Heat Transfer in a Heat Exchanger

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
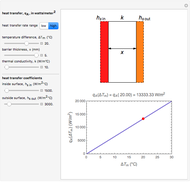
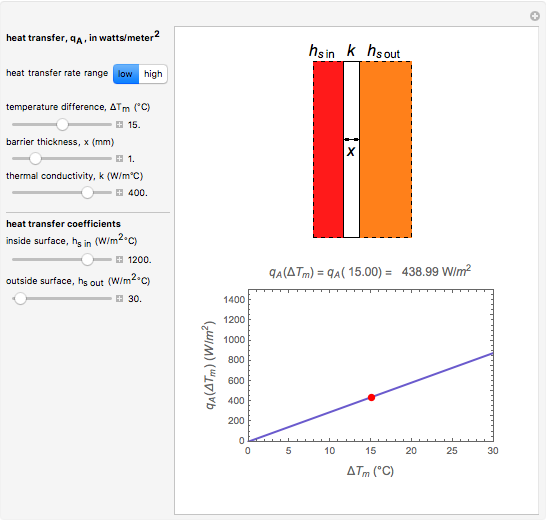
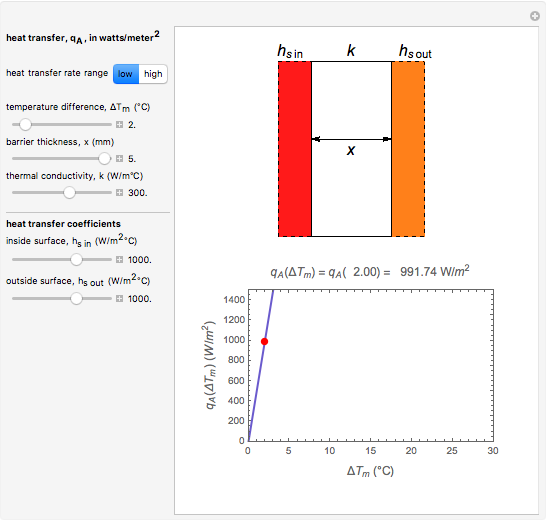
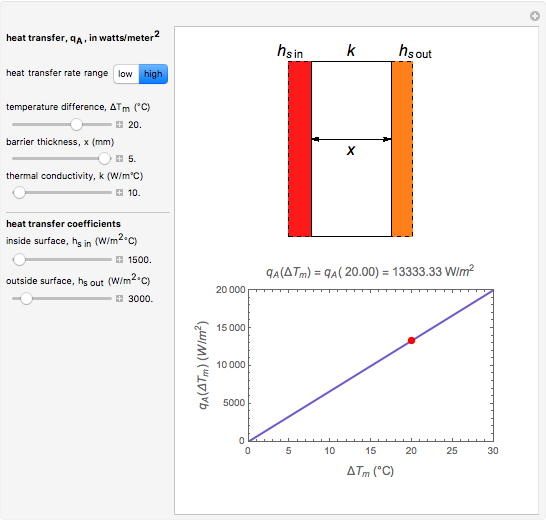
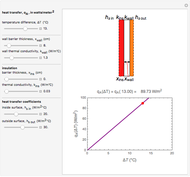
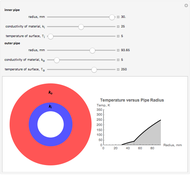
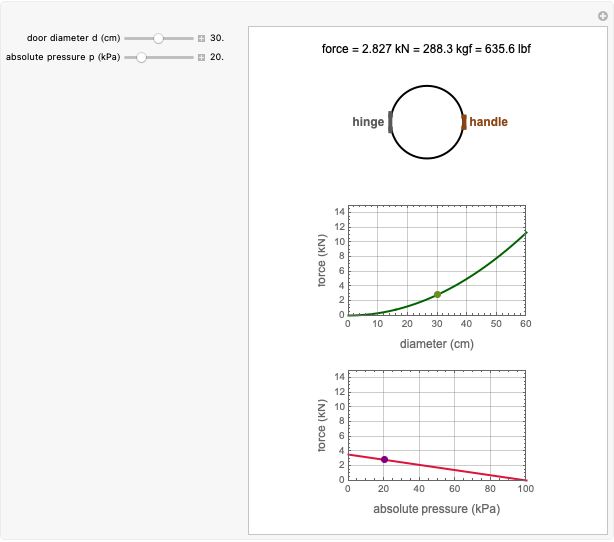
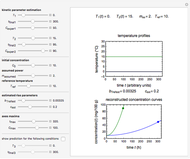
This Demonstration calculates and plots the heat flow,  (in watts/
(in watts/ ), through a heat exchanger's wall of a chosen thickness,
), through a heat exchanger's wall of a chosen thickness,  (in mm), and thermal conductivity,
(in mm), and thermal conductivity,  (in watts/m °C), with chosen surface heat transfer coefficients at either side of the wall,
(in watts/m °C), with chosen surface heat transfer coefficients at either side of the wall,  and
and  (in watts/
(in watts/ °C), and logarithmic mean temperature difference, Δ
°C), and logarithmic mean temperature difference, Δ (in °C), between them. Since the heat transfer coefficients can vary over a very large range, the
(in °C), between them. Since the heat transfer coefficients can vary over a very large range, the  and
and  parameters can be specified as being high or low using a setter bar. The calculations are done using the equation
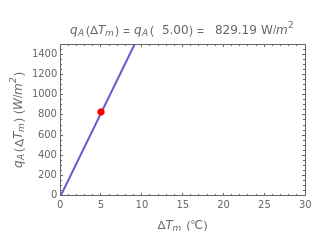
parameters can be specified as being high or low using a setter bar. The calculations are done using the equation  , whose parameters can be modified by moving sliders. The red dot on the plot marks the heat flow per unit area for a Δ
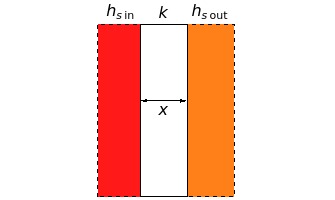
, whose parameters can be modified by moving sliders. The red dot on the plot marks the heat flow per unit area for a Δ chosen by moving the top slider. The top graphic depicts the heat resistances as a schematic diagram (not to scale).
chosen by moving the top slider. The top graphic depicts the heat resistances as a schematic diagram (not to scale).
Contributed by: Mark D. Normand, Maria G. Corradini, and Micha Peleg (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Snapshot 1: heat transfer through a thin, good conducting wall with flowing liquid on the inside and moving air on the outside
Snapshot 2: heat transfer through a thick, good conducting wall with flowing liquids on both sides
Snapshot 3: heat transfer through a thick, poorly conducting wall with flowing liquids on both sides
Snapshot 4: heat transfer through a thick, poorly conducting wall with condensing liquids on both sides
Reference: R. L. Earle with M. D. Earle, Unit Operations in Food Processing, NZIFST, Inc., 1983. (http://www.nzifst.org.nz/unitoperations/)
Permanent Citation
"Heat Transfer in a Heat Exchanger"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/HeatTransferInAHeatExchanger/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011