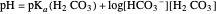pH Buffering in Human Blood

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
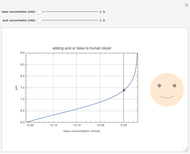
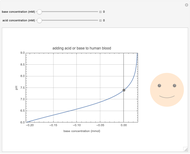
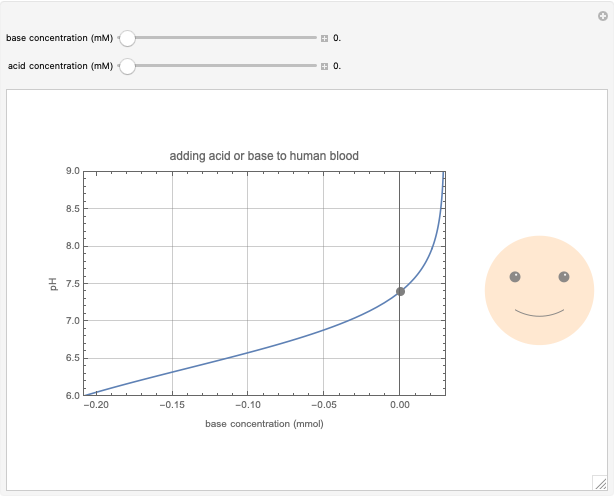
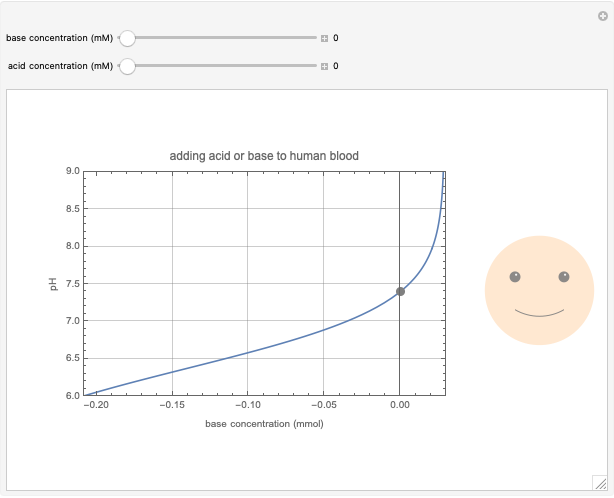
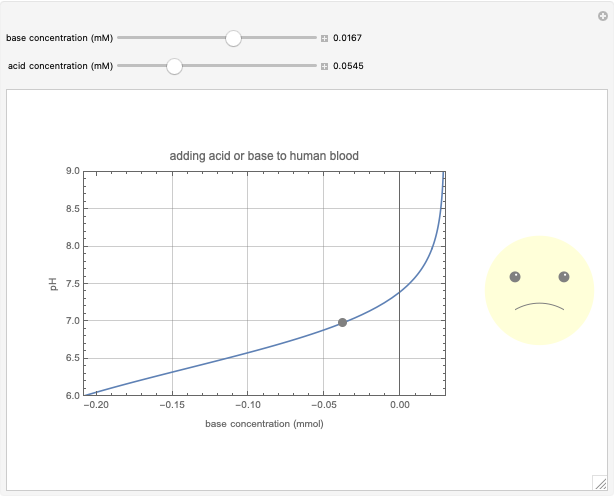
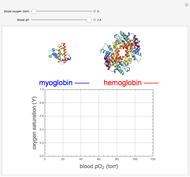
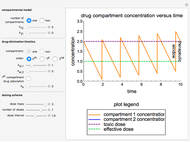
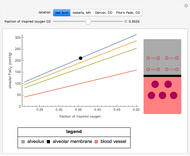
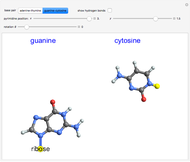
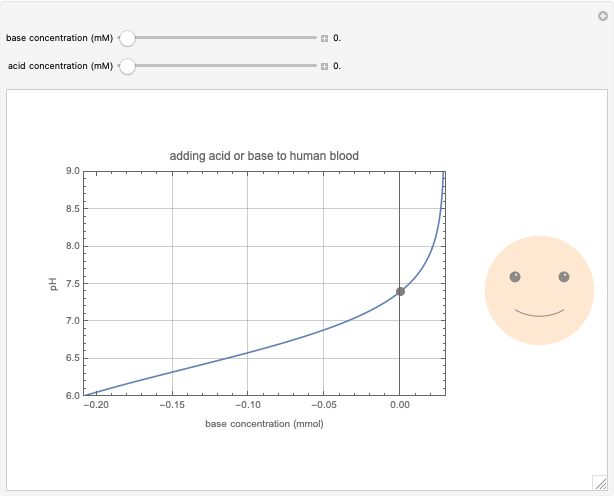
This Demonstration simulates the buffer system in human blood, showing its resistance to a change in pH by the addition of acid or base. Human blood contains carbonic acid  and bicarbonate anion
and bicarbonate anion  , which form a buffer to maintain blood pH between 7.35 and 7.45.
, which form a buffer to maintain blood pH between 7.35 and 7.45.
Contributed by: Claire Chen and Hongdi Wu (August 2022)
With additional contributions by: Dalia Hassan, Yifan Lai and Kristina M. Lenn
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
[1] J. Pietri and D. Land. "Blood as a Buffer." (Nov 24, 2021) chem.libretexts.org/@go/page/1297.
[2] Wikipedia. "Bicarbonate Buffer System." (Nov 24, 2021) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bicarbonate_buffer_system.
[3] Khan Academy. "Chemistry of Buffers and Buffers in Our Blood." (Nov 24, 2021) www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/chemical-processes/acid-base-equilibria/a/chemistry-of-buffers-and-buffers-in-blood.
Permanent Citation