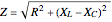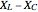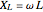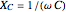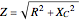Electrical Impedance of Biological Tissues
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
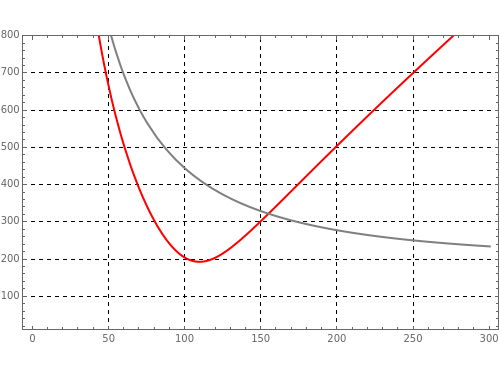
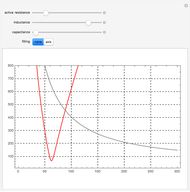
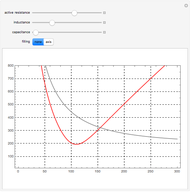
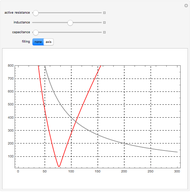
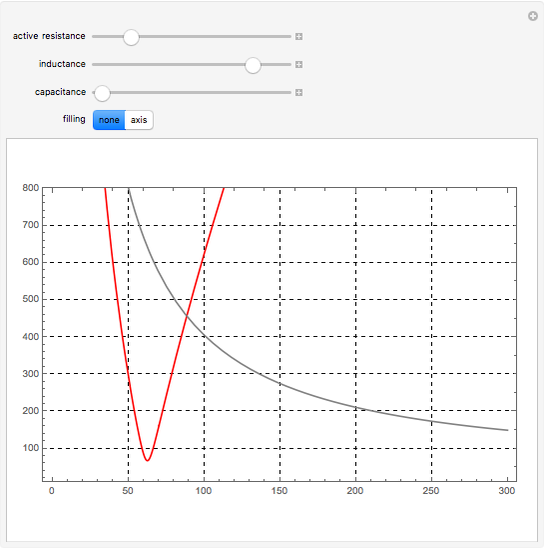
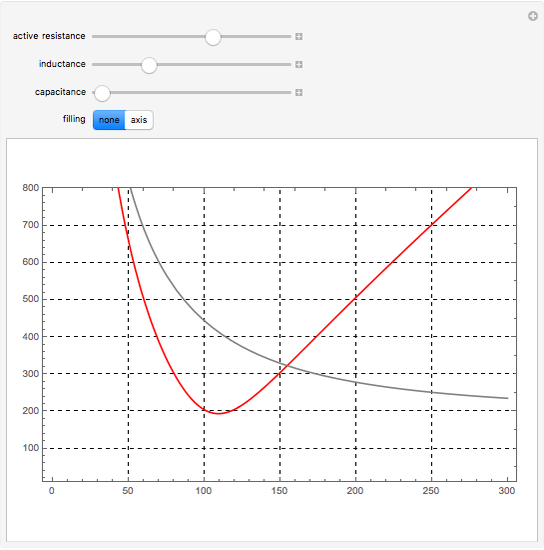
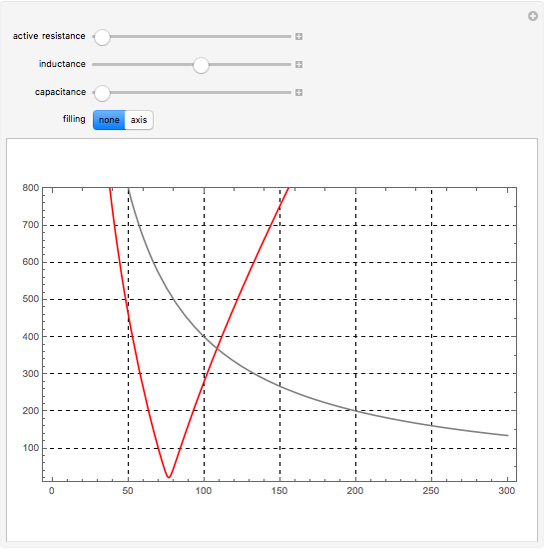
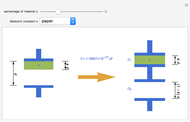
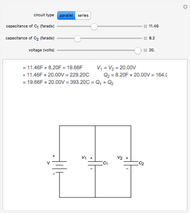
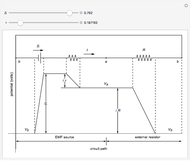
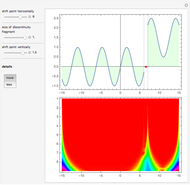
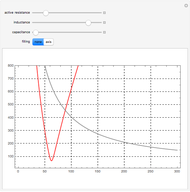
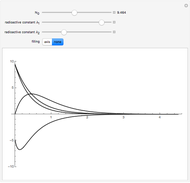
Electrical impedance (or simply impedance or total resistance) 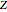 measures opposition to a sinusoidal alternating current (AC). Electrical impedance extends the concept of resistance to AC circuits. Impedance is the complex generalization of resistance. In most cases, impedance is a function of the frequency (ω in radians/sec or
measures opposition to a sinusoidal alternating current (AC). Electrical impedance extends the concept of resistance to AC circuits. Impedance is the complex generalization of resistance. In most cases, impedance is a function of the frequency (ω in radians/sec or 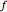 in hertz), resistance
in hertz), resistance 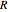 (in ohms), inductance
(in ohms), inductance 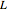 (in henries), and capacitance
(in henries), and capacitance 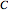 (in farads):
(in farads):
Contributed by: Olexandr Eugene Prokopchenko (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation