Chinese Postman Problem

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
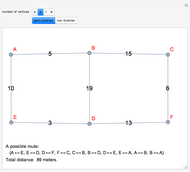
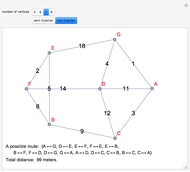
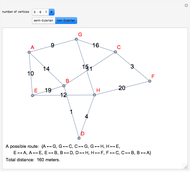
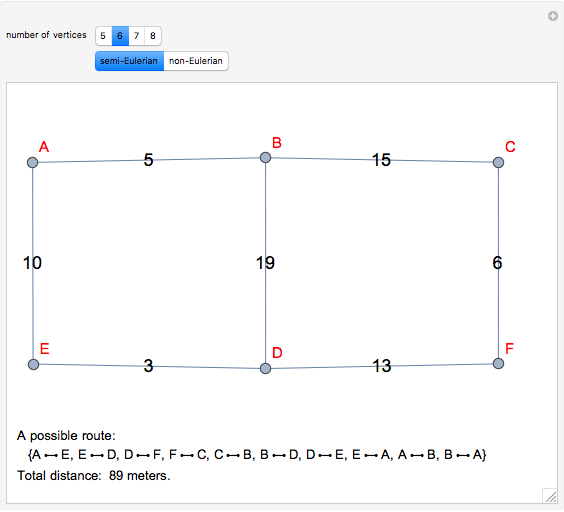
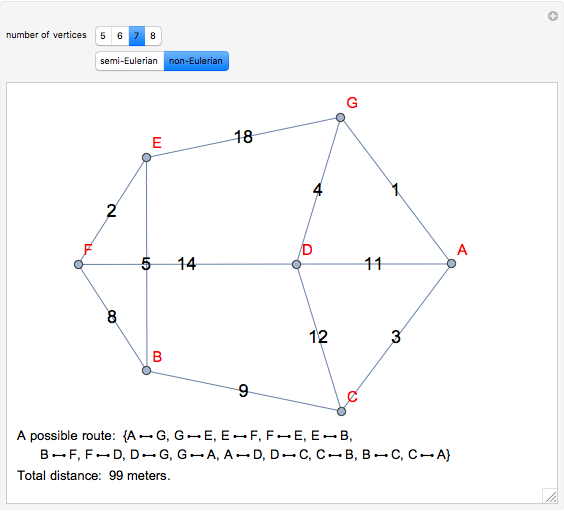
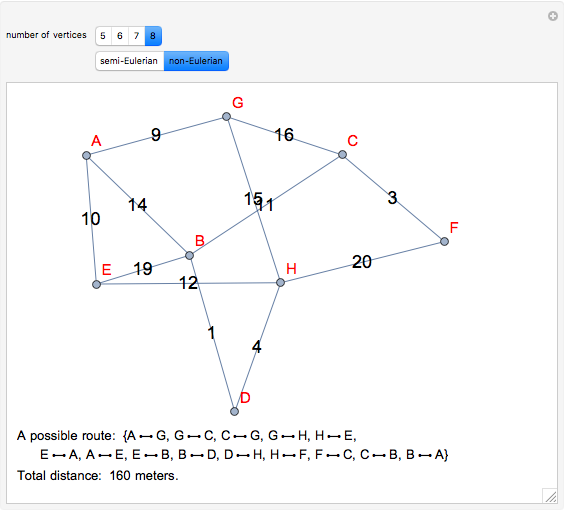
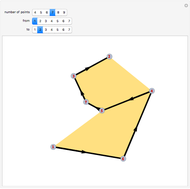
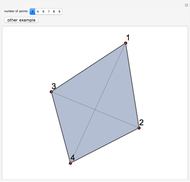
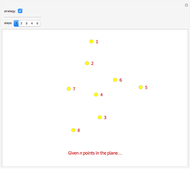
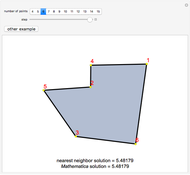
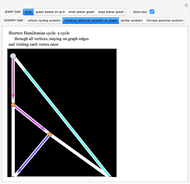
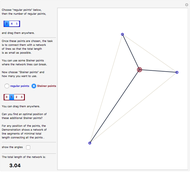
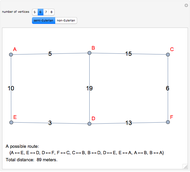
The Chinese postman problem asks for the shortest route that covers all the edges in a graph, starting and ending at the same vertex. The route may repeat some edges. The total distance traversed is the sum of the lengths of all the edges in the route. There are many possibilities, which can be generated using random graphs or other techniques.
Contributed by: Rinashini Arunasalam (August 2016)
(OEMS IntiPakar Corporation Sdn Bhd)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
To determine the shortest path:
1. Find the degree of each vertex. If there is a pair of vertices of odd degree, the graph is semi-Eulerian. If there are more than two vertices of odd degree, the graph is non-Eulerian.
2. Create additional paths using pairs of vertices of odd degree.
3. Determine the minimum of these additional paths.
4. Trace a possible route starting and ending at a particular vertex.
5. Calculate the total distance traveled.
There may be more than one possible route.
Reference
[1] Wikipedia. "Route Inspection problem." (Aug 8, 2016) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Route_inspection_problem.
Permanent Citation
"Chinese Postman Problem"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ChinesePostmanProblem/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: August 10 2016