The Mass Spectrometer

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
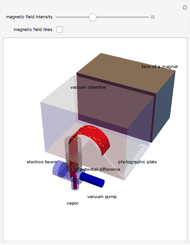
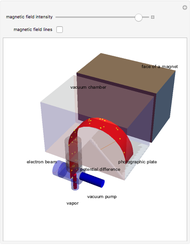
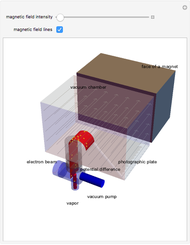
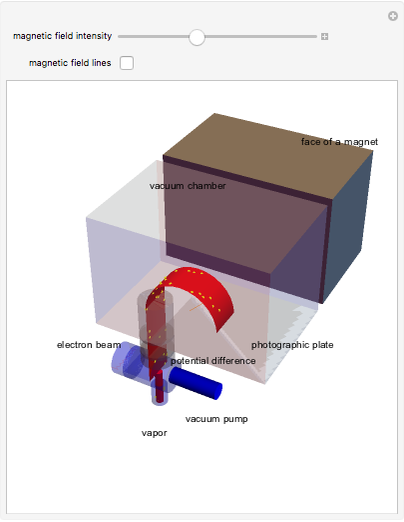
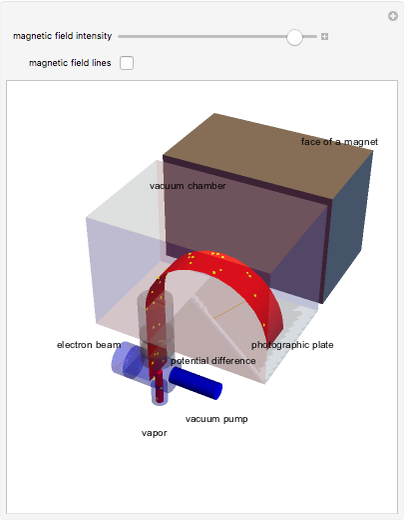
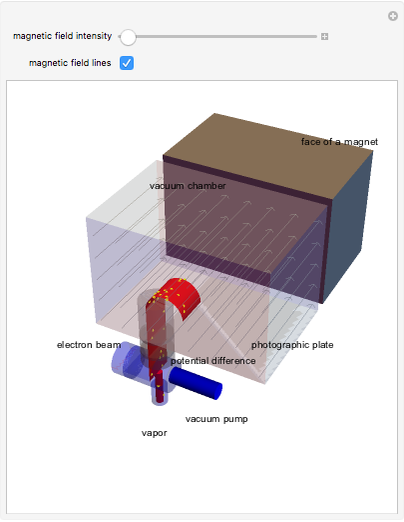
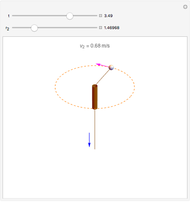
The mass spectrometer is a device used to study isotopes of ions produced in a cathode ray tube. Isotopes of an element share the same chemical properties but have different masses and produce different values for their charge-to-mass ratio. An electron beam strikes vapor atoms that yield positive ions accelerated by a potential difference and deflected by a uniform magnetic field to hit a photographic plate. Mass spectrometry can also be used to identify molecules by analyzing the masses of its fragments.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The charge-to-mass ratio  of an ion can be derived from Newton's second law and the Lorenz force, yielding
of an ion can be derived from Newton's second law and the Lorenz force, yielding
 ,
,
where  is the charge,
is the charge,  is the mass,
is the mass, 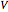 is the potential difference,
is the potential difference, 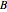 is the magnetic field intensity, and
is the magnetic field intensity, and  is the radius of gyration.
is the radius of gyration.
Permanent Citation