Iterated Games

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
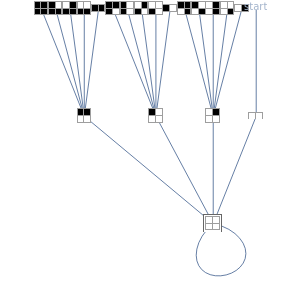
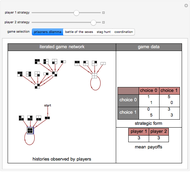
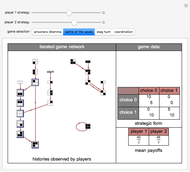
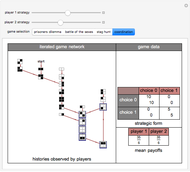
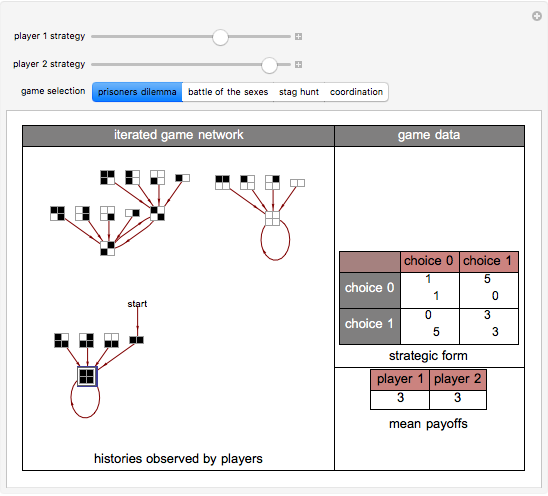
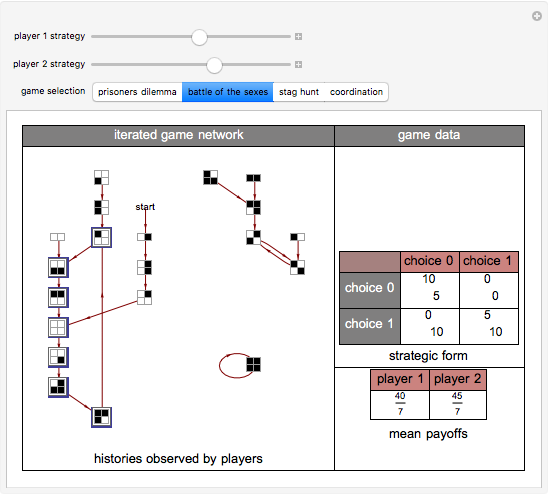
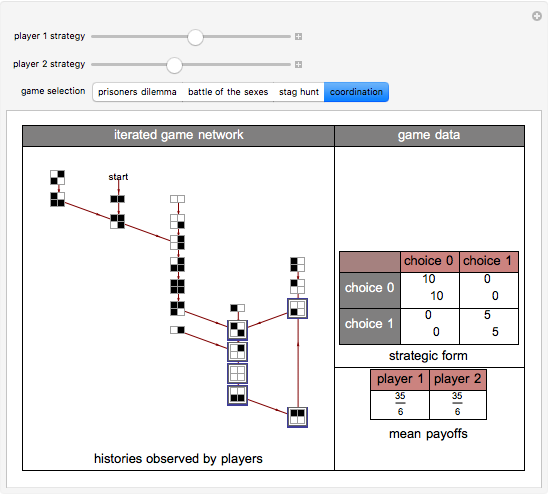
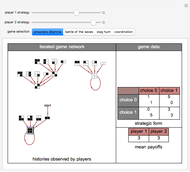
Often players in a scenario that can be modeled as a strategic form game engage in repeated interactions with each other. In such instances, their selection of a strategy on a given "iteration" may depend on their history of previous interactions. By way of example, a player might start by playing strategy 1 and continue playing it unless the history of interactions were such that the opposing player had played 0 on his/her last two turns. This Demonstration permits a selection for each player from the 2,097,152 (2^21) strategies that depend on the prior two interactions of the players. It shows the resulting "directed graph" of histories the players could observe, the steady-state cycle of histories that will be observed, the payoffs from the selected strategic form game, and the mean payoffs received by the players in the steady state.
Contributed by: Seth Chandler (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Histories that are part of the steadyâ€Âstate cycle are shown as framed.
There are 2^42 (≈ 4.4 trillion) possible strategy combinations that the players can employ in this game and that can be selected using the two top sliders.
A "tit-for-tat" strategy can be implemented by having player 1 use strategy 1398101 and by having player 2 use strategy 1973785.
Permanent Citation
"Iterated Games"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/IteratedGames/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011