Kinetics of Chemical Reaction with an Intermediate Product

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
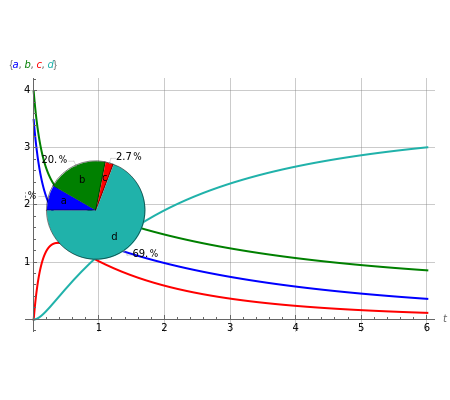
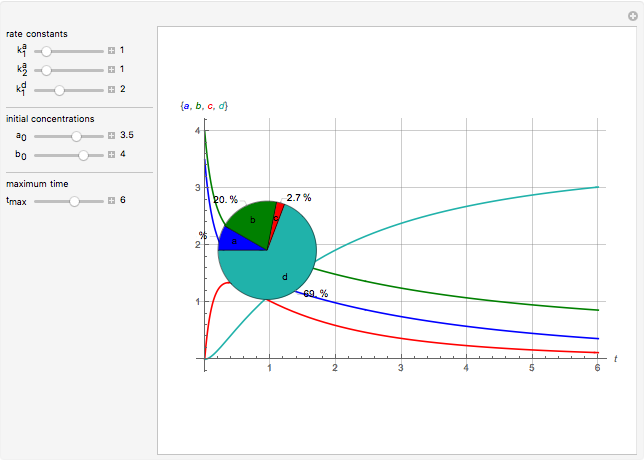
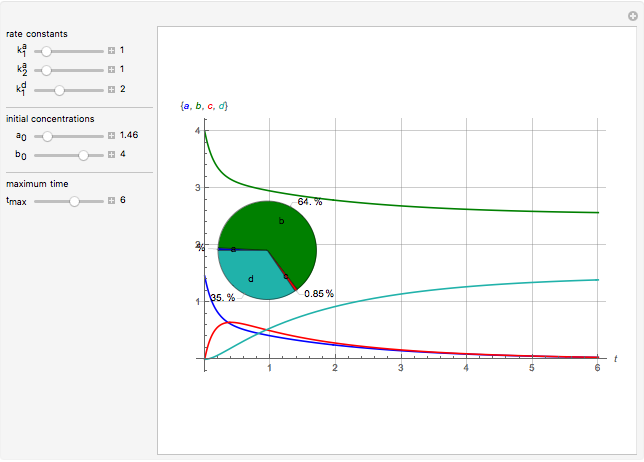
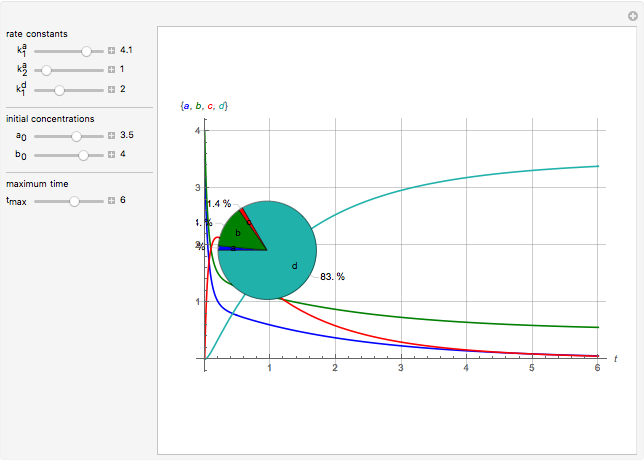
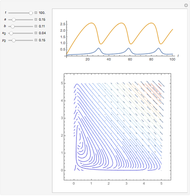
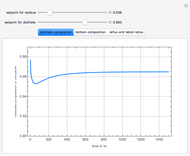
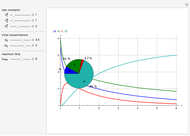
This Demonstration shows a simulation of the time course of differential rate equations. The ordinate denotes concentration in mmol/L and the abscissa denotes time in seconds. The maximum time of reactions is  ,
, 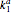 and
and 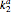 are the association rate constants,
are the association rate constants, 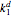 is the dissociation rate constant,
is the dissociation rate constant, 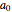 and
and 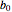 are the initial concentrations of reactants
are the initial concentrations of reactants 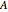 and
and 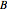 at time
at time  . The pie chart shows concentrations at time
. The pie chart shows concentrations at time  in percentage terms.
in percentage terms.
Contributed by: Vladimir Gantovnik and Cynthia Gibas (University of North Carolina at Charlotte, Department of Bioinformatics & Genomics) (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
After work by I. Chorkendorff and J. W. Niemantsverdriet, Concepts of Modern Catalysis and Kinetics, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2003.
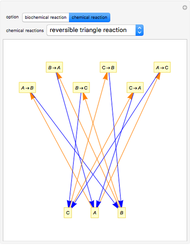
These reactions present the simplest possible reaction in heterogeneous catalysis:
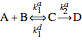 ,
,
where 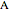 and
and 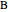 are the reactants,
are the reactants,  is the intermediate product,
is the intermediate product, 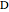 is the final product,
is the final product, 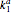 and
and 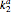 are the association rate constants, and
are the association rate constants, and 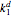 is the dissociation rate constant. The system of differential equations has the following form:
is the dissociation rate constant. The system of differential equations has the following form:
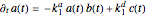 ,
,
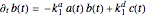 ,
,
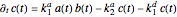 ,
,
 ,
,
where 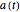 ,
, 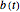 ,
,  , and
, and 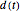 are the concentrations of
are the concentrations of 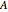 ,
, 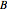 ,
, 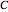 , and
, and 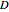 , respectively. Initial conditions at time
, respectively. Initial conditions at time  are
are 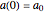 ,
, 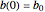 ,
, 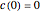 ,
, 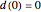 .
.
Permanent Citation