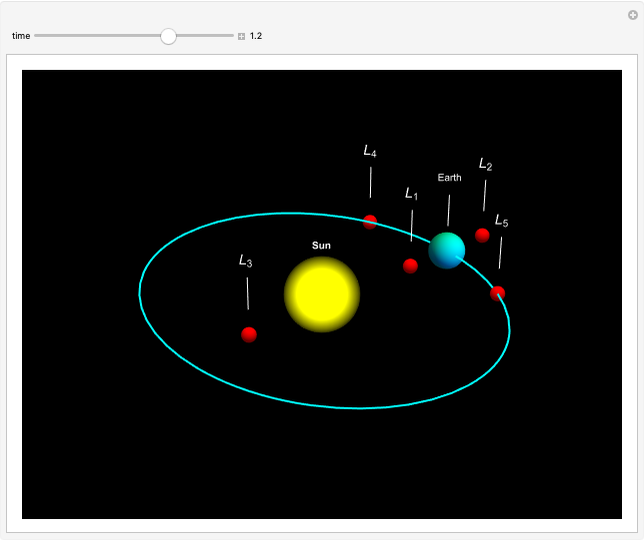
Lagrange Points for Sun-Earth System

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
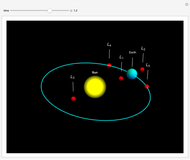
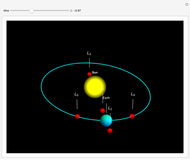
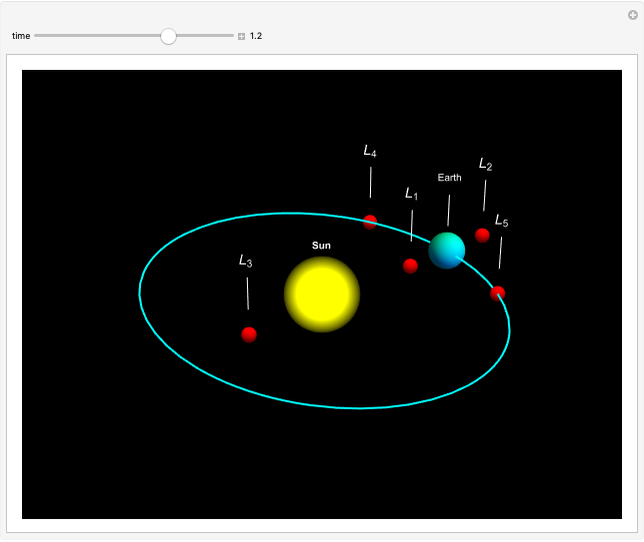
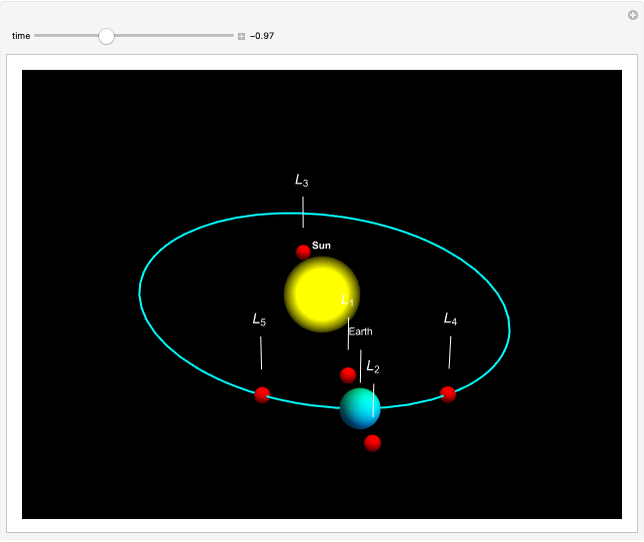
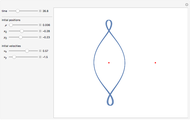
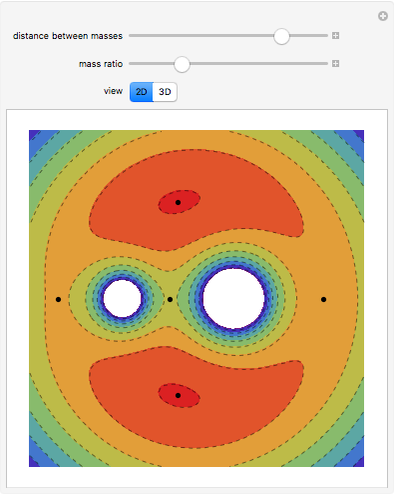
In astrodynamics, a Lagrange point is an equilibrium point of a small object (such as a satellite) experiencing the gravitational pull of two large objects (such as the Sun and Earth). Mathematically, Lagrange points represent positions where the gravitational pull of two large masses precisely balances the centripetal force on a much lighter body. It arises in solutions of the restricted three-body problem, in which two bodies are far more massive than the third.
[more]
Contributed by: Akram Masoud (August 2022)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation