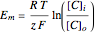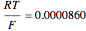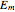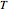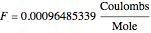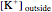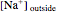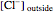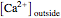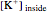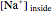Nernst Equation for Cellular Membranes
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
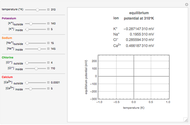
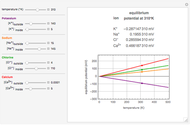
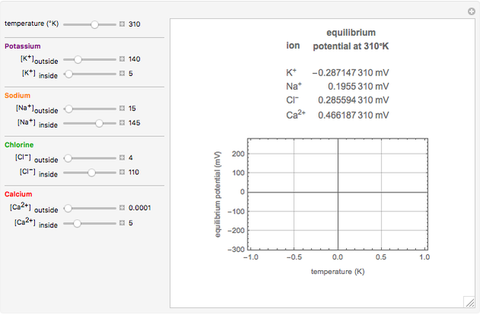
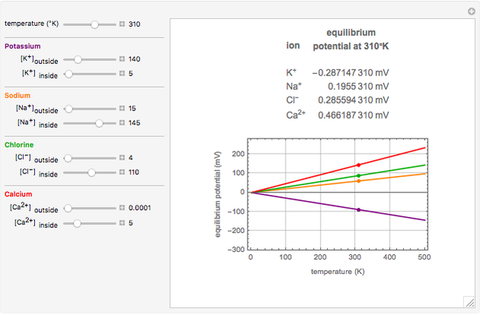
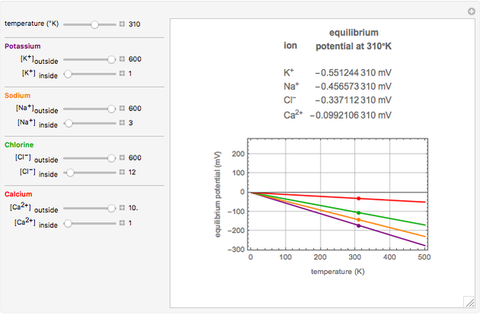
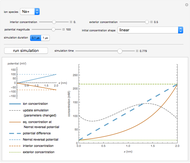
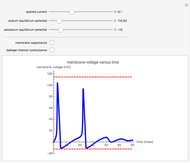
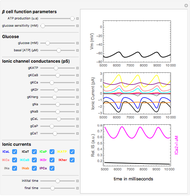
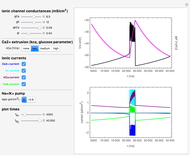
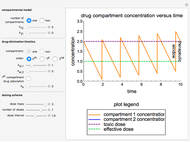
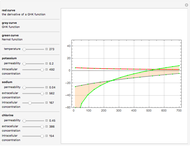
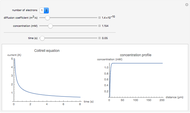
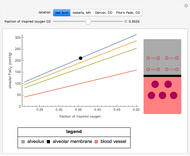
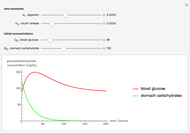
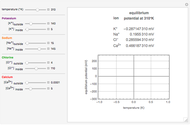
The Nernst equation is used to determine the potential of an ion of charge  across a membrane using both extracellular and intracellular concentrations. It can be written as
across a membrane using both extracellular and intracellular concentrations. It can be written as
Contributed by: Apoorva Mylavarapu (February 2014)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] D. H. Terman and G. B. Ermentrout, Foundations of Mathematical Neuroscience, New York: Springer, 2010 pp. 2–5.
Permanent Citation