Waves from a Moving Source
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
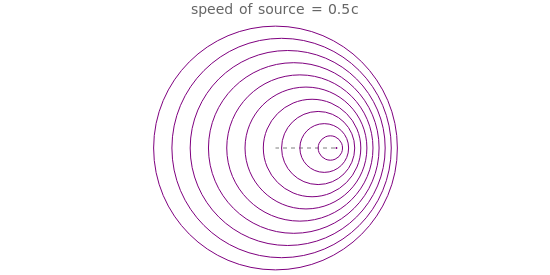
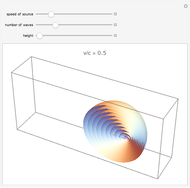
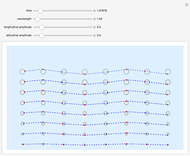
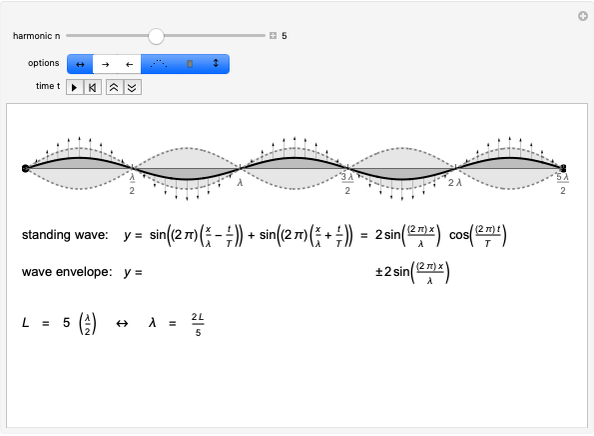
Below the wave speed, waves emitted from a moving source pile up in front and spread out behind, leading to a Doppler shift. Above the wave speed, waves accumulate at the sides, forming a shock wave.
Contributed by: Stephen Wolfram (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
For sound, v/c is the Mach number. For light, it is the fraction of the local speed of light. Objects travelling faster than the local speed of light (e.g. in water) emit Cerenkov radiation. The angle of the shock wave sharpens as the speed of the source increases.
Permanent Citation