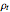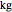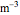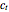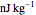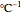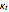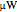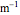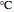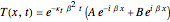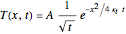Tissue Heat Conduction in Millisecond-Picosecond Range

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
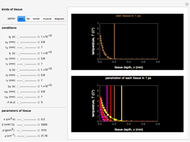
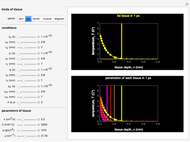
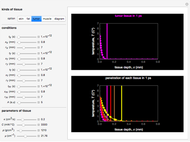
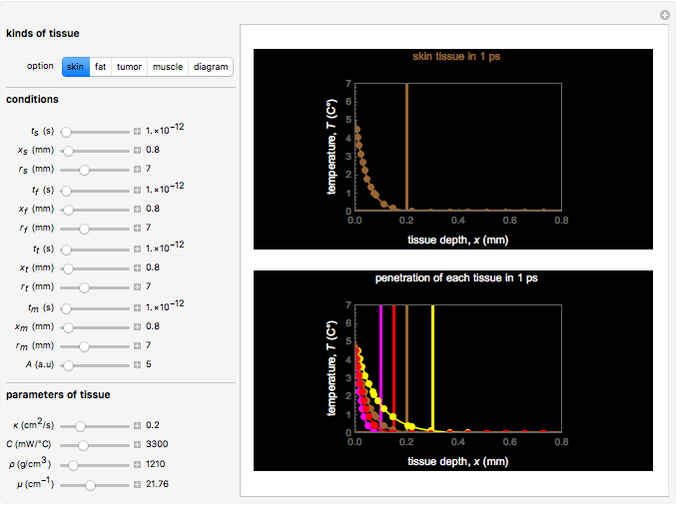
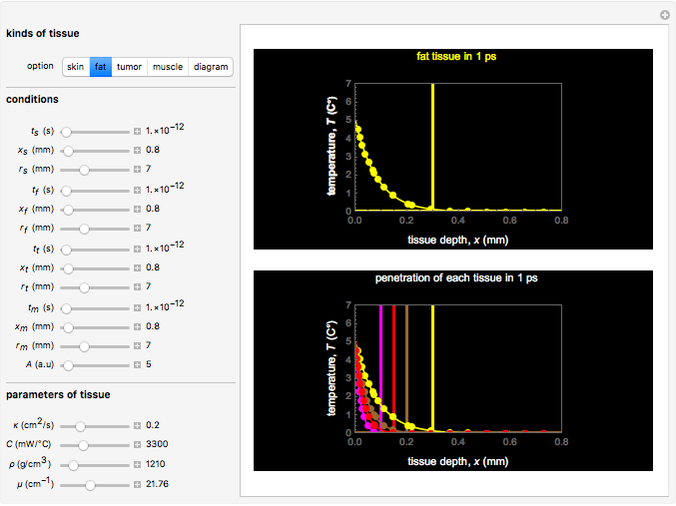
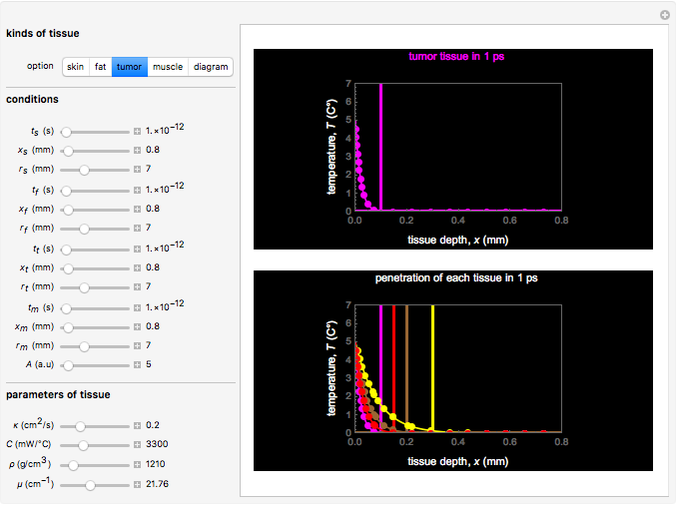
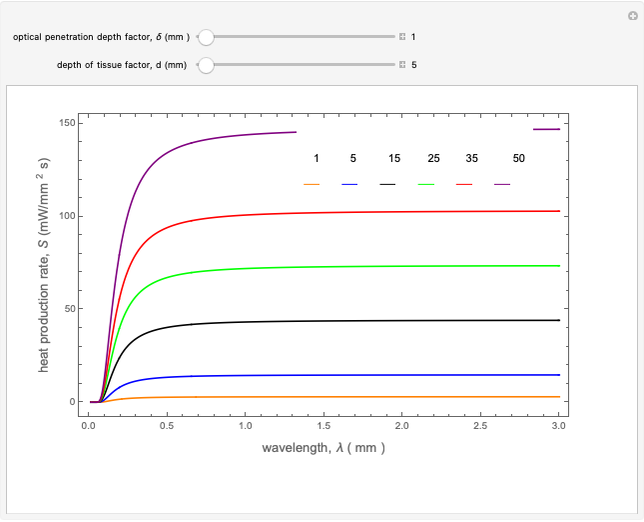
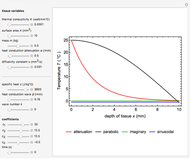
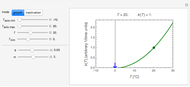
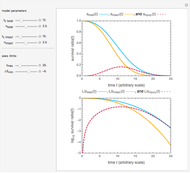
This Demonstration explores transient 1D heat conduction through several types of biological tissue in the millisecond to picosecond time range, based on theoretically derived analytical solutions. We are interested particularly in relaxation times of pulse propagation. The results for time intervals of one second or longer show a constant temperature or a steady state centered about one temperature. By contrast, millisecond to picoseconds time ranges display a small but significant temperature change as the depth varies from  mm to a depth at which
mm to a depth at which 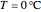 . You can select time intervals for several types of tissue (skin, fat, tumor, or muscle) to obtain temperature distributions as functions of tissue depth.
. You can select time intervals for several types of tissue (skin, fat, tumor, or muscle) to obtain temperature distributions as functions of tissue depth.
