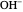E2 Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
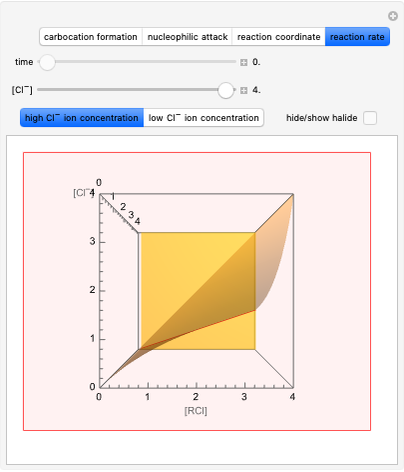
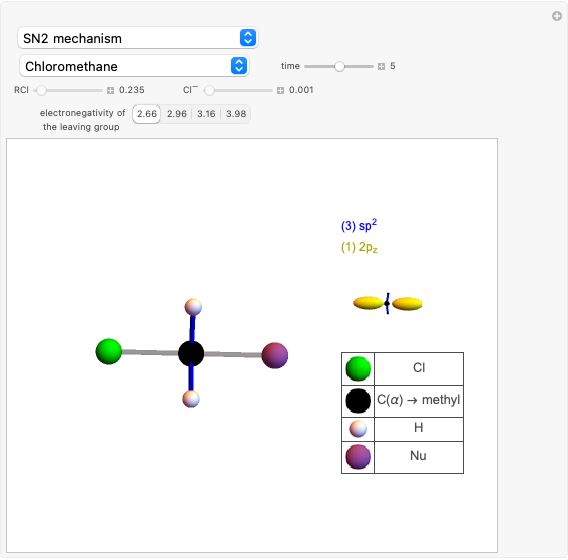
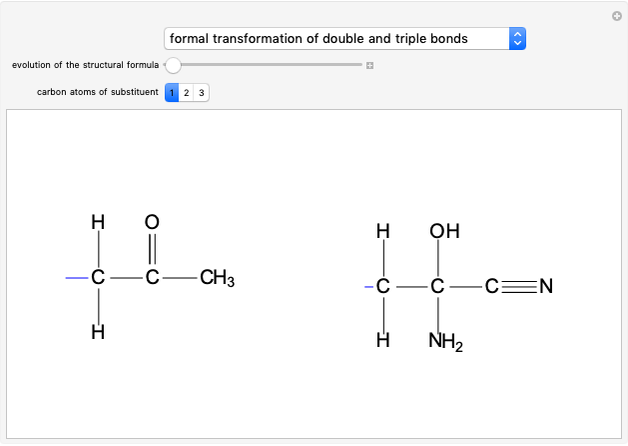
This Demonstration considers the chemical kinetics of the E2 elimination reaction, a reaction of alkyl halides that proceeds in competition with nucleophilic substitution SN2 [1].
[more]
Contributed by: D. Meliga, V. Giambrone, L. Lavagnino and S. Z. Lavagnino (January 2023)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
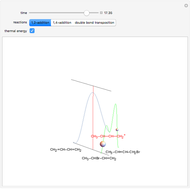
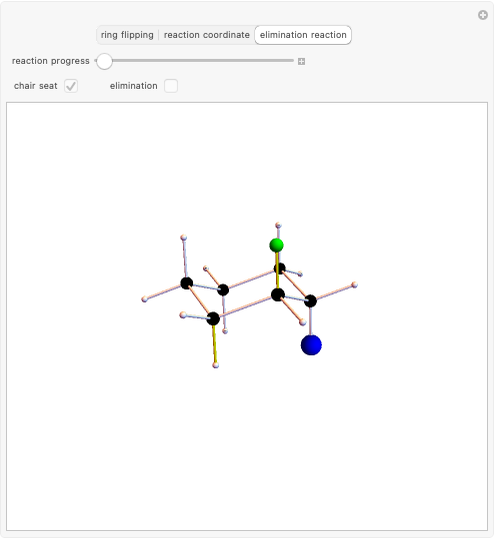
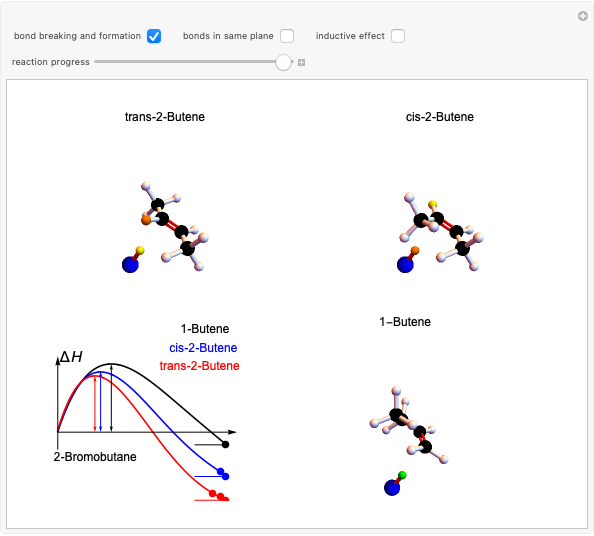
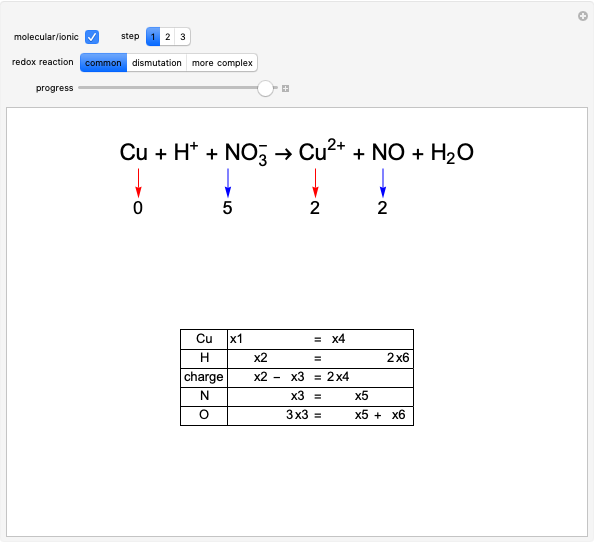
Snapshot 1: bonds breaking (green) and forming (red) in the course of the reaction. Faster compound formation requires a lower activation energy and gives a greater yield. The halogen that comes off must be a good leaving group, such as bromine, and must be in an anti-position with respect to the hydrogen that binds to the nucleophile (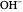 ), in order to promote the formation of the bond
), in order to promote the formation of the bond 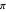 .
