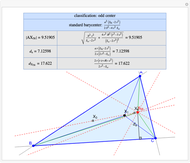
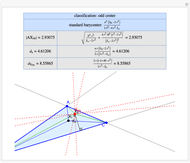
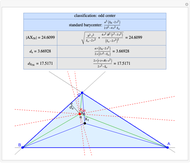
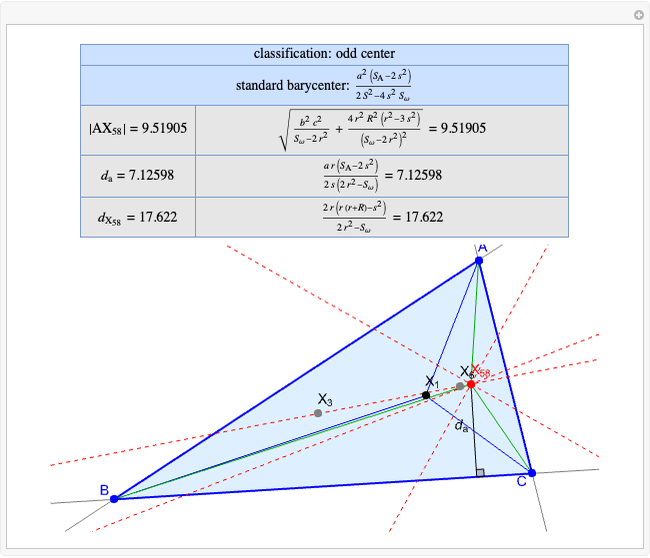
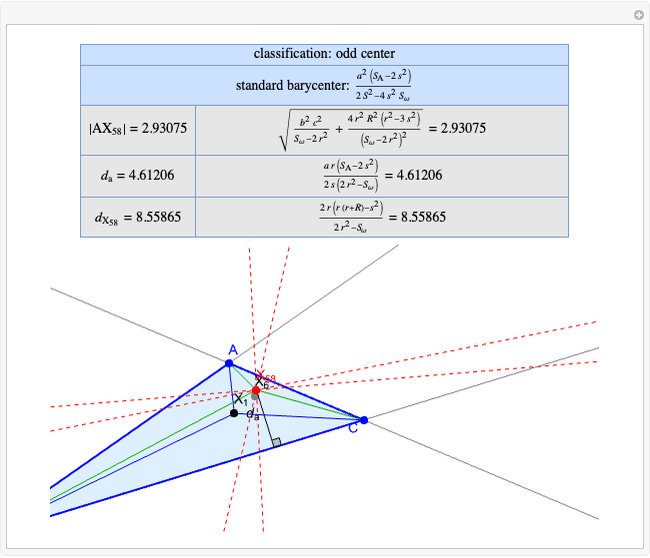
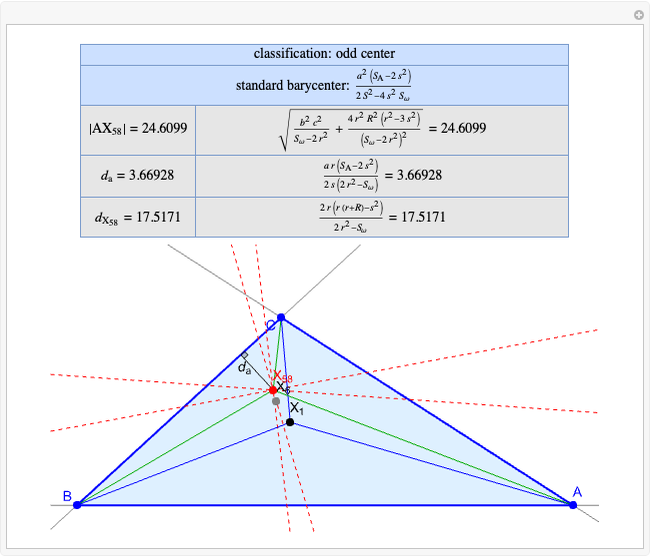
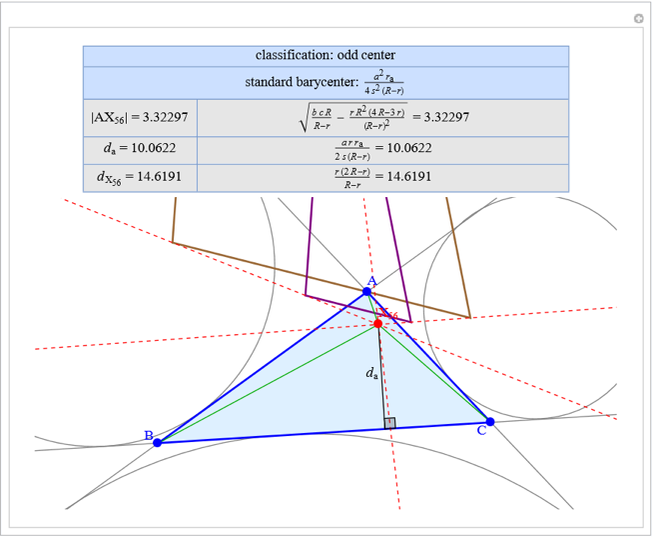
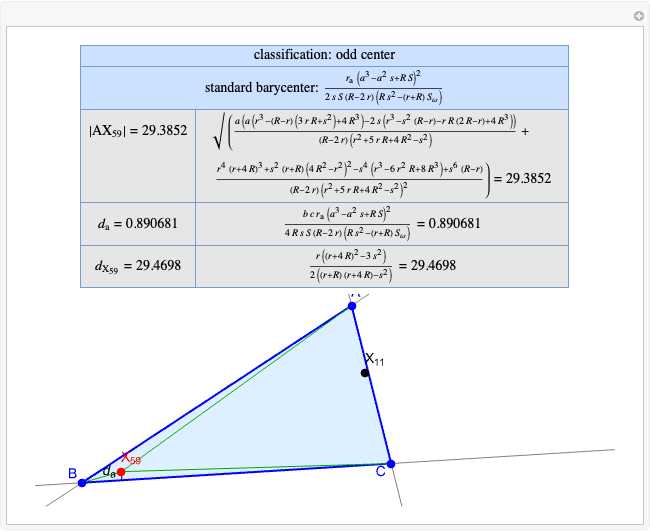
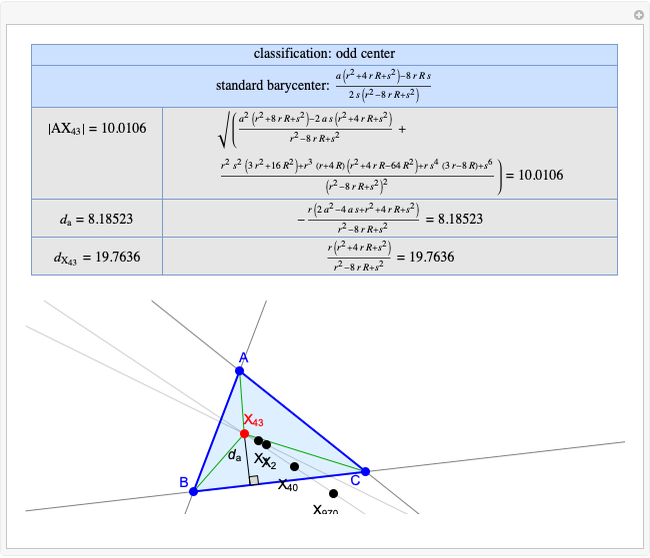
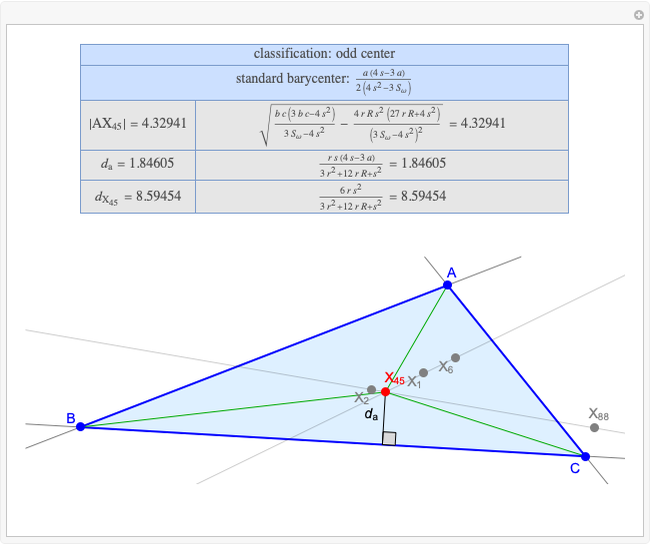
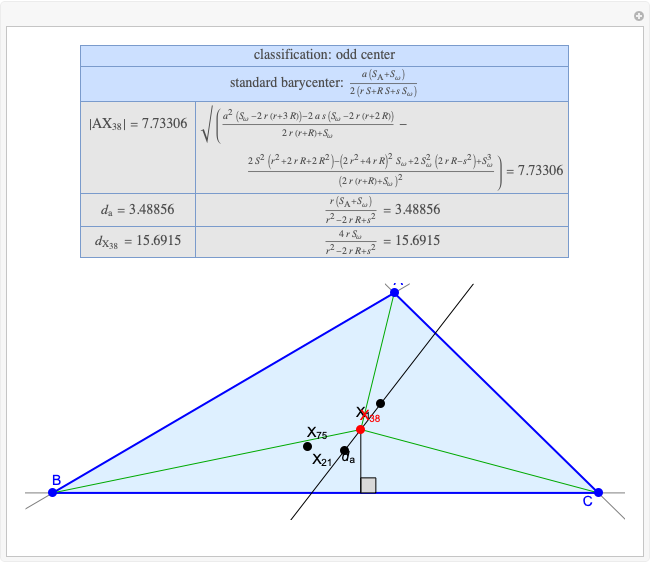
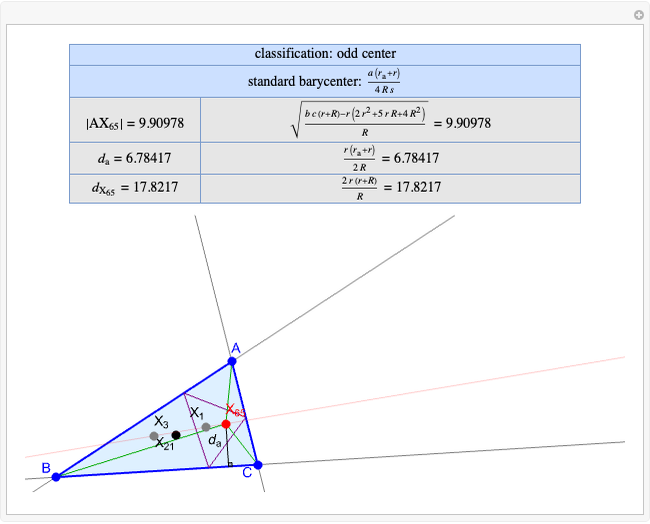
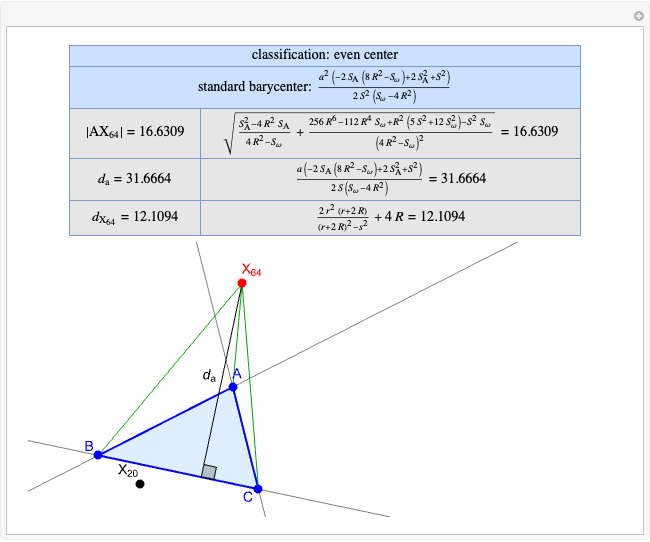
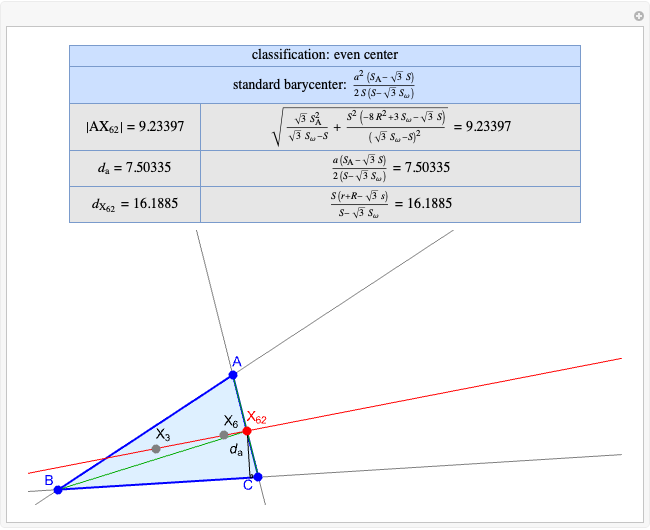
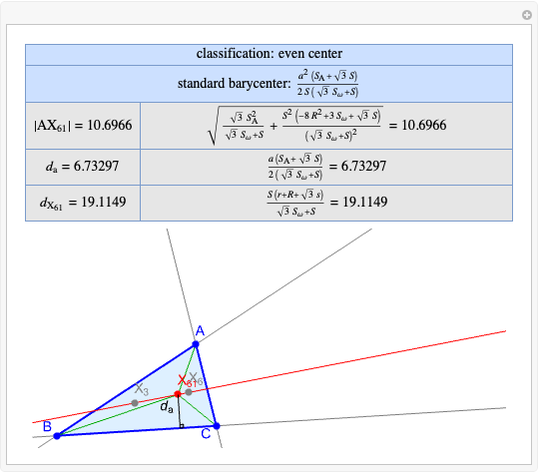
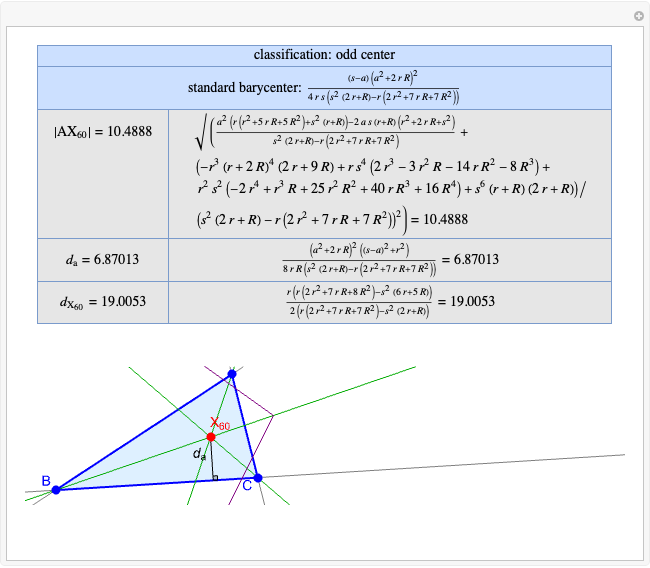
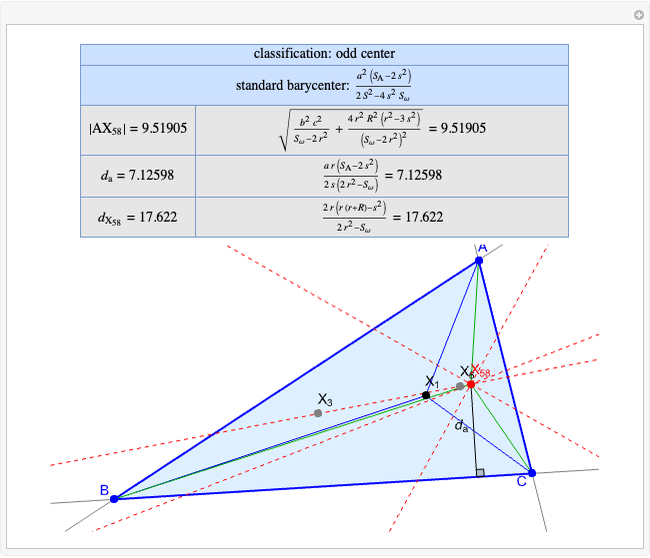
