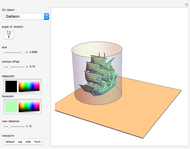
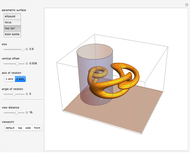
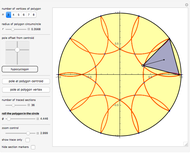
Dimensions of a Stranded Wire

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
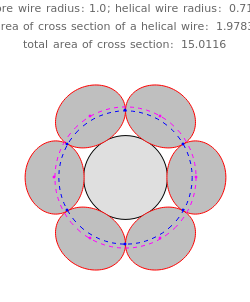
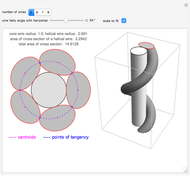
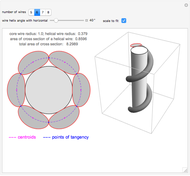
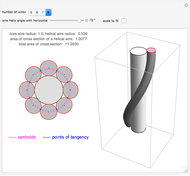
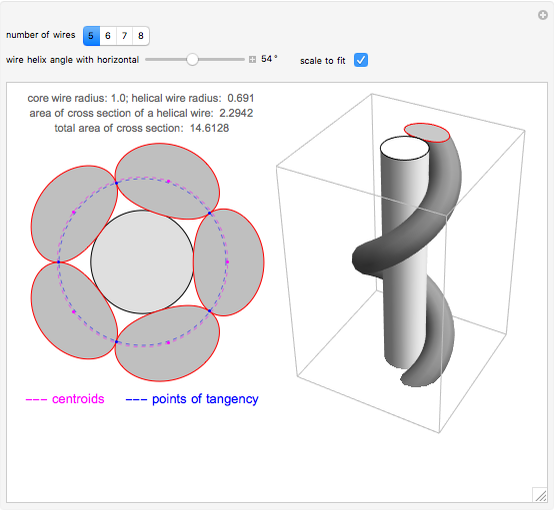
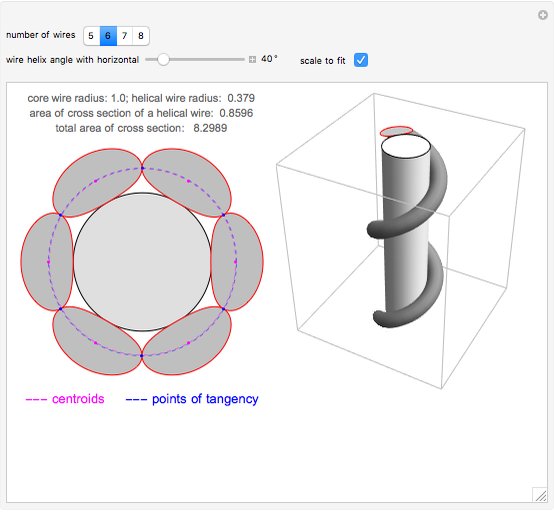
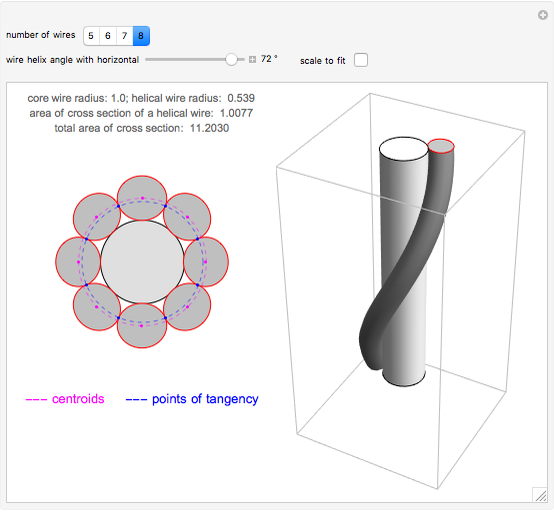
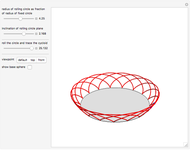
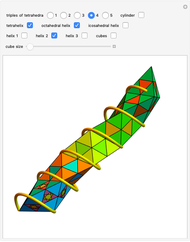
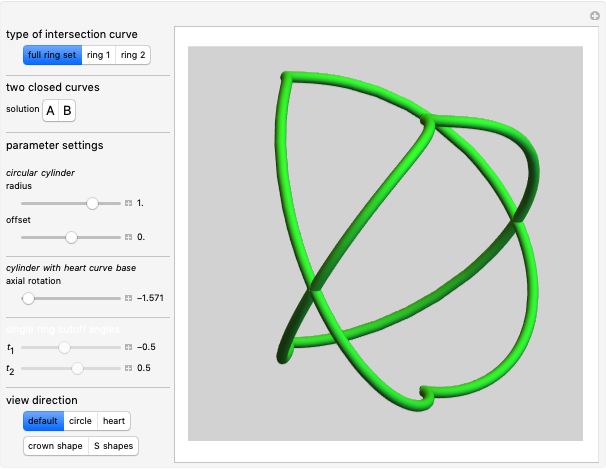
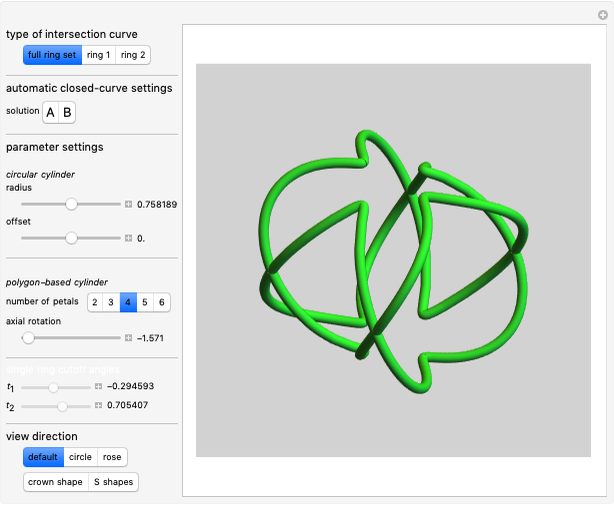
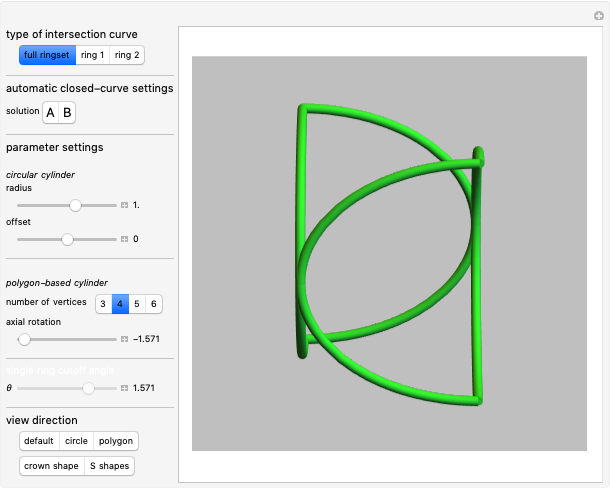
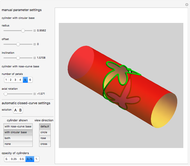
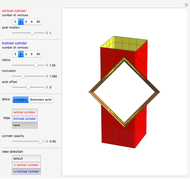
A wire strand consists of a central core wire with a number of helical wires wrapped around it. Its principal characteristics are the helix (or winding) angle and the radius of the wires.
