Free Energy Changes in Homogeneous Nucleation

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
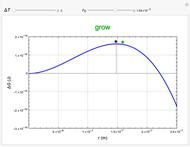
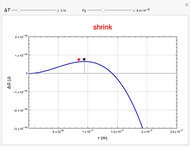
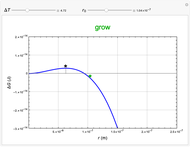
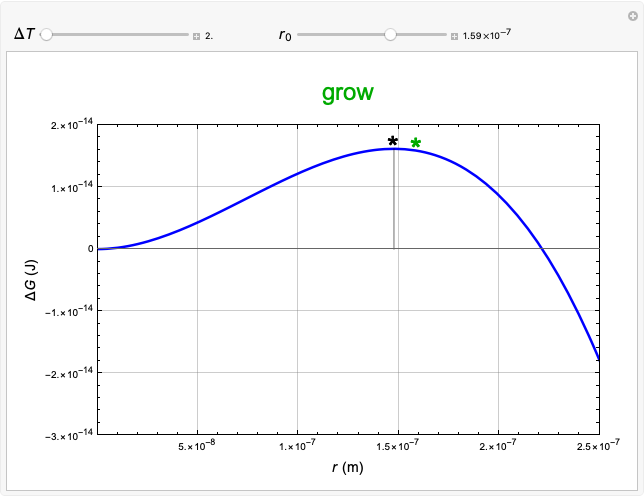
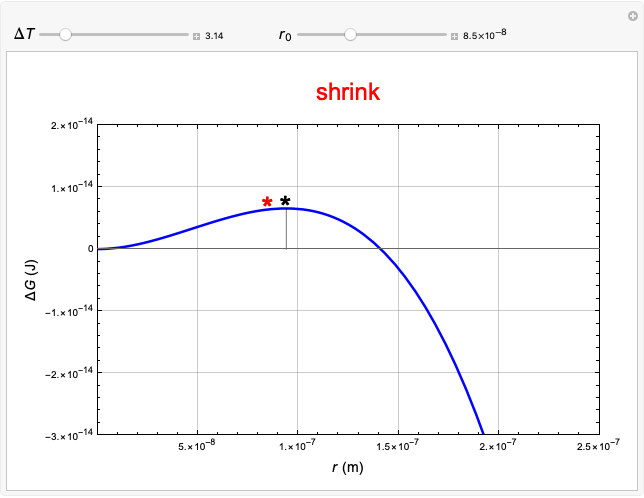
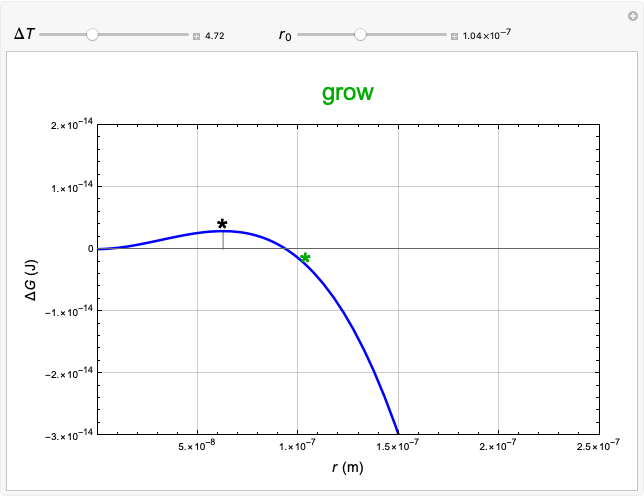
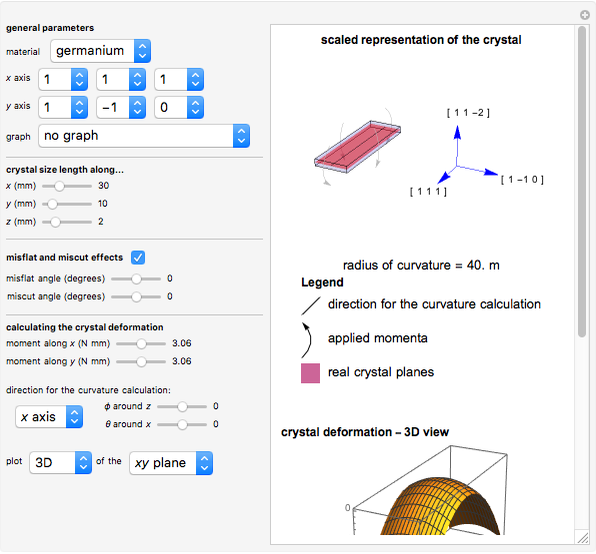
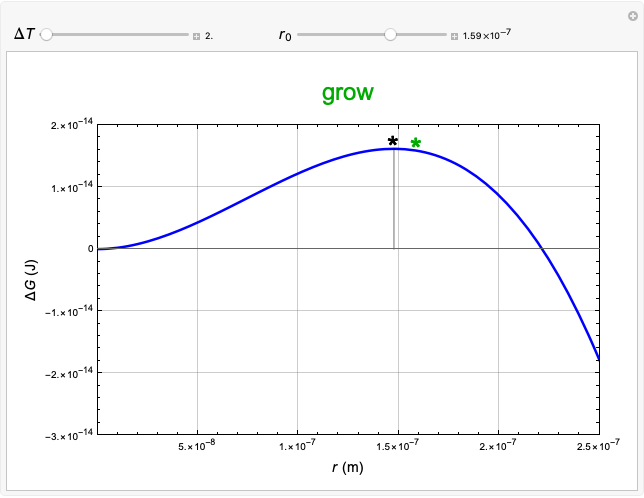
This Demonstration considers the free energy changes involved in homogeneous nucleation and growth. The plot represents the free energy of a grain (in J) as a function of the radius (in m):  . As
. As  increases, the volume and surface area both increase. The interfacial term
increases, the volume and surface area both increase. The interfacial term  scales quadratically with the radius, while the volumetric term
scales quadratically with the radius, while the volumetric term  scales as the cube of the radius. There is no increase in free energy from interaction between like particles within a grain, thus the volumetric term decreases free energy. As the radius increases, volume increases faster than surface area, thus minimizing energetically unfavorable surface formation compared to the increase in volume.
scales as the cube of the radius. There is no increase in free energy from interaction between like particles within a grain, thus the volumetric term decreases free energy. As the radius increases, volume increases faster than surface area, thus minimizing energetically unfavorable surface formation compared to the increase in volume.
Contributed by: Ethan Hall, Brian Winchester and Joshua Paul Steimel. (June 13)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Details
Reference
[1] J. P. Steimel, "Materials Science and Engineering," Pacific Open Texts. (Sep 22, 2021) scholarlycommons.pacific.edu/open-textbooks/8.
Snapshots
Permanent Citation