Solving a Double Scissor Truss

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
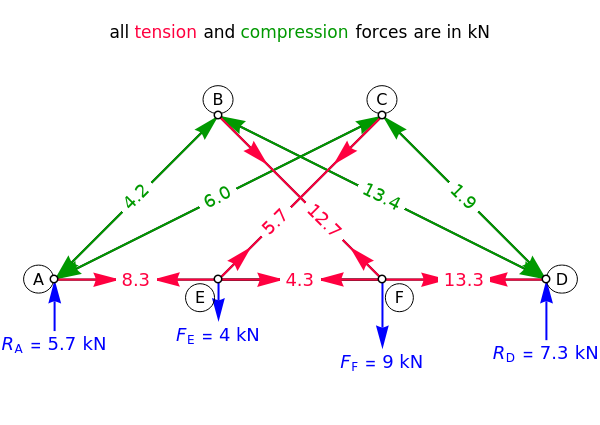
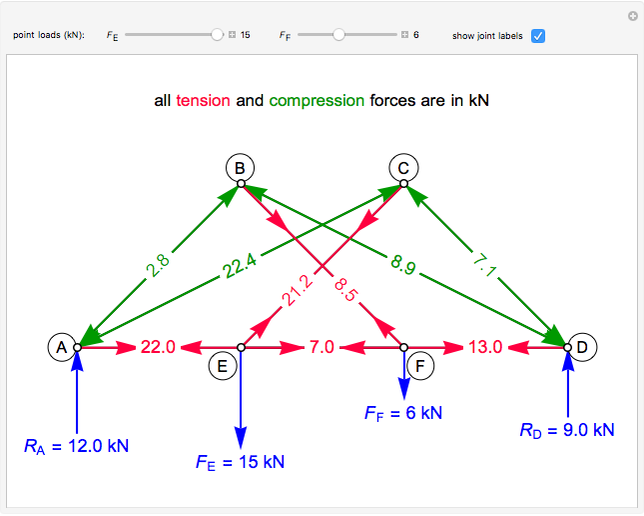
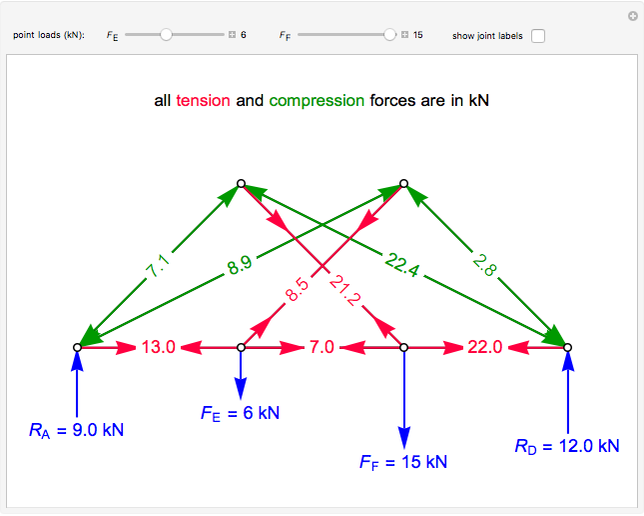
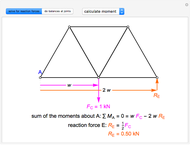
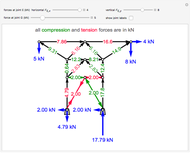
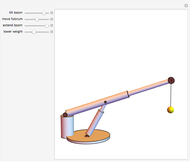
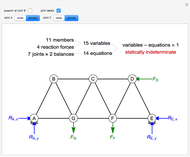
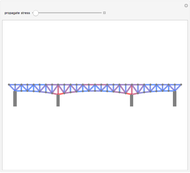
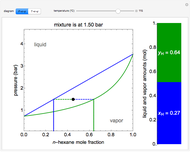
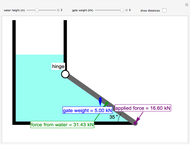
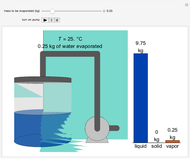
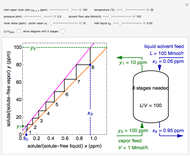
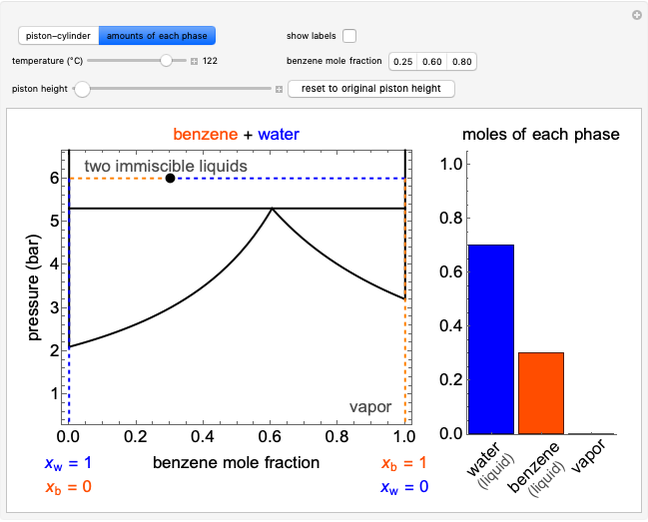
This Demonstration uses the method of joints to solve the member forces in a double scissor truss. The point loads ( ,
,  ) and reaction forces (
) and reaction forces ( ,
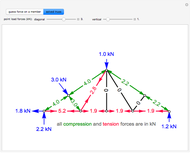
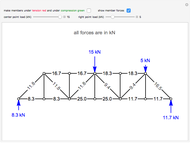
, 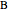 ) are shown in blue. Set the point loads with sliders. Check "show joint labels" to show the labels assigned to each joint. Arrows that point outward represent the member response to compression forces (green), and arrows that point inward represent the member response to tension forces (red). Compression acts to shorten the member, and tension acts to lengthen the member. Black members are zero members; that is, these members are neither in tension nor in compression, so the force is 0 kN. The purpose of zero members is to provide stability and extra support to the structure in case another member fails. The member forces are shown on the diagram in kN.
) are shown in blue. Set the point loads with sliders. Check "show joint labels" to show the labels assigned to each joint. Arrows that point outward represent the member response to compression forces (green), and arrows that point inward represent the member response to tension forces (red). Compression acts to shorten the member, and tension acts to lengthen the member. Black members are zero members; that is, these members are neither in tension nor in compression, so the force is 0 kN. The purpose of zero members is to provide stability and extra support to the structure in case another member fails. The member forces are shown on the diagram in kN.
Contributed by: Rachael L. Baumann (September 2017)
Additional contributions by: John L. Falconer
(University of Colorado Boulder, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation
"Solving a Double Scissor Truss"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/SolvingADoubleScissorTruss/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: September 8 2017