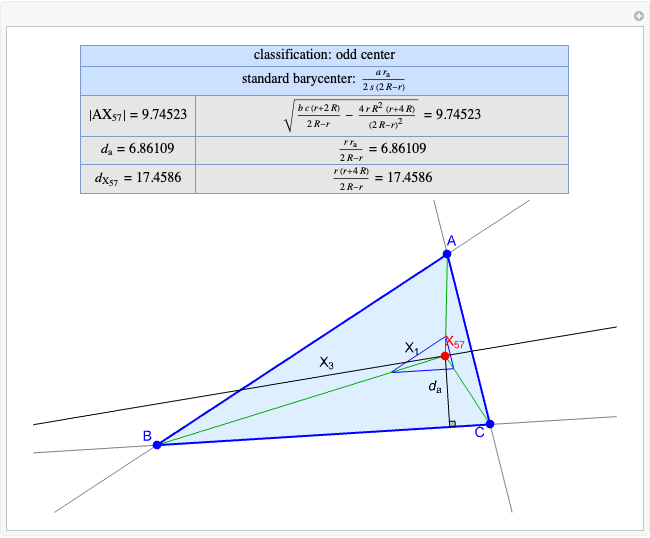
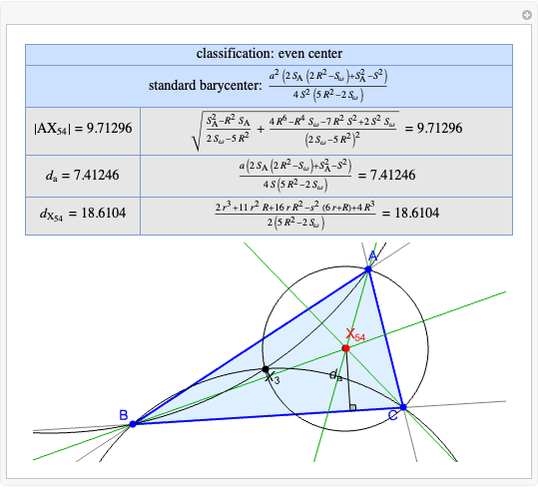
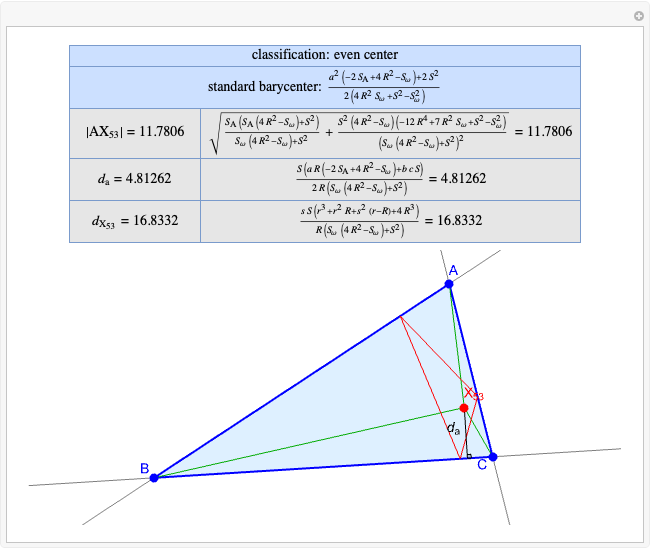
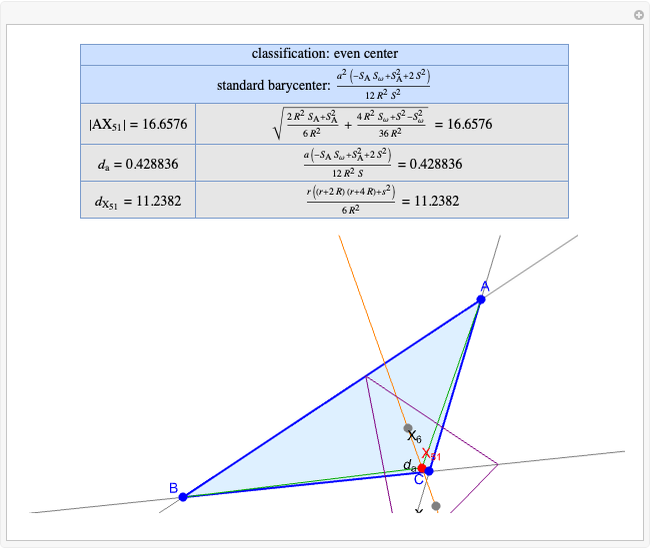
Basic Parameters of the Kimberling Center X(58)

