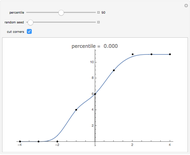
Riemann Sums: A Simple Illustration

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
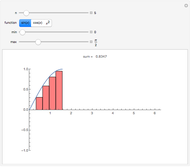
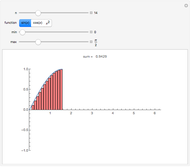
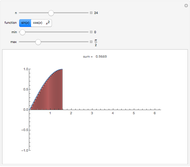
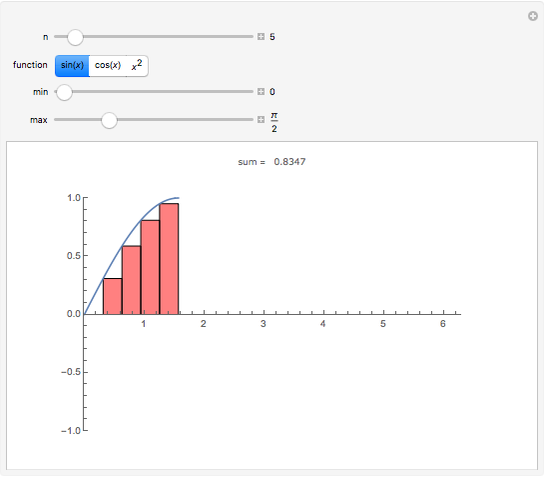
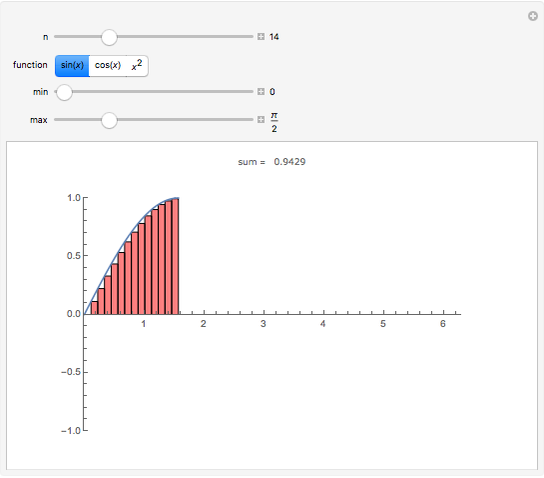
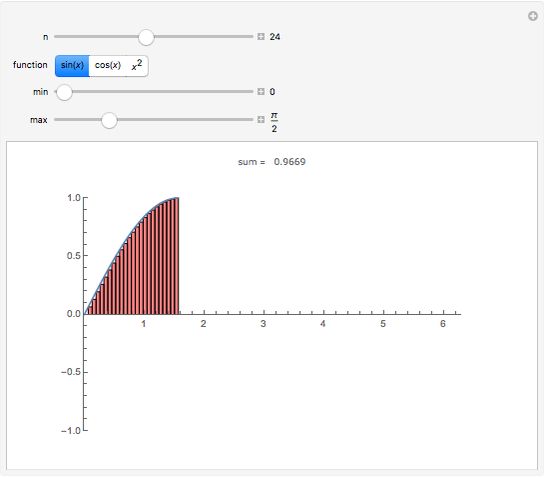
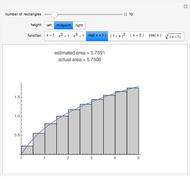
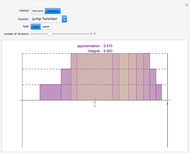
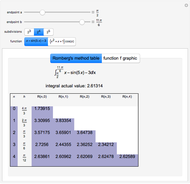
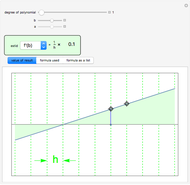
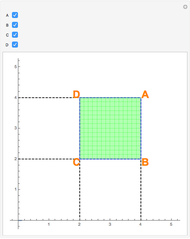
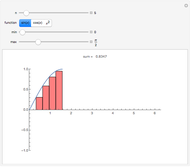
A Riemann sum is an approximation to the area between a curve and the  axis, made by adding together the areas of a set of rectangles. A summation calculation is involved, of the form
axis, made by adding together the areas of a set of rectangles. A summation calculation is involved, of the form 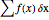 , where
, where 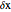 is the width of each rectangle. The limit of the Riemann sum as
is the width of each rectangle. The limit of the Riemann sum as 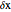 approaches zero is the (Riemann) integral of the function. This manipulation uses a left Riemann sum, in which the value of
approaches zero is the (Riemann) integral of the function. This manipulation uses a left Riemann sum, in which the value of 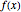 that is used is the one at the left edge of each rectangle. It is easy to adapt the code for right Riemann sums and for the trapezoidal rule; try it!
that is used is the one at the left edge of each rectangle. It is easy to adapt the code for right Riemann sums and for the trapezoidal rule; try it!
Contributed by: Phil Ramsden (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Riemann Sums: A Simple Illustration"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/RiemannSumsASimpleIllustration/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011