Generalized Pythagoras Theorem

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
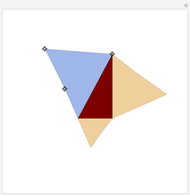
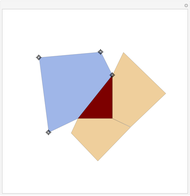
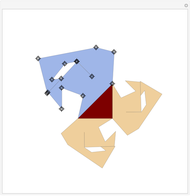
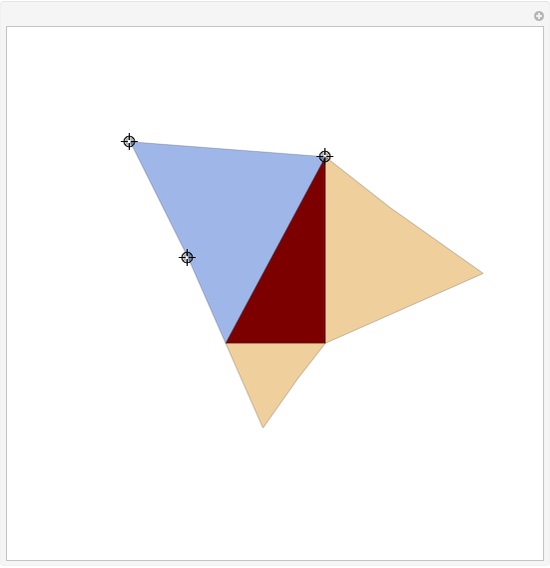
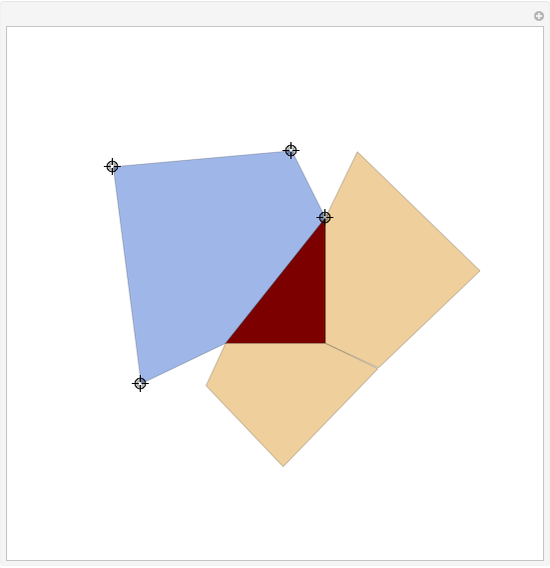
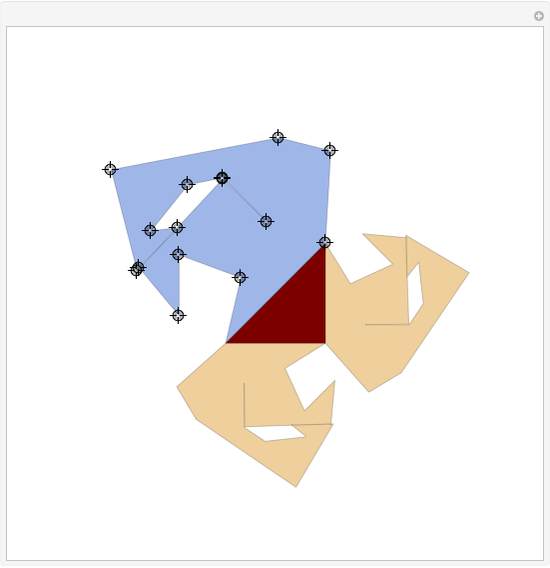
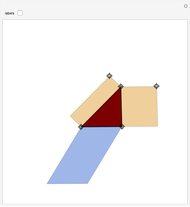
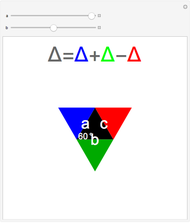
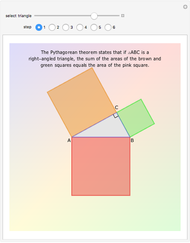
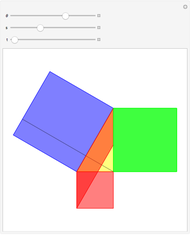
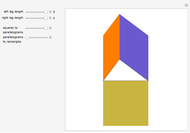
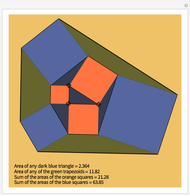
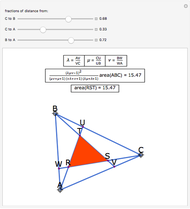
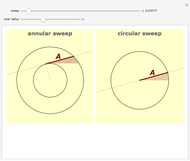
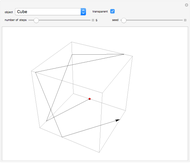
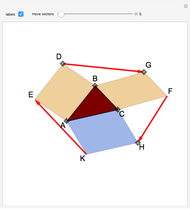
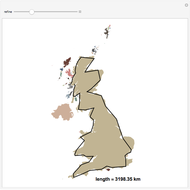
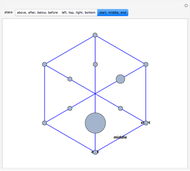
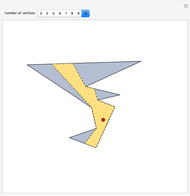
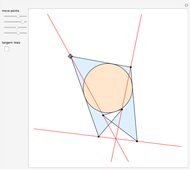
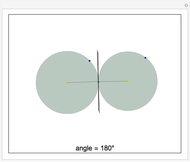
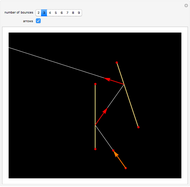
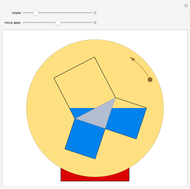
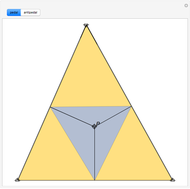
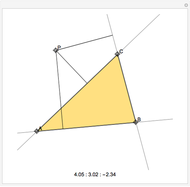
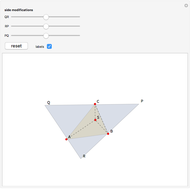
When placing three similar polygons with bases at the hypotenuse and legs of a right triangle, the area of the largest is equal to the sum of the areas of the other two. The Pythagorean theorem states that result in the case when the polygons are squares. This Demonstration illustrates that the area of the blue polygon equals the sum of the areas of the two tan polygons. You can adjust the height of the red right triangle and move or create the locators defining the blue area.
Contributed by: Jaime Rangel-Mondragon (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Generalized Pythagoras Theorem"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/GeneralizedPythagorasTheorem/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011