Six Triangle Orbits
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
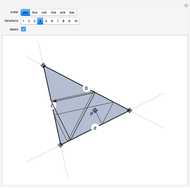
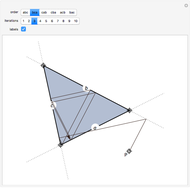
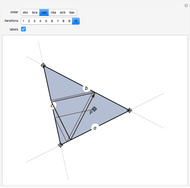
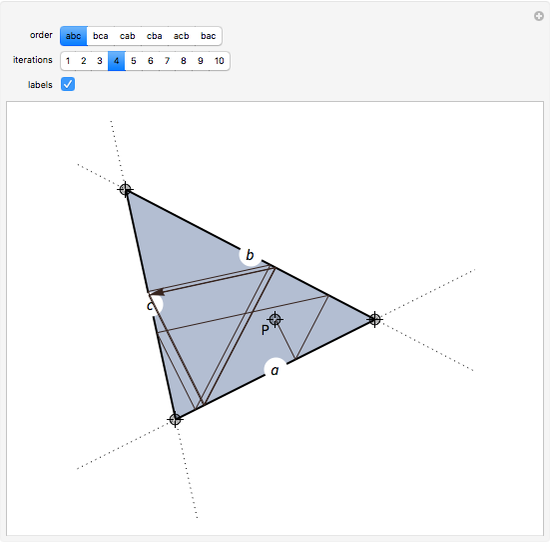
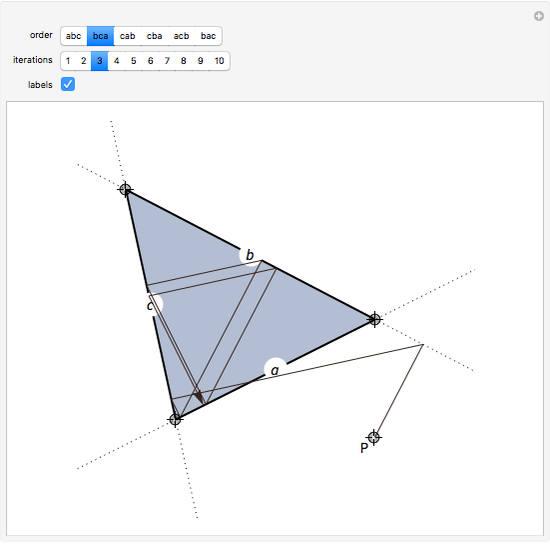
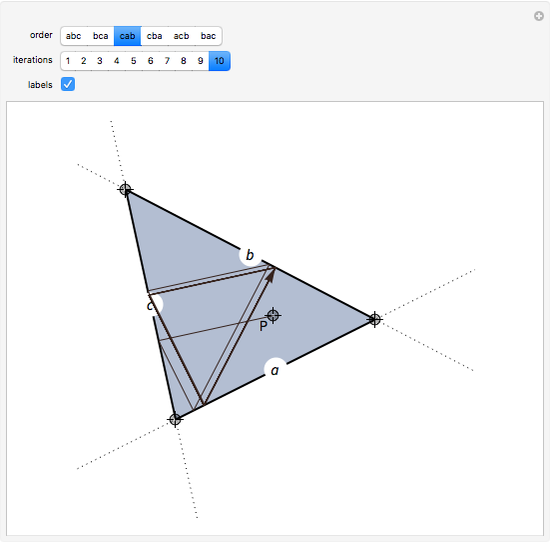
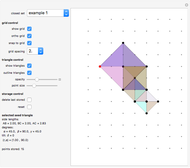
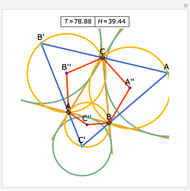
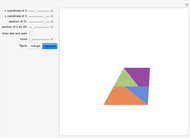
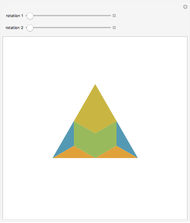
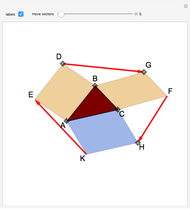
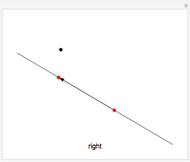
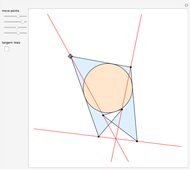
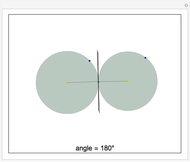
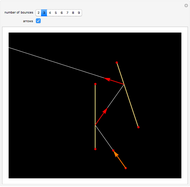
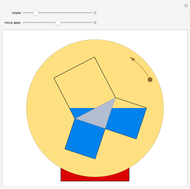
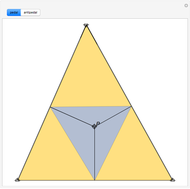
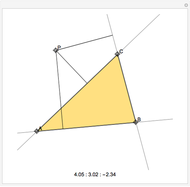
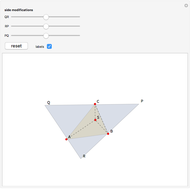
Consider a triangle with sides labeled  ,
,  ,
,  and a point
and a point 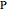 and its trajectory as it visits each side of the triangle in some prespecified order, always taking the shortest route (by side we mean the infinite line resulting from extending the actual side of the triangle in both directions.)
and its trajectory as it visits each side of the triangle in some prespecified order, always taking the shortest route (by side we mean the infinite line resulting from extending the actual side of the triangle in both directions.)
Contributed by: Jaime Rangel-Mondragon (August 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] M. Carvalho and M. Hager, "Geometric Orbits," The Mathematical Intelligencer, 34(2), 2012 pp. 56–62. doi:10.1007/s00283-012-9287-y.
Permanent Citation