Watt's Lemniscoidal Linkage

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
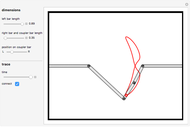
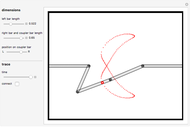
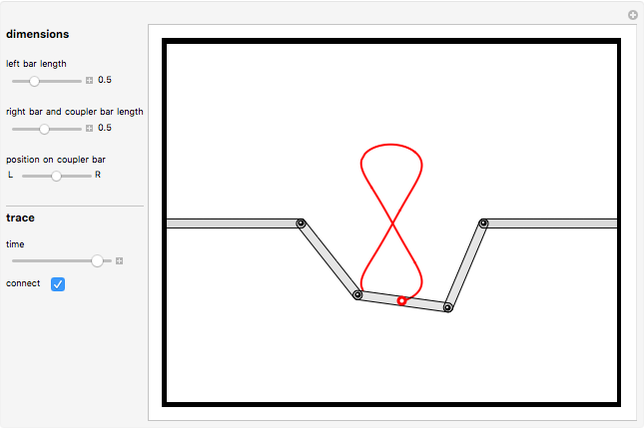
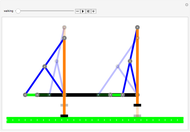
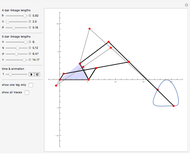
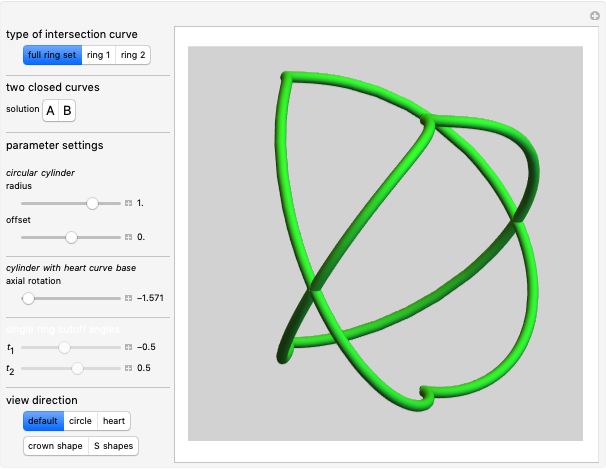
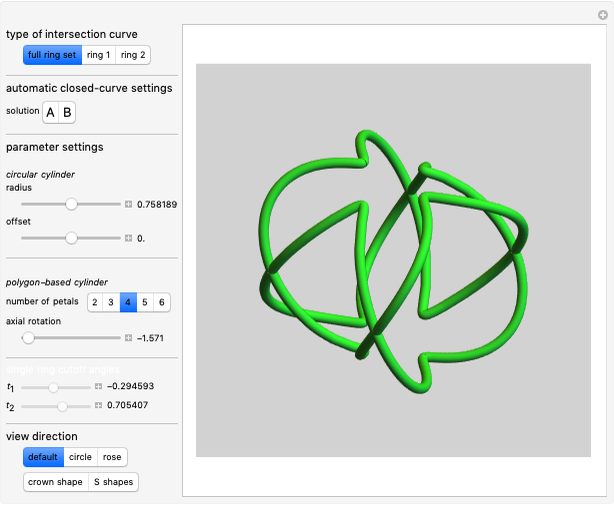
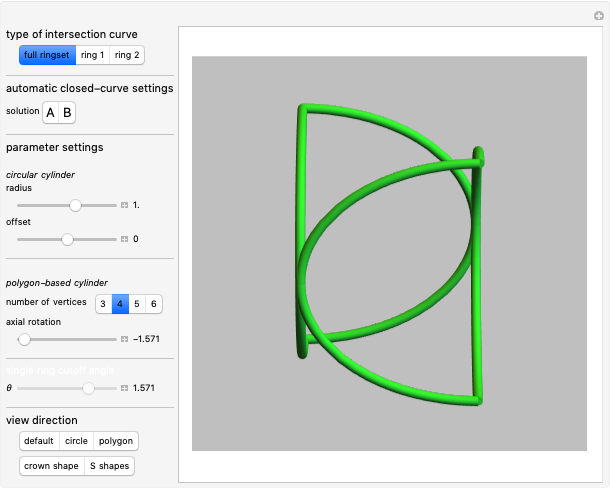
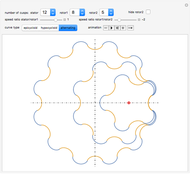
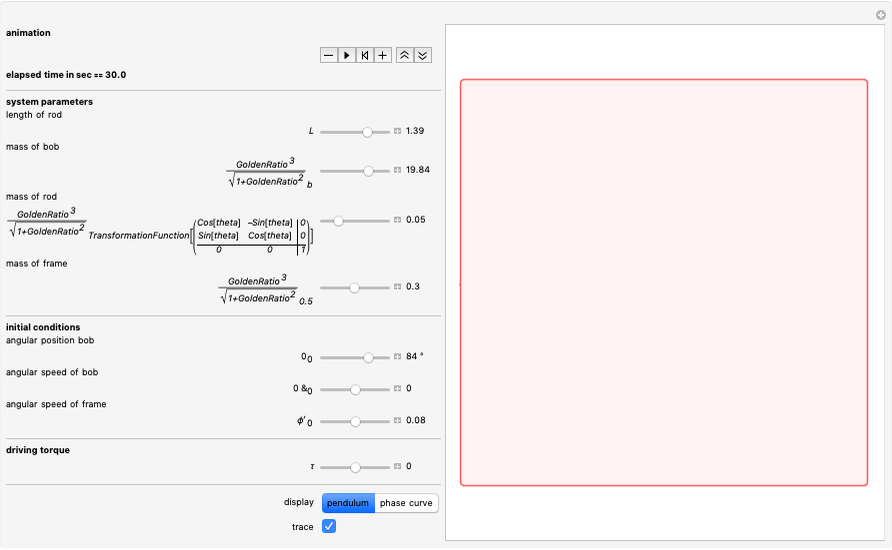
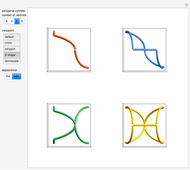
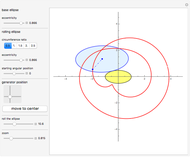
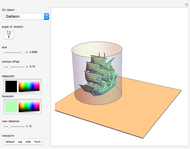
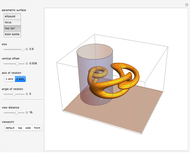
Watt's linkage is a four-bar mechanical linkage with one degree of freedom. The linkage was developed to convert rotary motion into approximate rectilinear motion.