Contributed by: Muhamad Hamdi and Yusof Munajat (September 2015)
Biophysics Department, University of Riau, Indonesia
Physics Department, University of Technology Malaysia, Johor Bahru
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
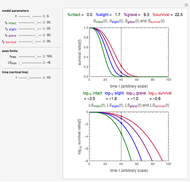
Snapshots 1, 2, 3, and 4: skin tissue shows heat conduction (with maximum tissue depth 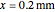 and time steps
and time steps 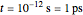 ) with a small temperature change gradually approaching zero. It is thinner than fat tissue (
) with a small temperature change gradually approaching zero. It is thinner than fat tissue (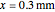 ) but thicker than tumor (
) but thicker than tumor (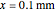 ) or muscle tissue (
) or muscle tissue (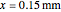 ), correlated with the contrasting tissue structures.
), correlated with the contrasting tissue structures.
References
[1] H. Ilham, Introduction to Biophysics, 1st ed., Pekanbaru, Riau, Indonesia: RUEDC-Press, 2007.
[2] M. Hamdi, Y. Munajat, R. Kamarulzaman Raja Ibrahim, and R. A. Rahman, "Terahertz Radiation Field Regime Absorption in Cancer-Health Tissue for Medical Application," Proceedings of Fourth International Conference & Workshops on Basic and Applied Science & Eleventh Regional Annual Fundamental Science Symposium (ICOWOBAS-RAFSS 2013), Senai, Johor Bahru, Malaysia, September 3–5, 2013 pp. 286–291. www.ibnusina.utm.my/links/icowobasrafss2013proceedings/ICOWOBASRAFSS2013Proceedings.pdf.
[3] M. Hamdi, " Investigation on Bio-electromagnetic Field of Terahertz Radiation Behaviors at the Interface of Brain-Fat Tissue," Asian Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 1(2), 2012. journal.uii.ac.id/index.php/inovasi_kewirausahaan/article/view/2826.
Permanent Citation