Spacetime Curvature for a Falling Object near the Earth's Surface

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
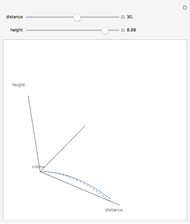
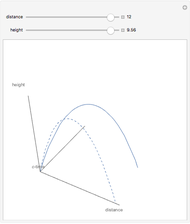
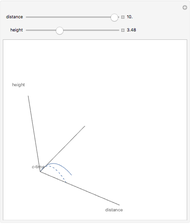
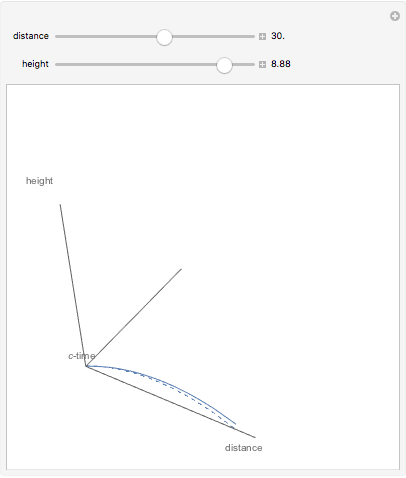
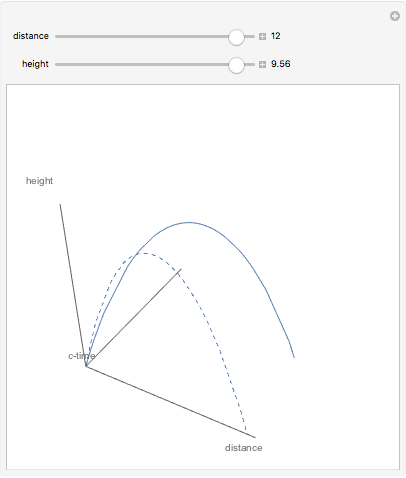
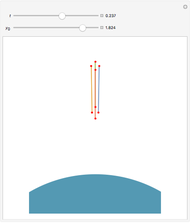
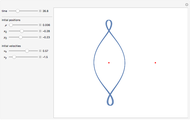
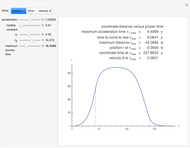
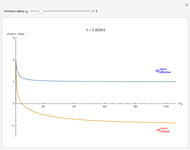
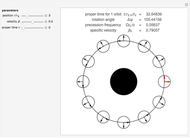
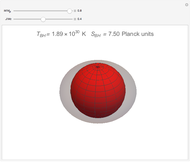
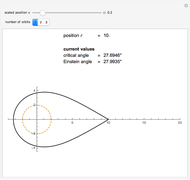
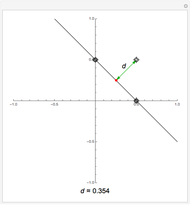
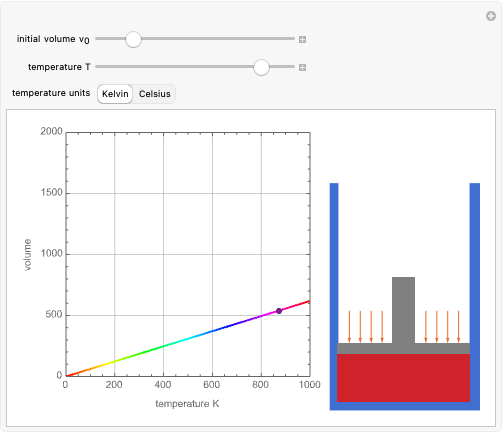
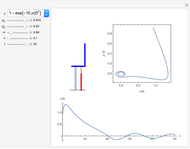
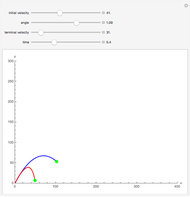
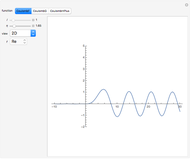
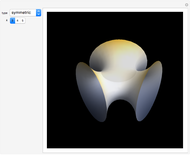
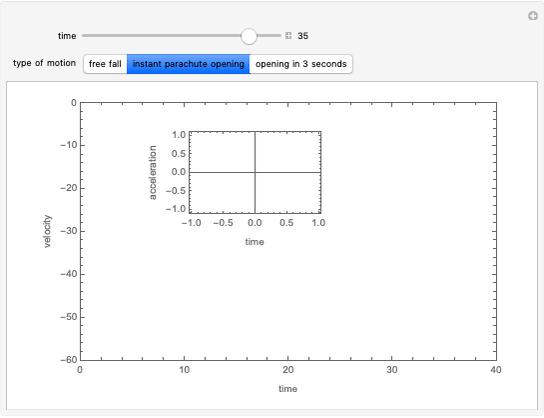
The graphic shows a projection of the path followed by a falling object in four-dimensional spacetime into three-dimensional space. Objects fall because they follow geodesics in this spacetime. They are of maximal length, maximizing proper time. For all trajectories, the initial angle or speed does not matter and the curvature is the same,  . Near a very massive object such as a black hole, this value is considerably greater.
. Near a very massive object such as a black hole, this value is considerably greater.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (October 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Spacetime Curvature for a Falling Object near the Earth's Surface"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/SpacetimeCurvatureForAFallingObjectNearTheEarthsSurface/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: October 5 2011