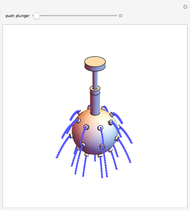
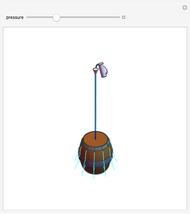
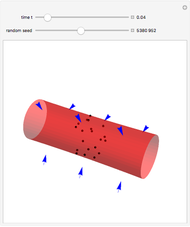
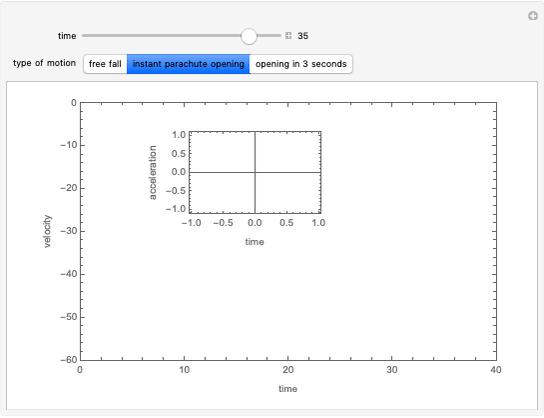
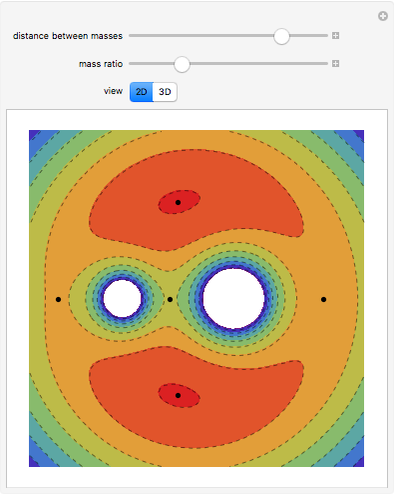
Forces Exerted on an Immersed Object
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
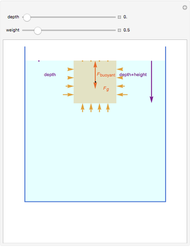
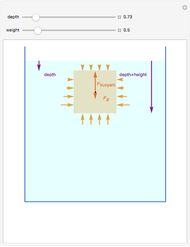
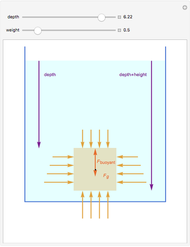
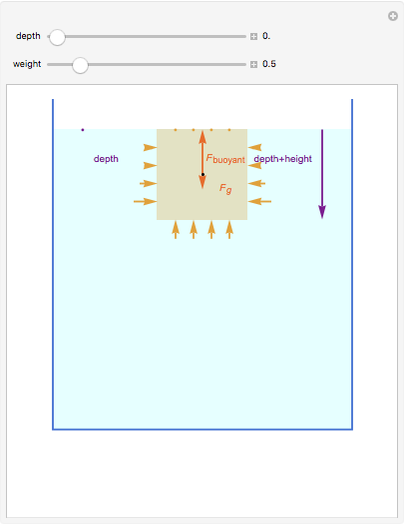
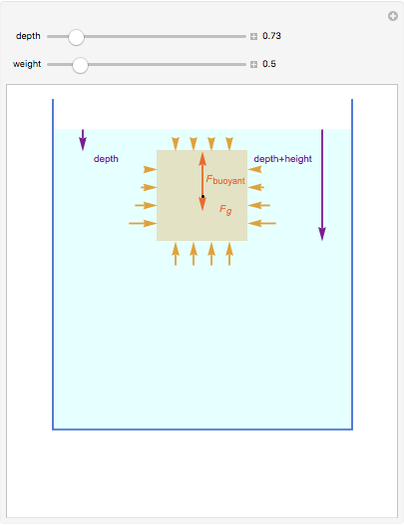
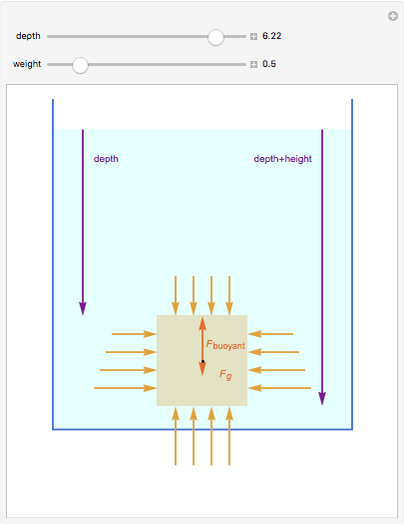
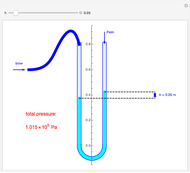
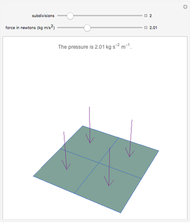
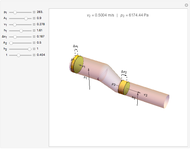
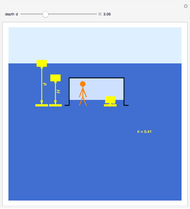
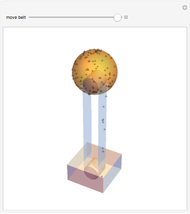
An object is immersed in a fluid, which can be a liquid or a gas. Buoyancy is a net upward force that acts on the object.
[more]
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation