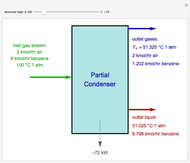
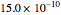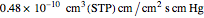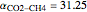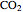Separation of Carbon Dioxide and Methane Using Well-Mixed Gas Permeation
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
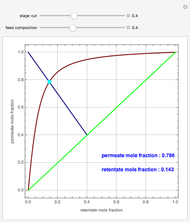
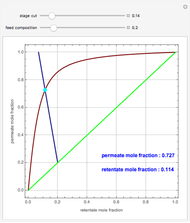
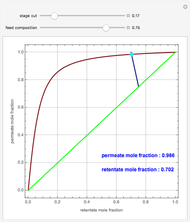
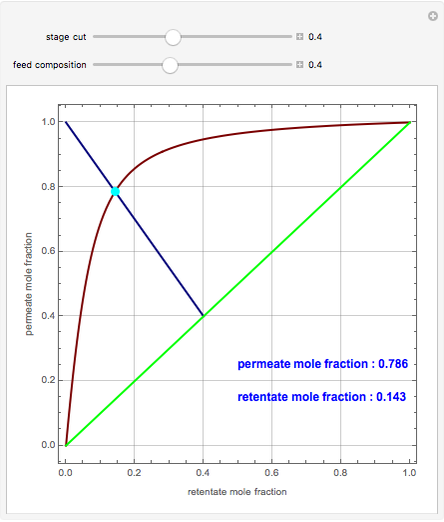
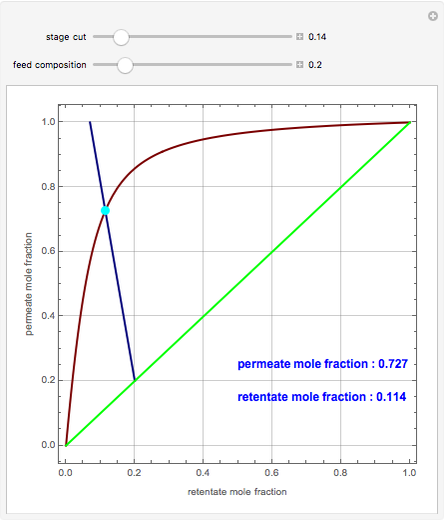
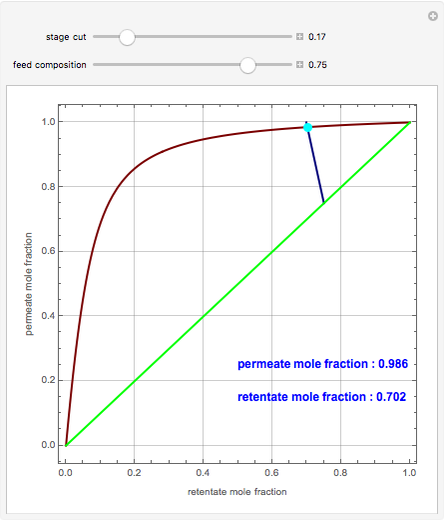
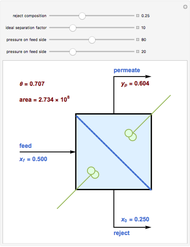
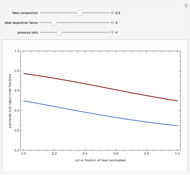
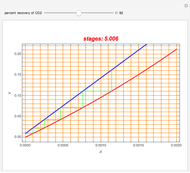
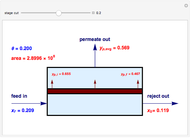
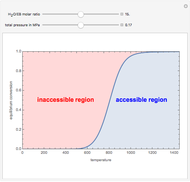
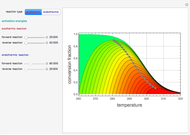
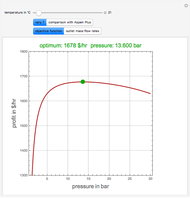
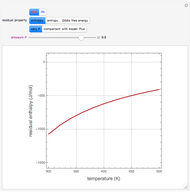
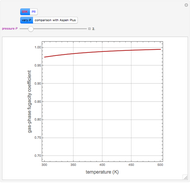
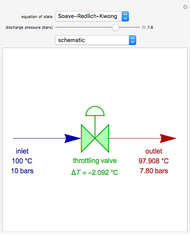
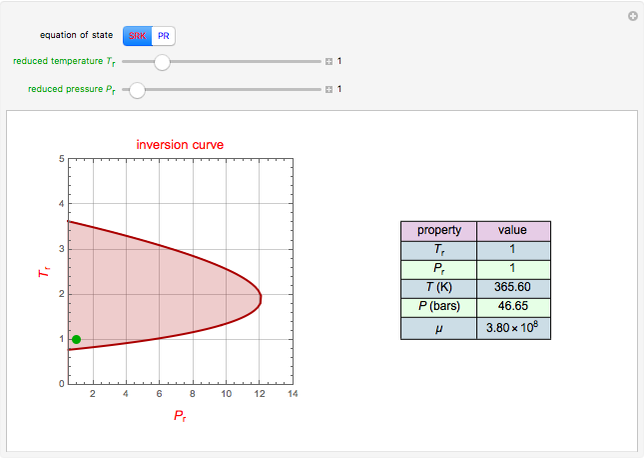
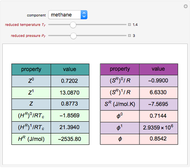
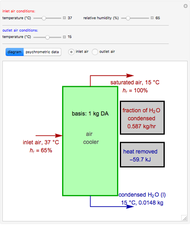
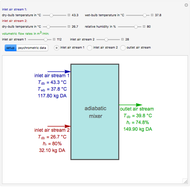
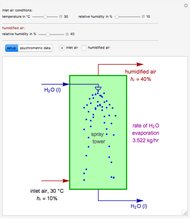
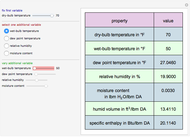
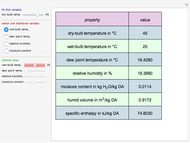
A mixture of carbon dioxide and methane are to be separated by a cellulose acetate membrane at 35 °C.
[more]
Contributed by: Housam Binous and Ahmed Bellagi (March 2011)
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals and École nationale d'ingénieurs de Monastir
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] P. C. Wankat, Separation Process Engineering, 2nd ed., Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2007.
Permanent Citation