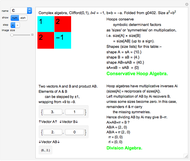
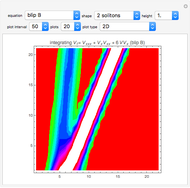
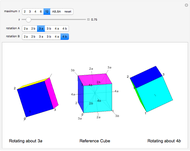
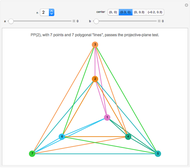
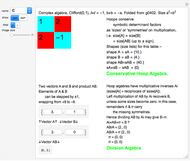
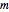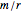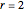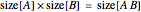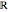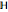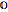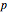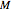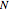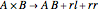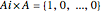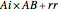Algebraic Loops (2); Symmetry-Conserving Vector-Division Hoop Algebras

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
An algebraic loop with the Moufang property, 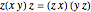 for all
for all  ,
, 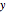 ,
,  in the loop, acts as a vector multiplication and division table for unsigned vectors. If
in the loop, acts as a vector multiplication and division table for unsigned vectors. If 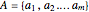 and
and 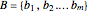 , then
, then 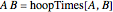 ; the left-multiplicative inverse is
; the left-multiplicative inverse is 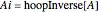 .
.
Contributed by: Roger Beresford (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
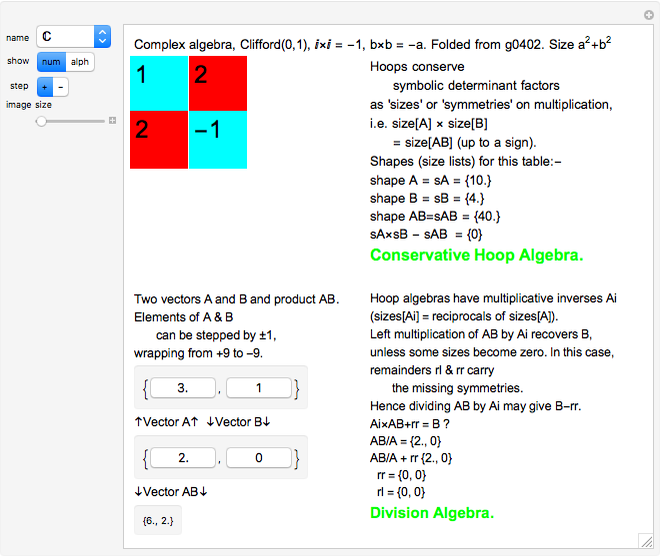
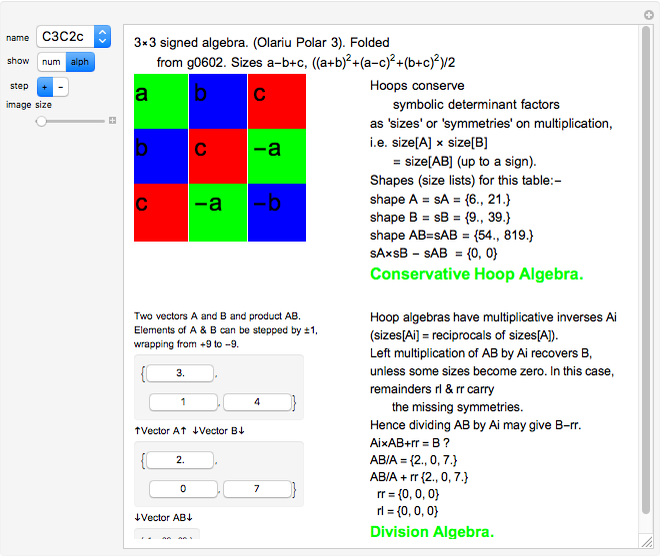
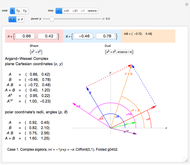
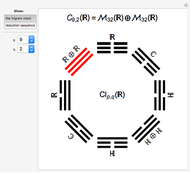
Algebraic loop Demonstrations are based on the GroupLoopHoop package in MathSource/4894, which contains much more information. The first develops loop properties and the third describes small groups and Moufang loops. Demonstrations of Abelian loops with Cartesian/polar duals, and Clifford (geometric) algebras (which are anticommutative hoops) are being prepared.
