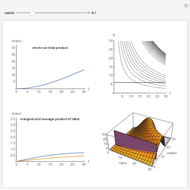
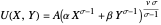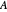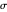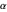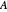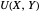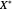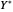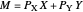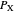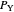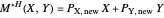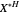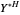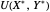Constant Elasticity of Substitution (CES) for Marshallian and Hicksian Demand Functions

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
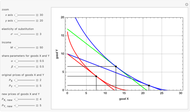
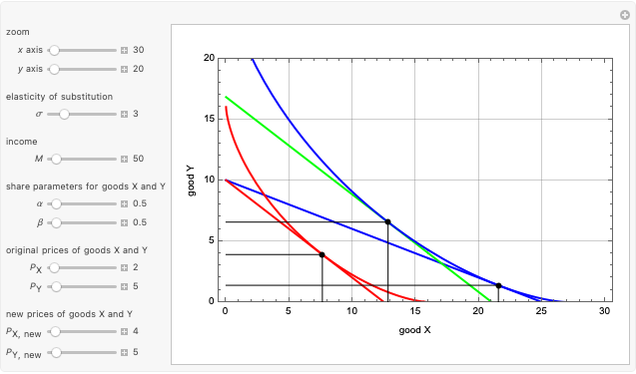
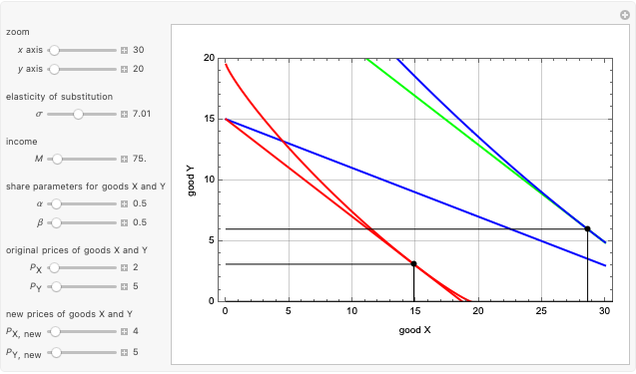
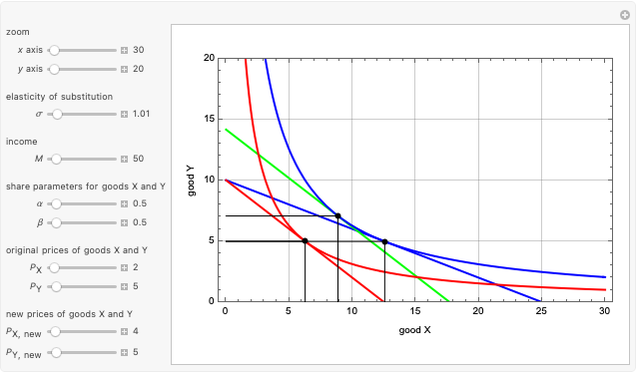
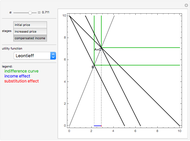
This Demonstration shows the relationships of iso-utility and iso-expenditures for the goods 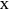 and
and 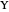 in the constant elasticity of substitution (CES) formulation for Marshallian and Hicksian levels of consumption. We consider both compensated and uncompensated income. Let
in the constant elasticity of substitution (CES) formulation for Marshallian and Hicksian levels of consumption. We consider both compensated and uncompensated income. Let  and
and 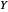 be the number of units of the goods.
be the number of units of the goods.
Marshallian consumption 2 (red curve and red line): maximization of 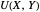 with optimal consumption
with optimal consumption 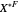 ,
, 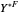 subject to uncompensated income
subject to uncompensated income 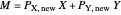 , where
, where 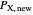 and
and 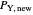 are the changed prices. (January 2023)
are the changed prices. (January 2023)
Contributed by: Carlos Angulo
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
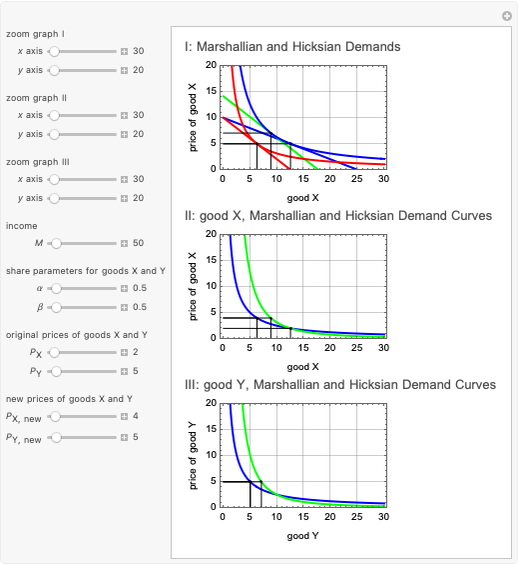
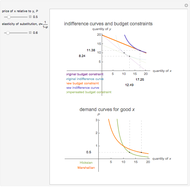
This Demonstration is based on [1], which develops further mathematical analysis from an idea in [2]. The purpose of this Demonstration is to explore how changes in the system parameters lead to changes in the equilibrium states. Hicksian substitution and income effects are represented in the following plots: (1) blue curve and blue line (original Marshallian consumption); (2) red curve and red line (final Marshallian consumption); and (3) blue curve and green line (Hicksian consumption).
References
[1] C. Angulo, "Creation of Wolfram Visualisation Tools for Microeconomic Pedagogy in Comparative Statics," Undergraduate Research Support Scheme research paper, University of Warwick, UK, forthcoming.
[2] K. Sydsæter, P. Hammond, A. Strøm and A. Carvajal, Essential Mathematics for Economic Analysis, 6th ed., Hoboken, NJ: Pearson, 2021.
Permanent Citation