[more]
Contributed by: Erik Mahieu (July 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
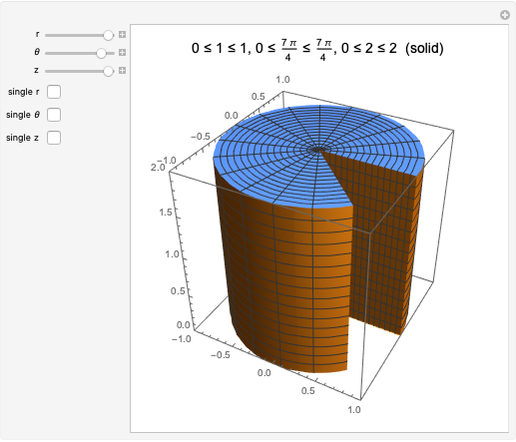
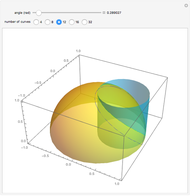
A helical cylinder with radius  and helix angle
and helix angle  can be described in parametric coordinates, as functions of
can be described in parametric coordinates, as functions of  and
and  :
:

where  is the helix radius,
is the helix radius,  is the helix angle, and
is the helix angle, and  is the cylinder radius.
is the cylinder radius.
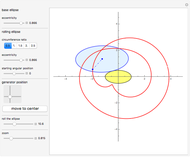
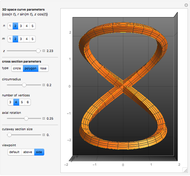
The cross section of a helical cylinder with the horizontal is given in terms of the parametric coordinate  , with the helix radius taken to be 1:
, with the helix radius taken to be 1:

Permanent Citation