Structure of Water in Acid and Basic Media

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
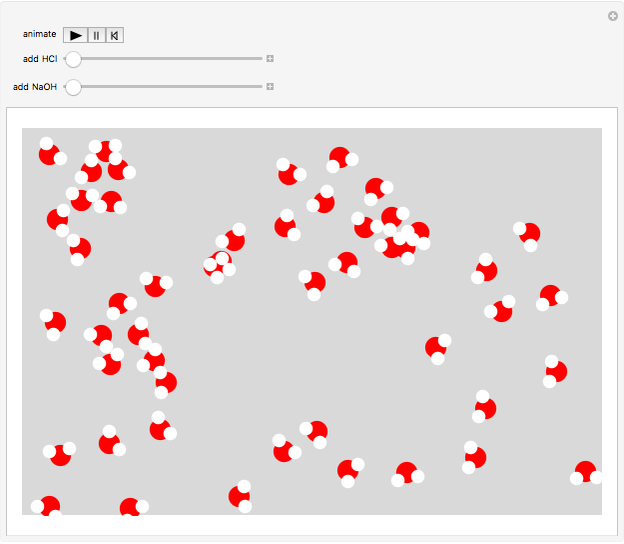
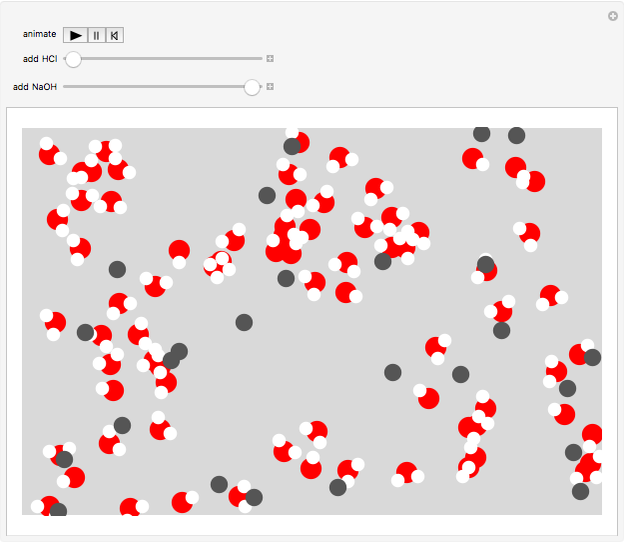
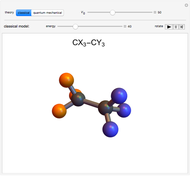
Water molecules have a distorted tetrahedral structure with protons occupying two vertices and unshared electron pairs extending toward the other two vertices. The structure 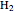 O
O  has protons rapidly exchanging positions and hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules. An acid, such as hydrochloric acid HCl, dissociates in water, with most of the protons associating with water molecules to form hydronium ions
has protons rapidly exchanging positions and hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules. An acid, such as hydrochloric acid HCl, dissociates in water, with most of the protons associating with water molecules to form hydronium ions 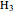
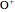
 , along with chloride ions
, along with chloride ions 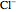
 . An acid solution has a
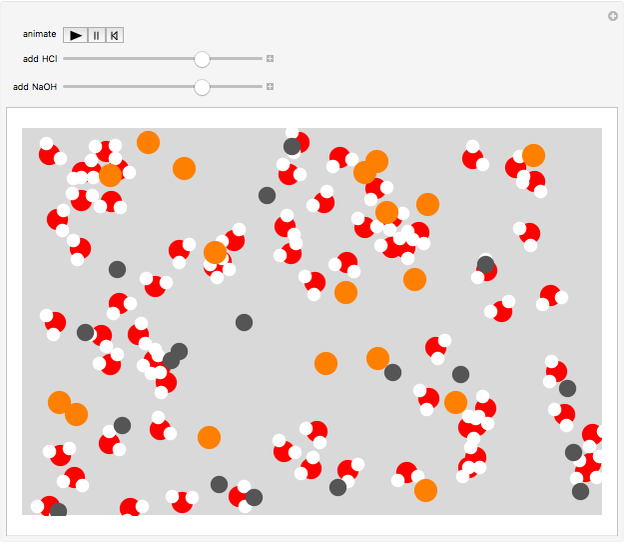
. An acid solution has a 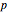 H less than 7. A base, such as sodium hydroxide NaOH, dissociates to give hydroxide ions
H less than 7. A base, such as sodium hydroxide NaOH, dissociates to give hydroxide ions 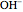
 and sodium ions
and sodium ions 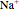
 . A basic solution has a
. A basic solution has a 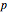 H greater than 7. The structures of the three hydrogen-oxygen species are highly dynamic, with protons continually exchanging and hydrogen bonds forming and breaking. Turn on the animation first to simulate this situation.
H greater than 7. The structures of the three hydrogen-oxygen species are highly dynamic, with protons continually exchanging and hydrogen bonds forming and breaking. Turn on the animation first to simulate this situation.
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
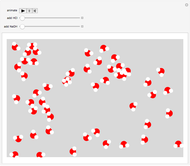
Snapshot 1: pure water
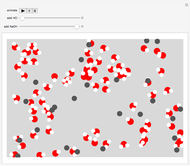
Snapshot 2: basic solution of NaOH
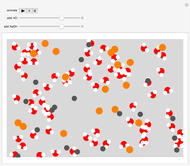
Snapshot 3: neutralized solution of NaCl and HCl
Permanent Citation
"Structure of Water in Acid and Basic Media"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/StructureOfWaterInAcidAndBasicMedia/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011