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
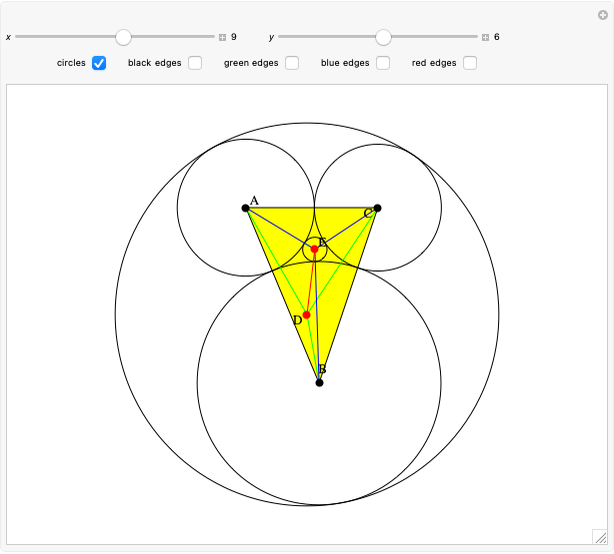
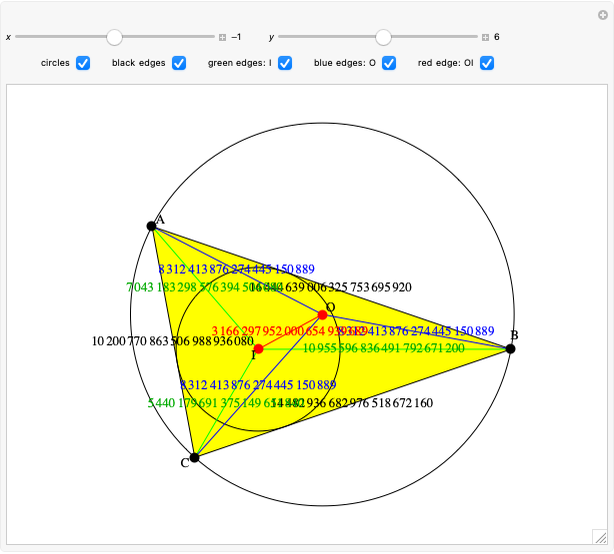
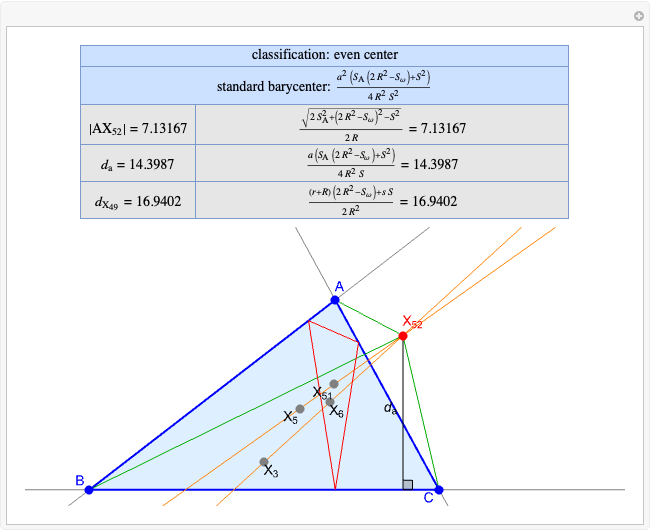
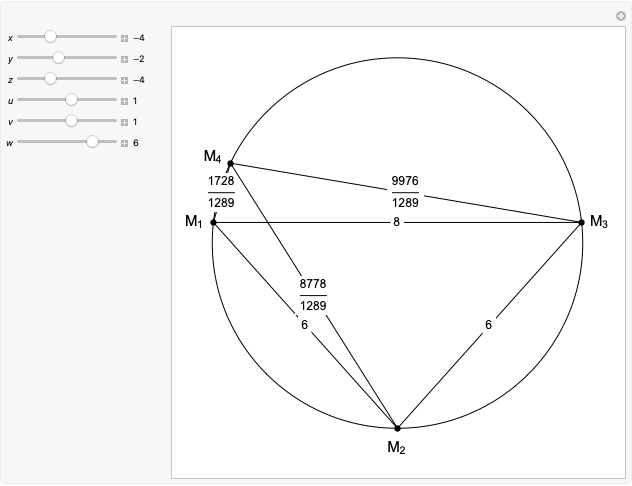
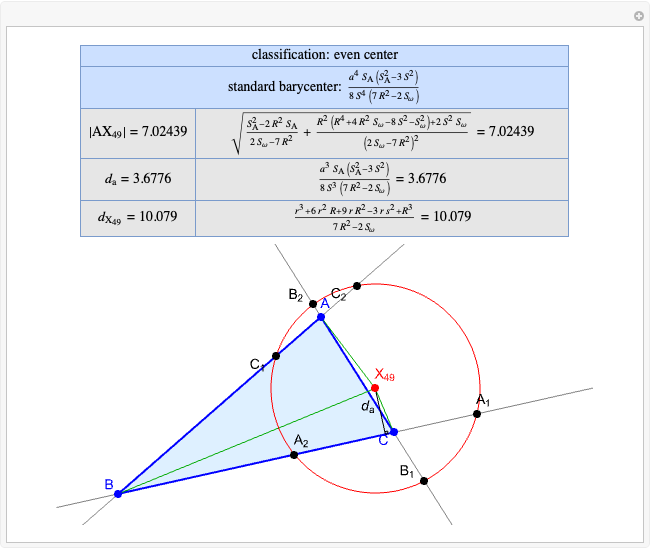
Given a triangle  , the Kimberling center
, the Kimberling center  is the intersection of the Brocard axis of the triangles
is the intersection of the Brocard axis of the triangles  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  (where
(where  is the incenter
is the incenter  ) [1]. The Brocard axis is the line joining the symmedian point and the circumcenter of
) [1]. The Brocard axis is the line joining the symmedian point and the circumcenter of  .
