Polarization of an Electromagnetic Wave

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
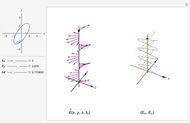
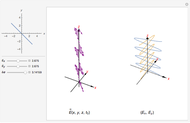
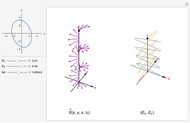
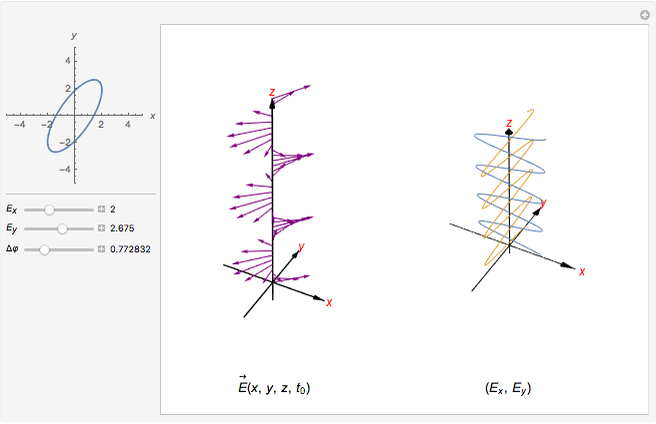
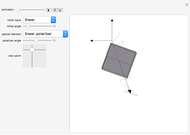
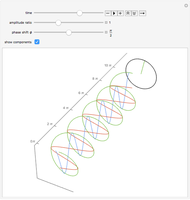
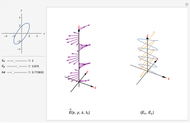
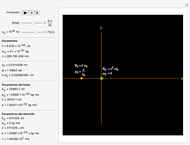
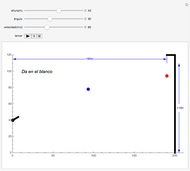
The polarization of an electromagnetic wave describes the orientation of the oscillating electric field. The wave is transverse and travels in the positive  direction. There is also a magnetic field in phase with the electric field and perpendicular to both the electric field and the direction of propagation. The electric field may be divided into two perpendicular components labeled
direction. There is also a magnetic field in phase with the electric field and perpendicular to both the electric field and the direction of propagation. The electric field may be divided into two perpendicular components labeled 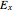 and
and 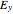 , such that
, such that 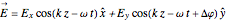 , where
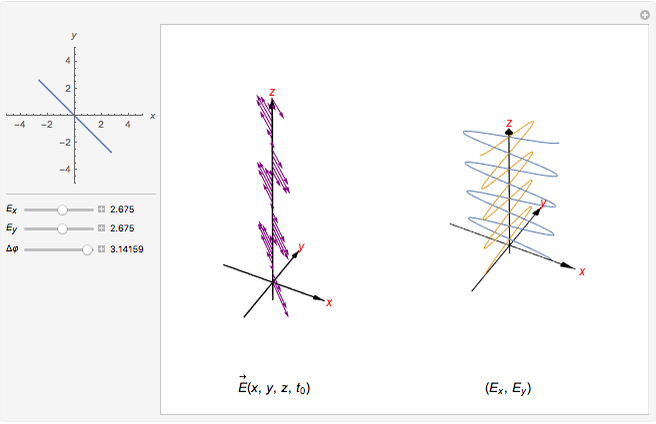
, where 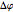 is the phase difference between the two components. When
is the phase difference between the two components. When 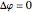 or
or 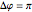 , the wave is said to be linearly polarized. If
, the wave is said to be linearly polarized. If 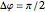 and
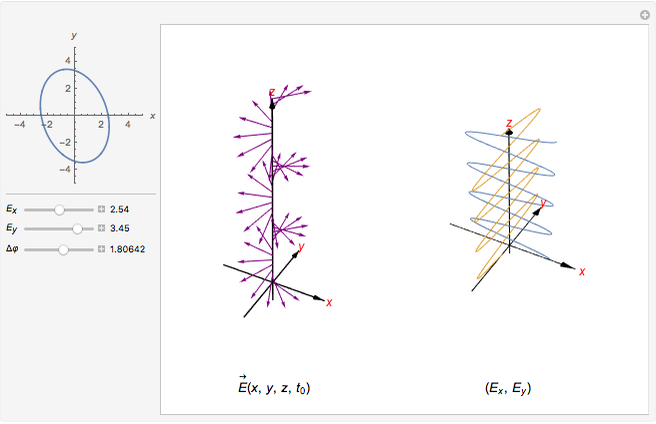
and 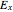 has the same magnitude as
has the same magnitude as 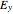 , then the wave is said to be circularly polarized; in all other cases, the wave is elliptically polarized.
, then the wave is said to be circularly polarized; in all other cases, the wave is elliptically polarized.
Contributed by: Luis Jonathan Cervantes Rosas (February 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Polarization of an Electromagnetic Wave"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/PolarizationOfAnElectromagneticWave/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: February 9 2012