Brinell Hardness of Materials

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
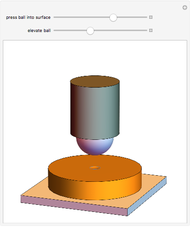
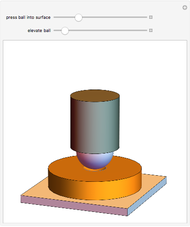
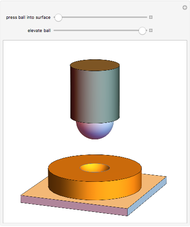
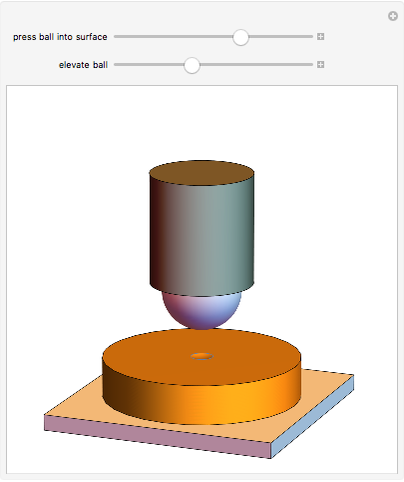
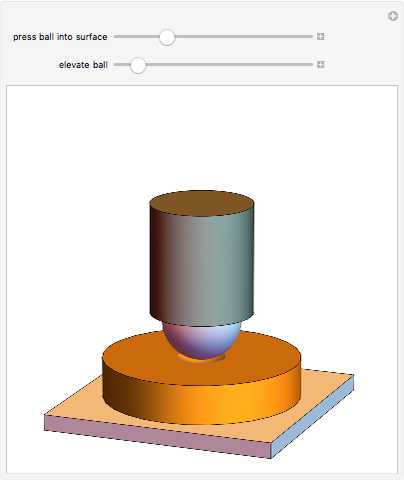
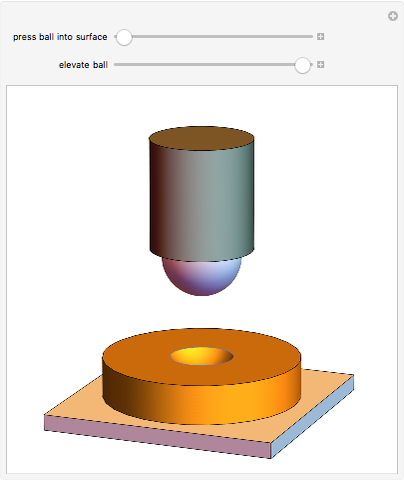
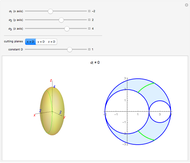
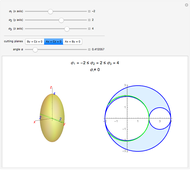
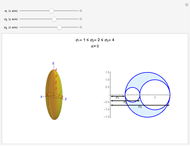
When a ball is pressed into a piece of material, the size of the indentation made by the ball is inversely proportional to the hardness of the material. This relationship was used by the Swedish engineer Dr. Johan August Brinell to develop a standardized testing method in 1900. The Brinnel hardness (HB) is calculated by dividing the applied force by the surface of indentation. Typical Brinnel hardness values include: aluminum 15 HB, copper 35 HB, mild steel 120 HB, hardened steel 1500 HB, rhenium diboride 4600 HB.
Contributed by: Sándor Kabai (October 2008)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
For details see the relevant Wikipedia entry.
Permanent Citation
"Brinell Hardness of Materials"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/BrinellHardnessOfMaterials/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: October 28 2008