Three Intermolecular Potential Models

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
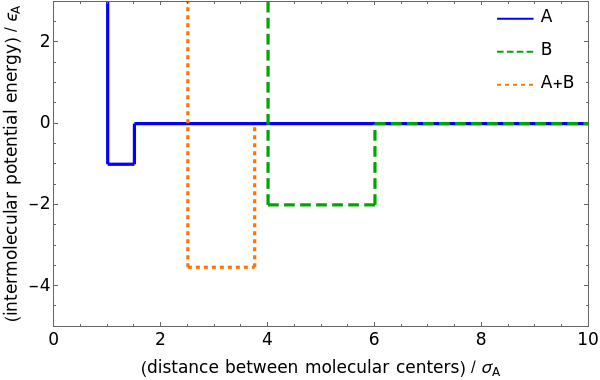
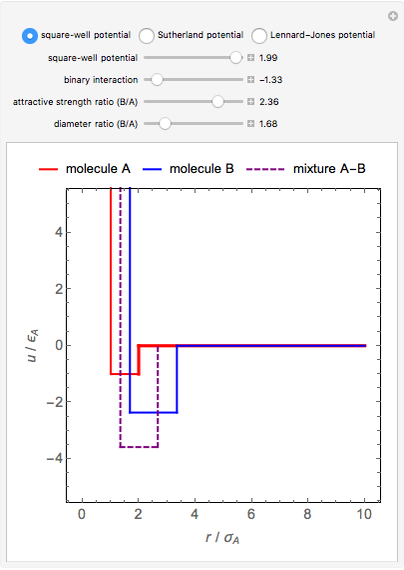
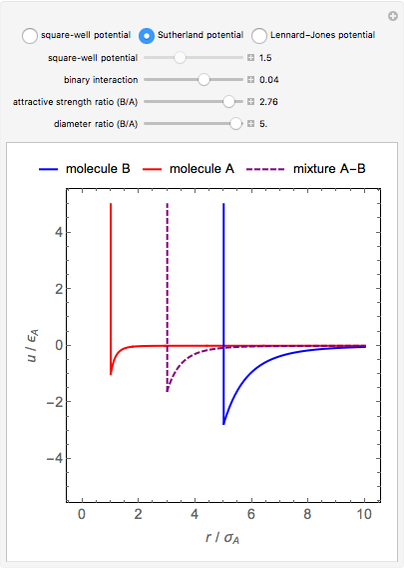
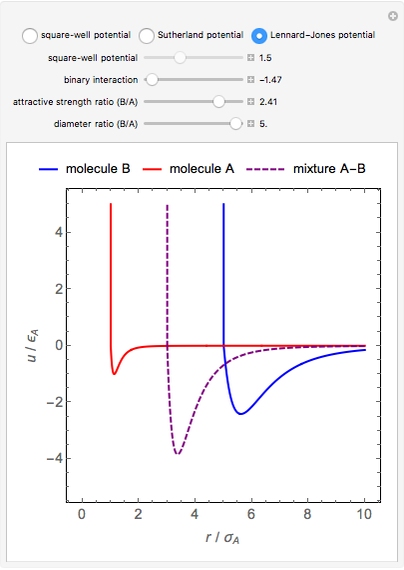
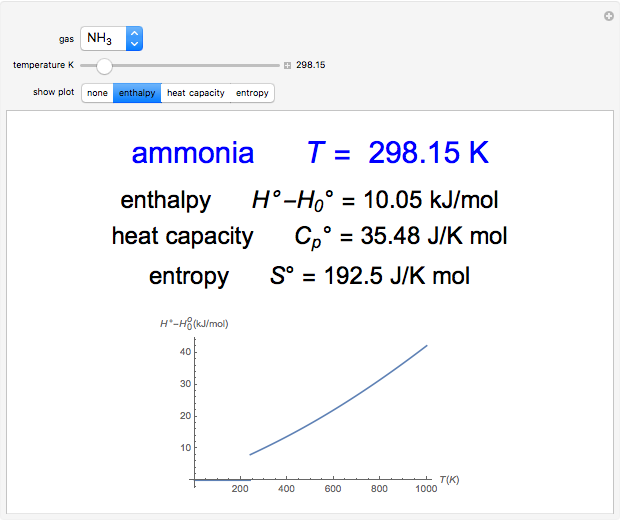
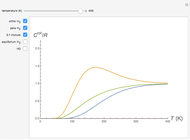
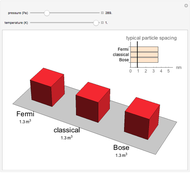
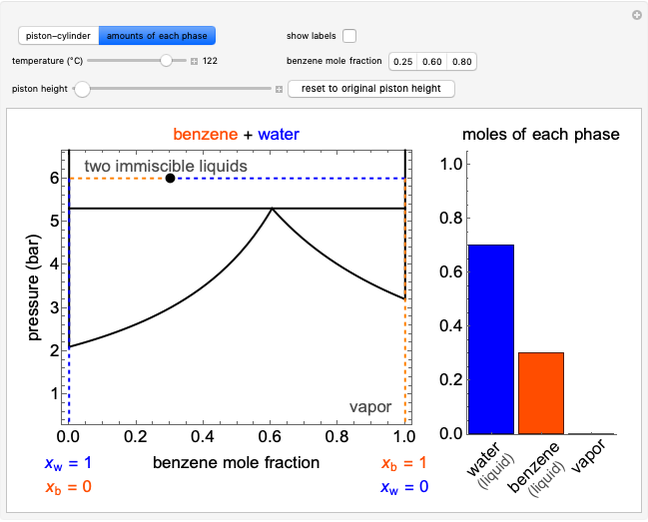
This Demonstration considers three models for intermolecular potentials: square-well, Sutherland, and Lennard-Jones. Potentials for molecule  (blue), molecule
(blue), molecule  (green), and an
(green), and an  mixture (orange) are shown. Use a slider to vary the binary interaction parameter
mixture (orange) are shown. Use a slider to vary the binary interaction parameter  , which represents how non-ideal the mixture is (
, which represents how non-ideal the mixture is ( for the ideal case). The attractive-strength ratio represents the relative well depths of
for the ideal case). The attractive-strength ratio represents the relative well depths of  to
to  . The diameter ratio represents the relative sizes of the molecules. The relative width is the ratio of attractive diameter to the repulsive diameter.
. The diameter ratio represents the relative sizes of the molecules. The relative width is the ratio of attractive diameter to the repulsive diameter.
Contributed by: Megan E. Maguire and Rachael L. Baumann (December 2013)
Additional contributions by: John L. Falconer and Nick Bongiardina
(University of Colorado Boulder, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The square-well potential is:

The Sutherland potential is:

The Lennard–Jones potential is:
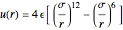
where  is the intermolecular potential,
is the intermolecular potential,  is the distance between the molecule centers,
is the distance between the molecule centers,  is the molecular diameter,
is the molecular diameter,  is the depth of the potential well, and
is the depth of the potential well, and  is the well width for square-well potential.
is the well width for square-well potential.
The attractive strength parameter of the mixture is given by:
 ,
,
where  is the binary interaction parameter, and
is the binary interaction parameter, and  and
and  are the attractive strength parameters for molecules
are the attractive strength parameters for molecules  and
and  .
.
A larger negative number for the binary interaction parameter represents stronger interactions between  and
and  relative to those between
relative to those between  and
and  or
or  and
and  . Analogously, a smaller positive number represents weaker interactions.
. Analogously, a smaller positive number represents weaker interactions.
The molecular diameter parameter for the mixture is:
 ,
,
where  and
and  are the diameter parameters for molecules
are the diameter parameters for molecules  and
and  .
.
A screencast video at [1] shows how to use this Demonstration.
Reference
[1] Three Intermolecular Potential Models. www.colorado.edu/learncheme/thermodynamics/ThreeIntermolecularPotentialModels.html.
Permanent Citation