Action of a Siphon

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
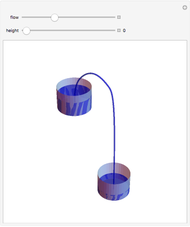
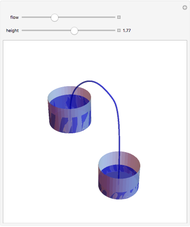
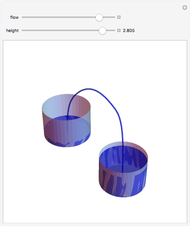
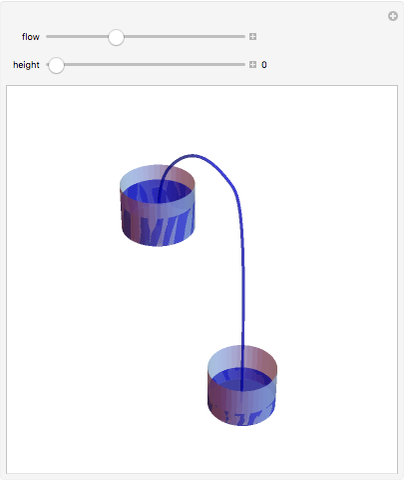
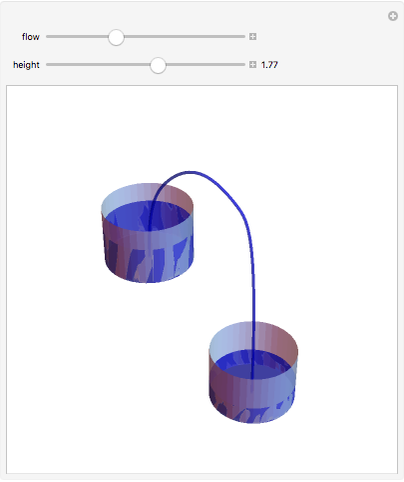
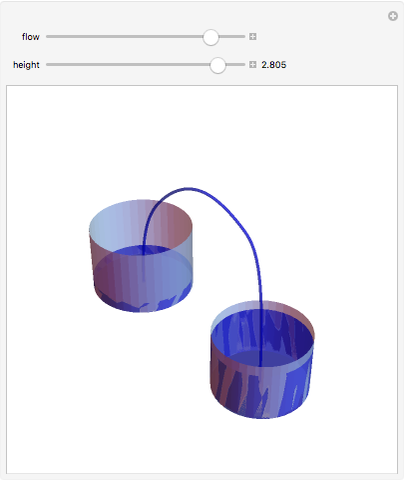
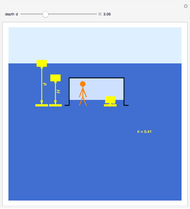
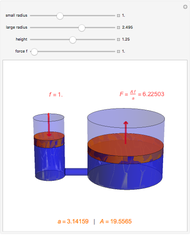
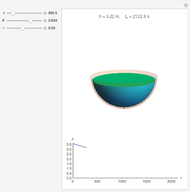
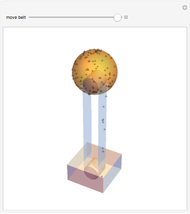
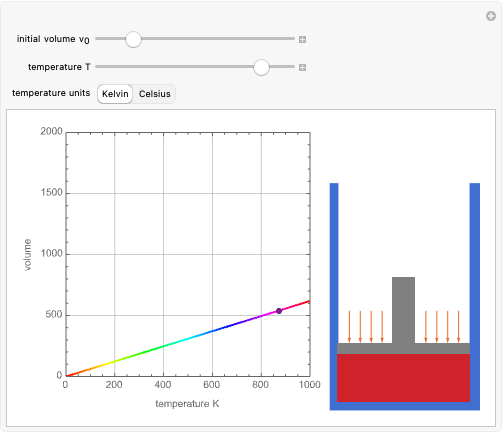
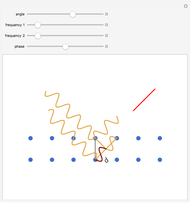
A siphon consists of a tube connecting two containers with liquids at different levels. Once the tube is filled, for example, by suction, the liquid flows into the lower container until the liquid levels are equalized. The driving force is the difference of hydrostatic pressure, as determined by Pascal's principle. The flow rate can be calculated using Bernoulli's equation.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
For a derivation, see the Wikipedia article for Siphon.
Permanent Citation
"Action of a Siphon"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ActionOfASiphon/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011