.
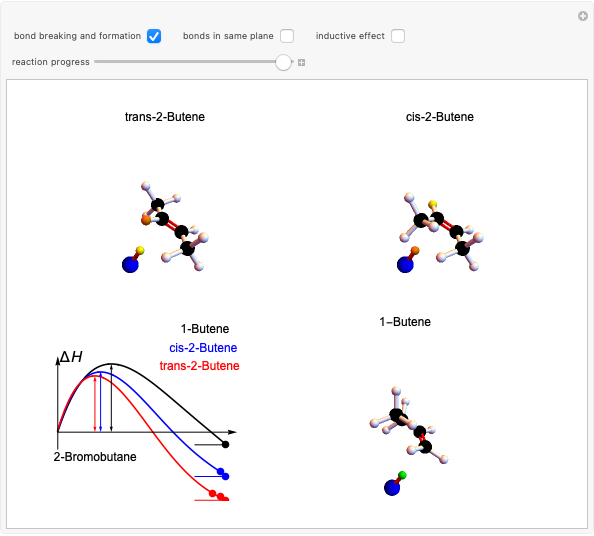
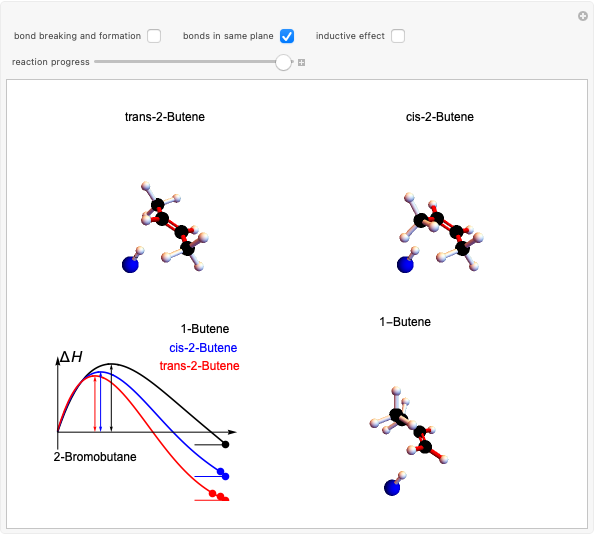
Snapshot 2: when the reaction is complete, it is possible to identify the atoms in the same plane; cis and trans structures for the 2-Butene and no geometric isomerism for the 1-Butene compound.
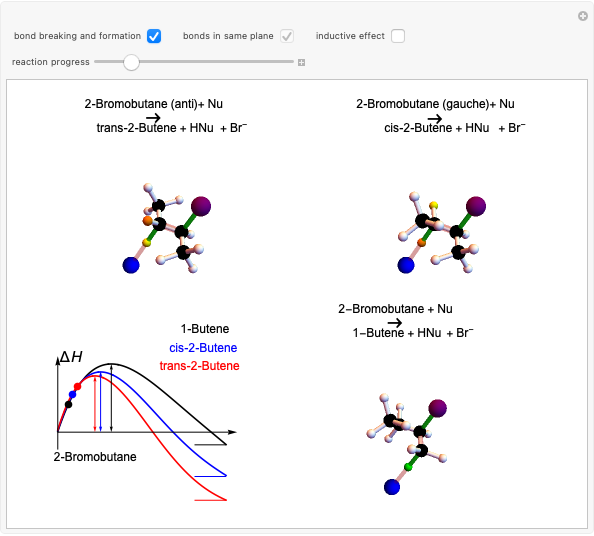
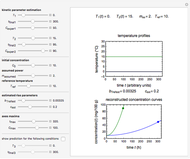
Snapshot 3: as the inductive effect helps to stabilize the final product of the reaction, the relative yield of each depends on the stability
References
[1] S. Z. Lavagnino. Eliminazioni E1 E2 [Video]. (Sep 15, 2022) www.youtube.com/watch?v=rnPxLZ44uO4&list=PLswwssc6Q2yb9Eo2i42BmIGR_Yo58tL7z&index=6.
[2] W. Reusch. "Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides." (Sep 15, 2022) www2.chemistry.msu.edu/faculty/reusch/virttxtjml/alhalrx3.htm.
Permanent Citation