Reflection and Transmission Coefficients of an Optical Cavity

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
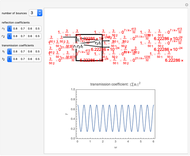
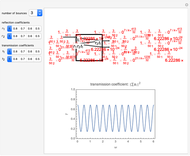
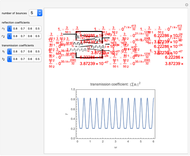
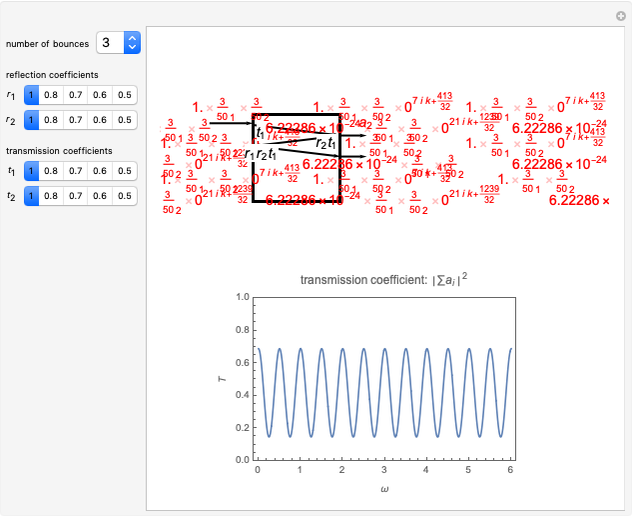
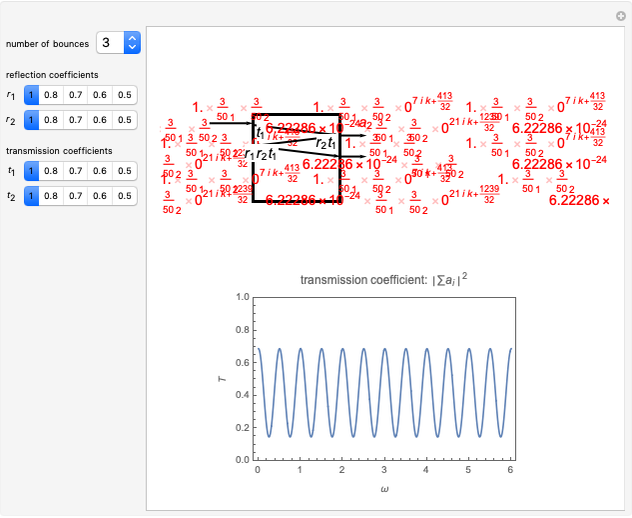
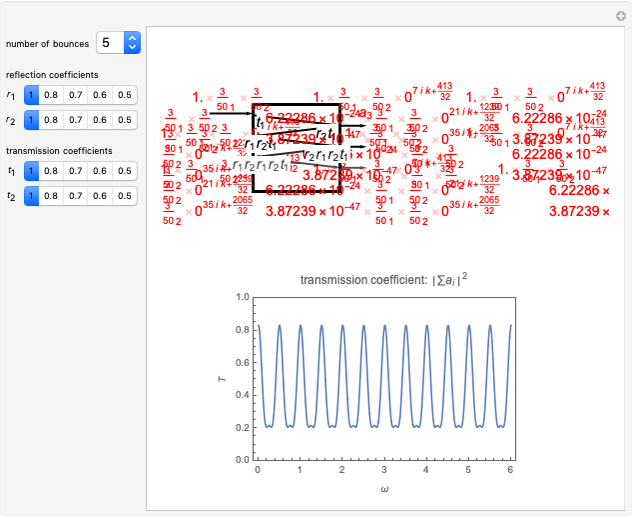
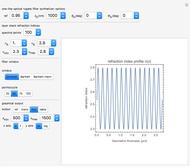
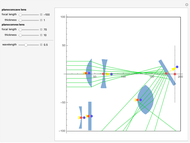
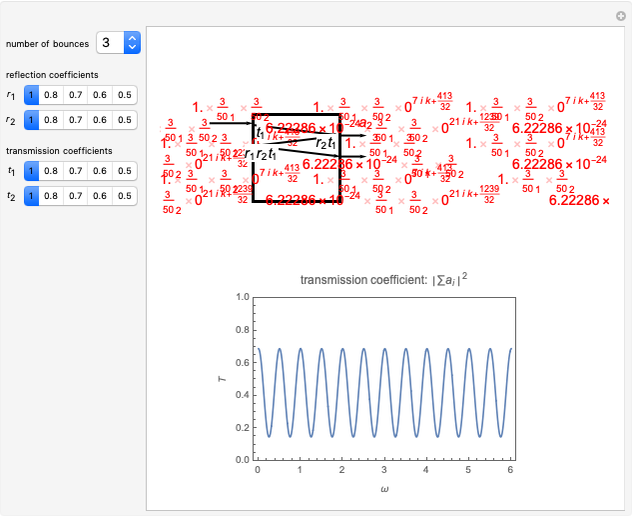
Consider a ray of light bouncing back and forth between two reflective surfaces with reflection and transmission coefficients  . As the light (represented by a complex exponential with wave vector
. As the light (represented by a complex exponential with wave vector  ) travels a length
) travels a length  through the cavity, the amplitude decreases with an optical loss factor
through the cavity, the amplitude decreases with an optical loss factor  . After
. After  bounces, the amplitude is multiplied by a factor
bounces, the amplitude is multiplied by a factor  , while the reflection coefficients
, while the reflection coefficients  ,
,  are multiplied by this factor
are multiplied by this factor  times. The phase after traveling
times. The phase after traveling  lengths is equal to
lengths is equal to  . The total transmission is given by the sum of rays
. The total transmission is given by the sum of rays  . This is a geometric series, so
. This is a geometric series, so  , where
, where  . Finally, we arrive at the total transmission
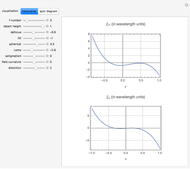
. Finally, we arrive at the total transmission  . From the plot, there will be resonant frequencies in the limit as
. From the plot, there will be resonant frequencies in the limit as  .
.
Contributed by: Lauren Cooper (December 2020)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] J. Hu. "Optical Resonant Cavities." Photonic Materials and Devices (3.156). Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology. studylib.net/doc/15437195/mseg-667-5--optical-resonant-cavities-prof.-juejun--jj--hu.
Permanent Citation