Synthetic Legal Precedent Structures: Feature Distance

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
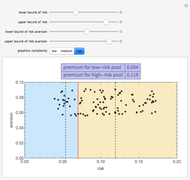
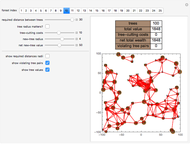
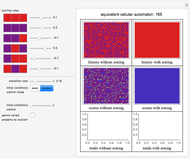
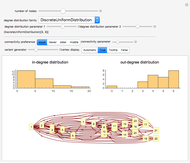
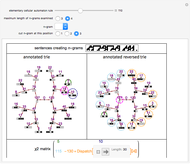
In common-law systems, legal cases tend to cite one another. This Demonstration synthesizes a legal precedent structure in which cases are given up to five features as well as a time of decision. Cases cite preceding cases whose features most closely resemble themselves. The user can control the number of cases in the legal system, the mean number of outgoing citations per case, the standard deviation of the number of outgoing citations per case, and the number of features of preceding cases examined. The user can also select from two network visualization functions. An interesting issue is whether this simple model is capable of generating precedent networks that resemble those of real common-law systems.
Contributed by: Seth J. Chandler (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
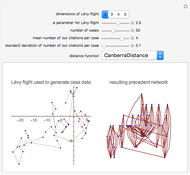
The "closeness" of cases is determined using the Euclidean distance of their compared features from each other. The number of outgoing citations is distributed in a log normal way. Early cases are deemed proximate to each other even if their features differ.
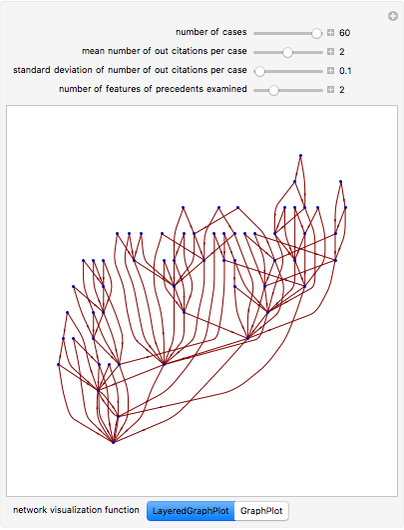
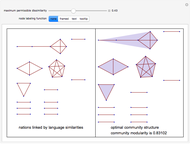
Snapshot 1: a larger number of cases in the judicial system
Snapshot 2: more outgoing citations
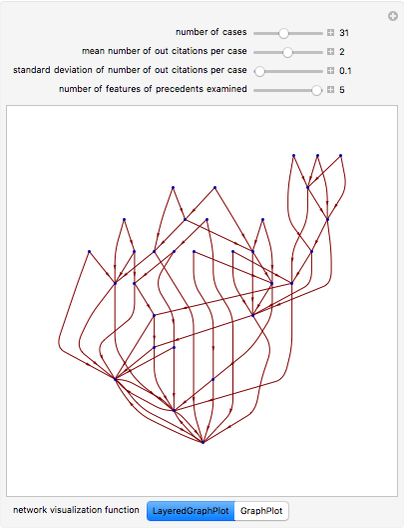
Snapshot 3: a larger number of features examined
Permanent Citation
"Synthetic Legal Precedent Structures: Feature Distance"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/SyntheticLegalPrecedentStructuresFeatureDistance/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011