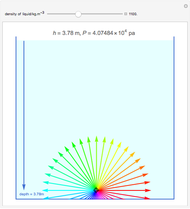
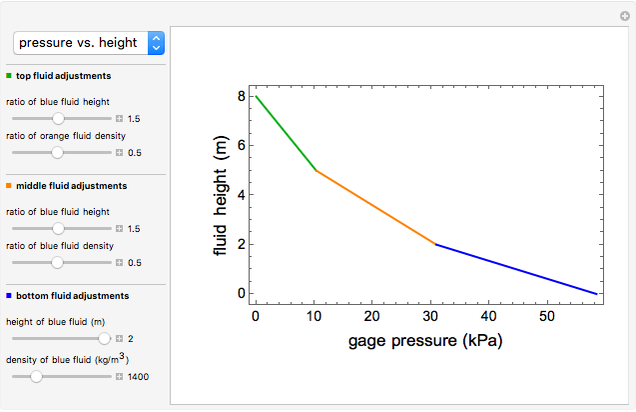
This Demonstration shows the effects of fluid height and density on hydrostatic pressure. You can vary fluid height and density of each fluid with sliders. This results in a total hydrostatic pressure profile that indicates the gage pressure at different heights in the container.
Contributed by: Jon Barbieri (May 2014)
Additional contributions by: Garret D. Nicodemus and Rachael L. Baumann
(University of Colorado Boulder, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Hydrostatic pressure is calculated by:
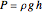 ,
,
where 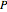 is hydrostatic gage pressure (kPa),
is hydrostatic gage pressure (kPa),  is fluid density (
is fluid density (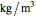 ),
),  is the gravitational constant and
is the gravitational constant and  is fluid height (m).
is fluid height (m).
In order to calculate the total pressure inside the container, the individual fluid pressure is added to the pressure acting on the fluid from above:
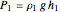 ,
,
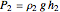 ,
,
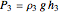 ,
,
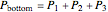 .
.
Plotting hydrostatic pressure versus height for each fluid generates a pressure profile for the container.
Permanent Citation