Physics of a Rear-End Collision

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
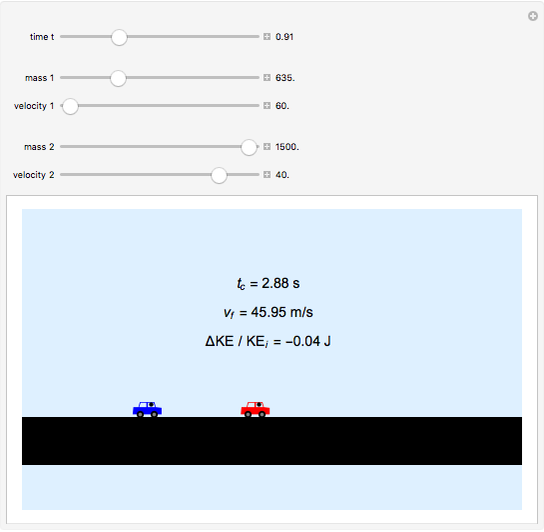
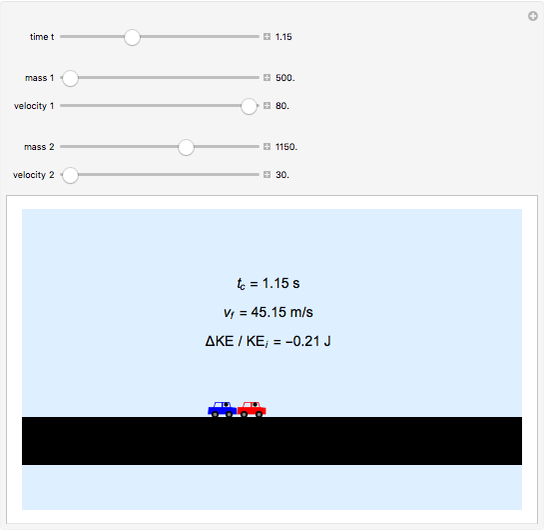
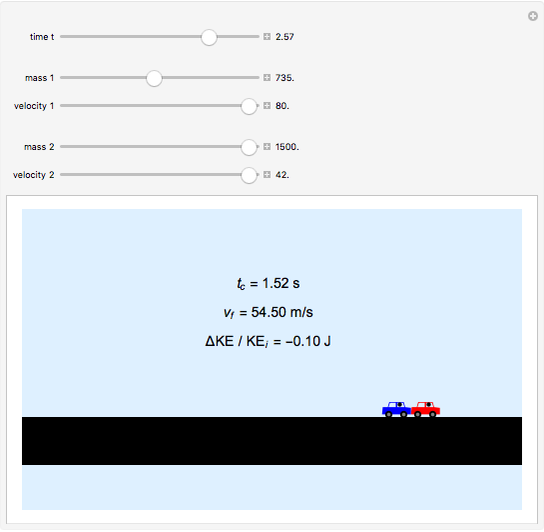
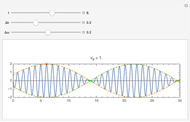
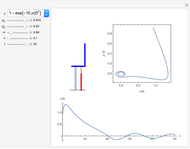
Two cars travel in the same direction on a slippery road. Initially they are 16 m apart. They have a rear-end collision at time  and travel together after that. Their masses are
and travel together after that. Their masses are  (blue) and
(blue) and  (red), and their velocities are
(red), and their velocities are  and
and  . Using conservation of momentum, the velocity after the collision is calculated, as is the kinetic energy lost in the collision.
. Using conservation of momentum, the velocity after the collision is calculated, as is the kinetic energy lost in the collision.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The velocity of the cars after collision is  . The kinetic energy lost is
. The kinetic energy lost is  , where
, where  and
and  are the kinetic energies of each car before the collision, and
are the kinetic energies of each car before the collision, and  is the kinetic energy of both cars considered as a single body after the collision.
is the kinetic energy of both cars considered as a single body after the collision.
Permanent Citation