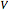Isotherms of Peng-Robinson Equation of State

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
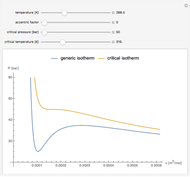
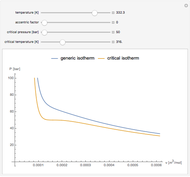
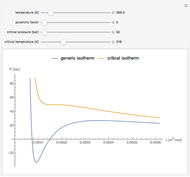
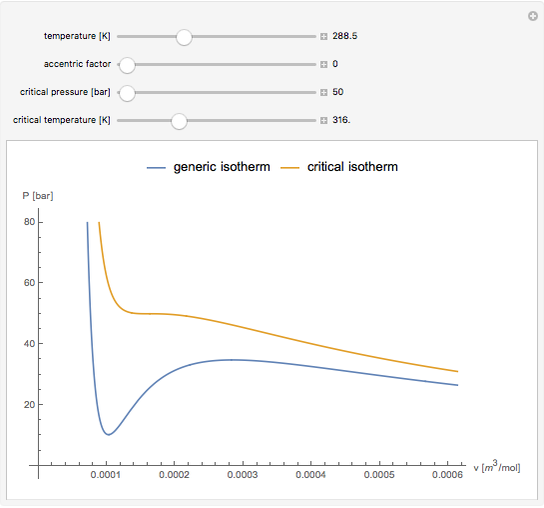
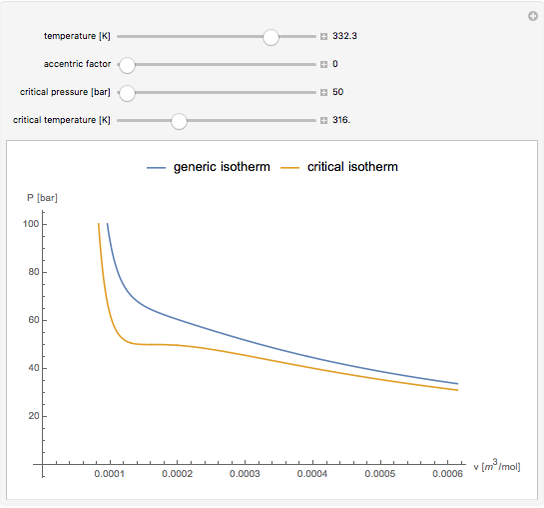
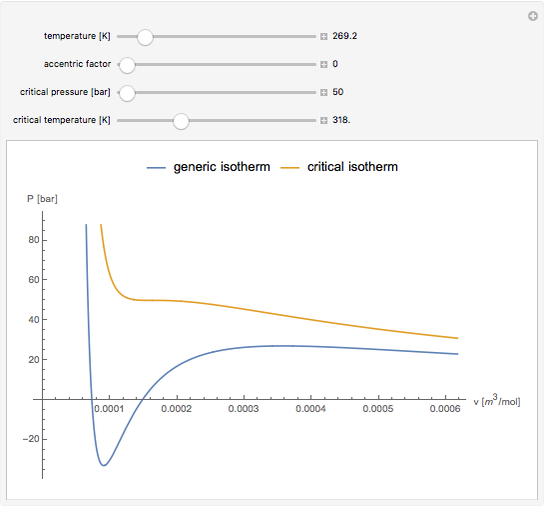
Equations of state, determined empirically or theoretically, can determine the thermodynamic properties of fluids. Equations of state correlate the temperature, pressure, and volume of fluids.
[more]
Contributed by: Fábio Fortkamp (August 2013)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
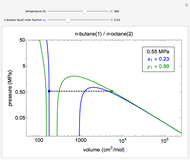
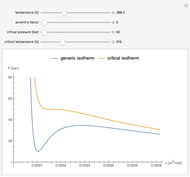
Snapshot 1: temperatures below critical value
Snapshot 2: temperatures above critical value
Snapshot 3: combination of parameters that produce non-physical negative pressures
Reference
[1] J. R. Elliot and C. T. Lira, Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1999.
Permanent Citation
"Isotherms of Peng-Robinson Equation of State"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/IsothermsOfPengRobinsonEquationOfState/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: August 22 2013