Bragg's Law

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
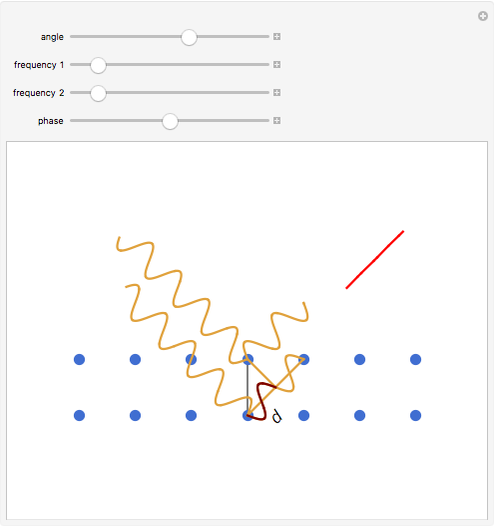
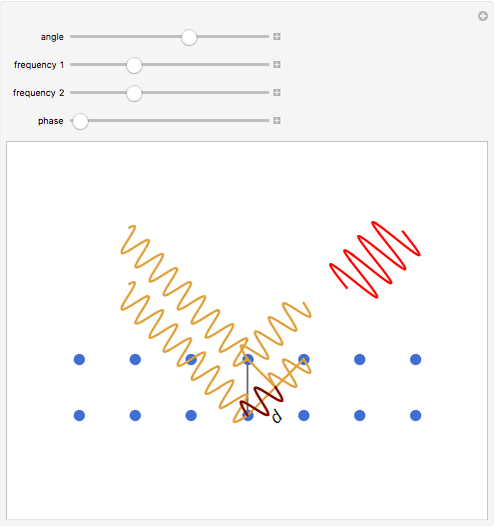
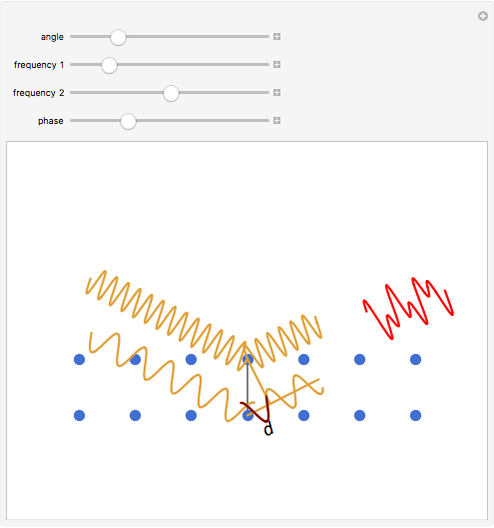
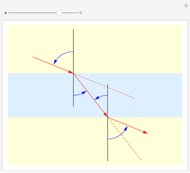
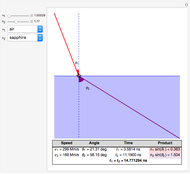
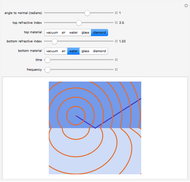
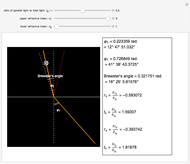
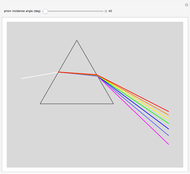
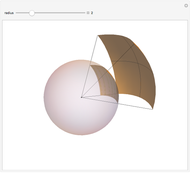
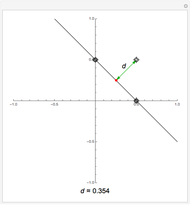
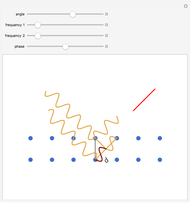
Bragg's law describes the reflection of a monochromatic xâ€Âray beam by two parallel crystalline planes separated by a distance  . The difference in path lengths is equal to
. The difference in path lengths is equal to  and this determines a necessary condition for constructive interference from a family of parallel planes. The Bragg condition enables spacings between many different sets of crystalline planes to be determined.
and this determines a necessary condition for constructive interference from a family of parallel planes. The Bragg condition enables spacings between many different sets of crystalline planes to be determined.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (February 2009)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
detailSectionParagraphPermanent Citation
"Bragg's Law"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/BraggsLaw/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: February 20 2009