Sherlock Holmes's Dancing Men Cipher

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
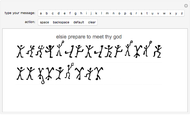
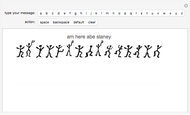
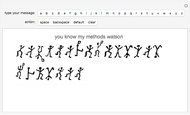
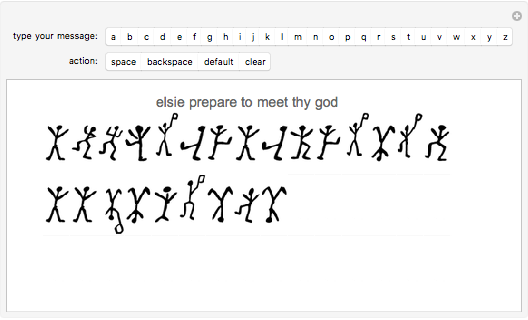
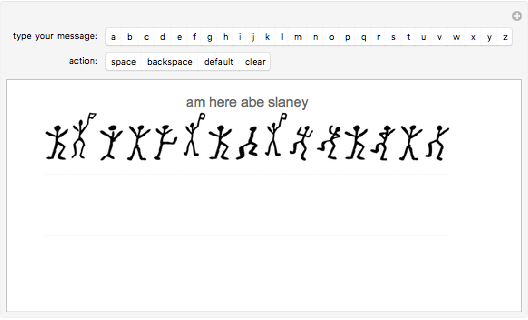
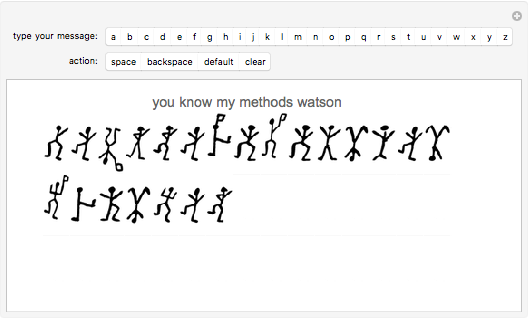
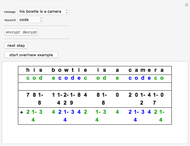
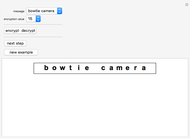
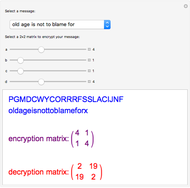
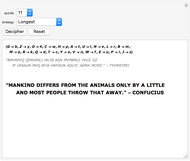
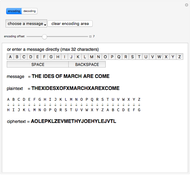
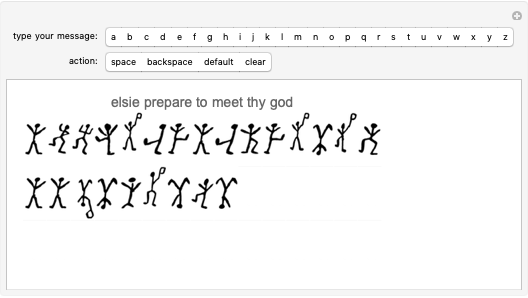
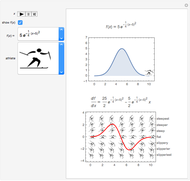
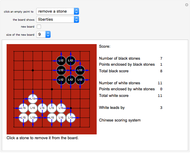
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle invented and used a cipher in "The Adventure of the Dancing Men," which featured Sherlock Holmes, his famous detective [1]. It is a substitution cipher in which a letter is always represented by the same dancing man, with a flag to indicate the end of a word. Sherlock Holmes uses frequency analysis and some other clues to decipher the encrypted messages. Since the story does not cover all letters, this Demonstration uses additional characters from the free font GL-DancingMen-Org, by Gutenberg Labo [2].
[more]
Contributed by: José Luis Gómez-Muñoz (December 2019)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Details
References
[1] A. C. Doyle, The Return of Sherlock Holmes (1905 ed.). (Dec 6, 2019) en.wikisource.org/wiki/The_Return_of_Sherlock_Holmes,_1905_edition/Chapter_3.
[2] Gutenberg Labo. "Dancing Men Font." (Dec 6, 2019) gutenberg.osdn.jp/font/en.html.
Snapshots
Permanent Citation