.
Contributed by: Minh Trinh Xuan (August 25)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Details
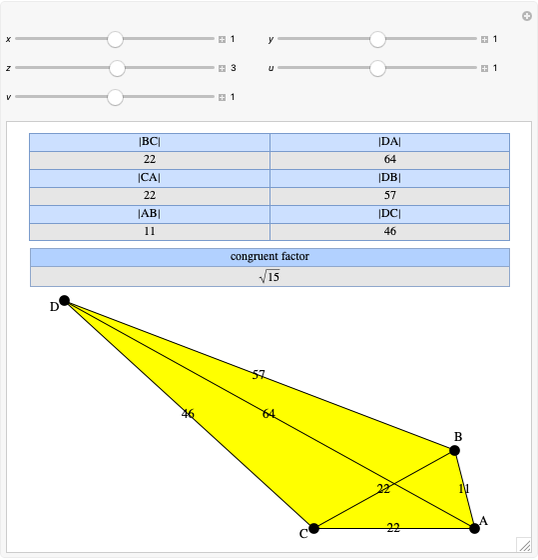
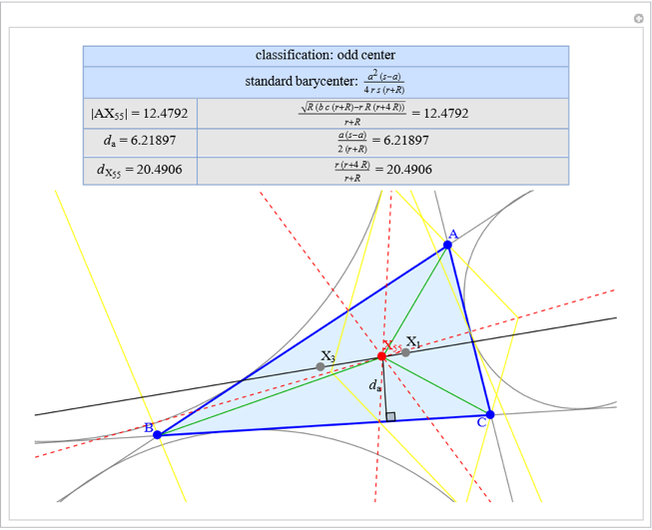
A triangle center is said to be even when its barycentric coordinates can be expressed as a function of three variables  ,
,  ,
,  that all occur with even exponents. If the center of a triangle has constant barycentric coordinates, it is called a neutral center (the centroid
that all occur with even exponents. If the center of a triangle has constant barycentric coordinates, it is called a neutral center (the centroid  is the only neutral center). A triangle center is said to be odd if it is neither even nor neutral.
is the only neutral center). A triangle center is said to be odd if it is neither even nor neutral.
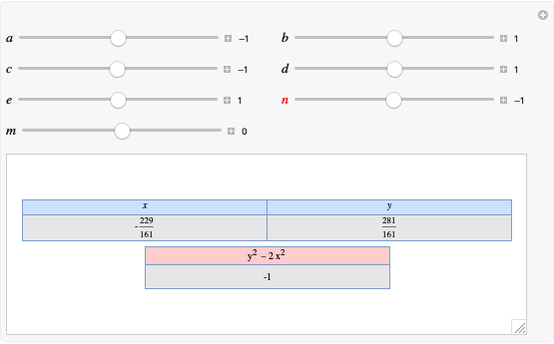
Standard barycentric coordinates of a point with respect to a reference triangle have a sum of 1.
References
[1] A. P. Hatzipolakis, F. van Lamoen, B. Wolk and P. Yiu, "Concurrency of Four Euler Lines," Forum Geometricorum, 1, 2001 pp. 59–68. forumgeom.fau.edu/FG2001volume1/FG200109.pdf.
[2] C. Kimberling. "Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers." (Jul 7, 2023) faculty.evansville.edu/ck6/encyclopedia.
Snapshots
Permanent Citation