[more]
Contributed by: Erik Mahieu (September 2016)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
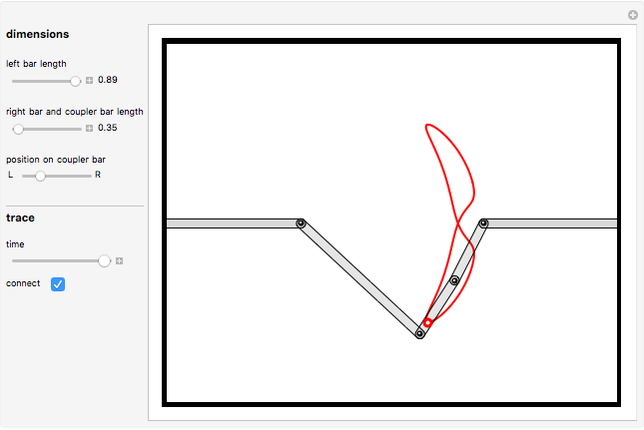
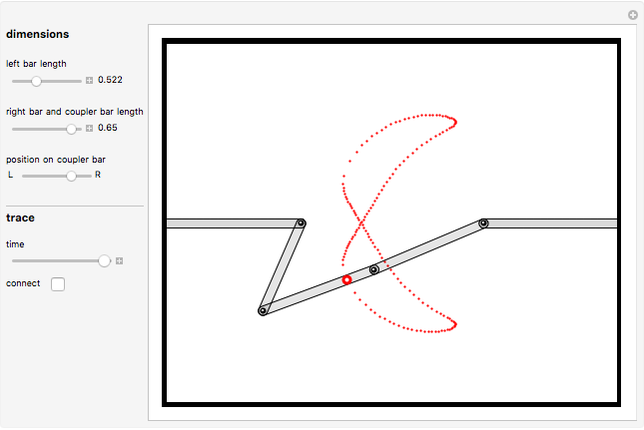
Snapshots
Details
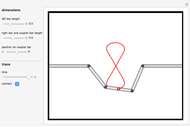
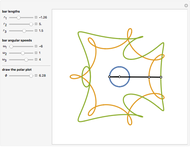
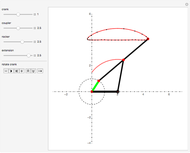
Snapshot 1: if the three bars have similar lengths, the center of the coupler bar draws a lemniscate with two substantial, almost rectilinear parts
Reference
[1] Cornell University, Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. "Model: S24 Lemniscoidal Linkage of the First Kind by Watt." (Sep 27, 2016) kmoddl.library.cornell.edu/model.php?m=145.
Permanent Citation