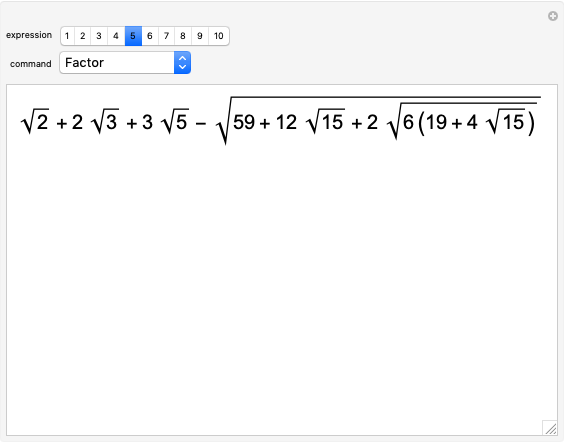
Integer elements are used for compactness, but real and complex numbers behave similarly. Output is real, to avoid bulky results involving square-root symbols.
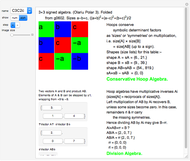
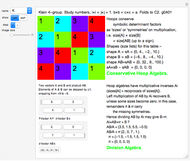
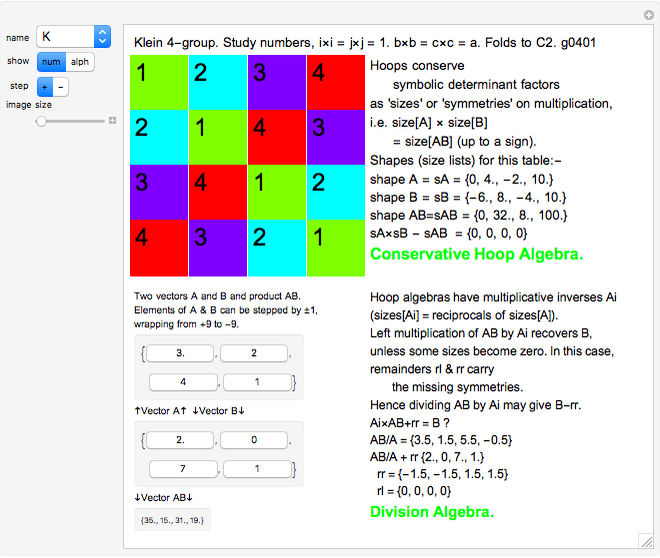
Multiplication 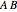 . If the table has
. If the table has  in row
in row 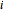 and column
and column 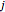 , then the
, then the 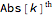 element of the product is the sum of A[[i]] B[[j]] Sign[k]. If the product has zero sizes where
element of the product is the sum of A[[i]] B[[j]] Sign[k]. If the product has zero sizes where 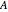 or
or 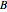 has a nonzero size (because
has a nonzero size (because 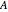 and
and 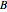 have disparate zero sizes), nonzero remainders are created with the missing size(s). The left remainder is
have disparate zero sizes), nonzero remainders are created with the missing size(s). The left remainder is 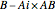 and the right remainder is
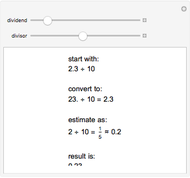
and the right remainder is 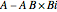 . Compare this with integer division
. Compare this with integer division 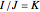 with remainder
with remainder 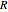 and
and 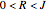 , so
, so 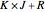 recovers
recovers 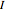 . As every vector has an inverse, division is simply multiplication by an inverse.
. As every vector has an inverse, division is simply multiplication by an inverse.
Inverse 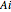 . If the shape of
. If the shape of 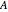 has symbolic form S[[k]] (a list of polynomials) and the table has a 1 (possibly signed) in row
has symbolic form S[[k]] (a list of polynomials) and the table has a 1 (possibly signed) in row  of column
of column 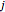 (this data is supplied in
(this data is supplied in 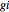 ), then the
), then the 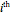 element of the (left) inverse is the signed sum of the derivations of S[[k] with respect to symbolic variable[[n]], divided by S[[k]]. This partial fraction is omitted if S[[k]] is zero; the zero has been factored out of the determinant.
element of the (left) inverse is the signed sum of the derivations of S[[k] with respect to symbolic variable[[n]], divided by S[[k]]. This partial fraction is omitted if S[[k]] is zero; the zero has been factored out of the determinant.
An outstanding research problem is the development of compact shape expressions for some tables (some are shown with "{0}" in their shapes); division cannot be implemented in such cases.
The discovery that hoops (including all Clifford algebras) have exactly conserved sizes (and not just norms with triangle inequalities) appears to be new.
Hoops include compact descriptions of all the polar-complex and planar-complex analytic algebras developed (at great length, but without shapes) in Sylviu Olariu's "Complex Numbers in n Dimensions".
Permanent Citation