Two-State Protein Melting Curve (N, P, T Ensemble)

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
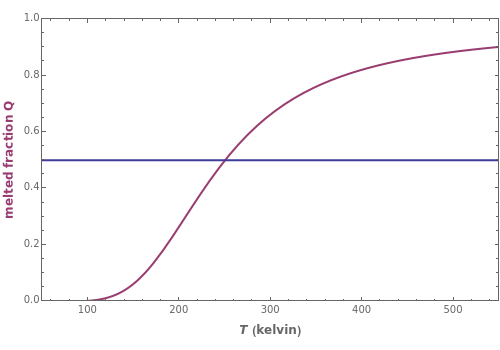
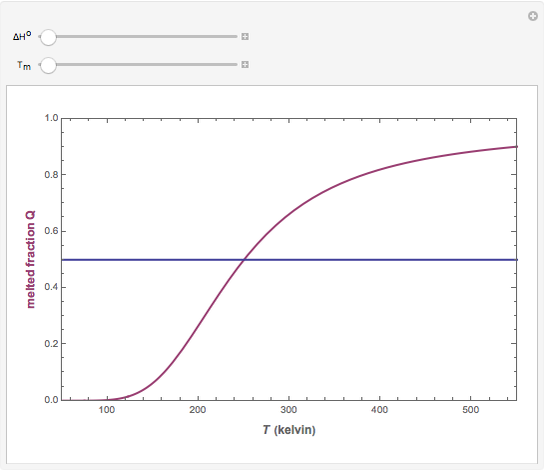
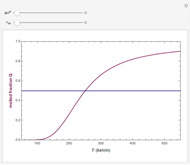
This Demonstration illustrates the fraction ( ) of a two‐state protein (or other biomolecule) that has melted at temperature
) of a two‐state protein (or other biomolecule) that has melted at temperature  . The two states of the protein are denoted
. The two states of the protein are denoted  (native or folded) and
(native or folded) and 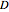 (denatured or melted) and we consider the dynamic equilibrium
(denatured or melted) and we consider the dynamic equilibrium  . The ratio of the two states' equilibrium concentrations is
. The ratio of the two states' equilibrium concentrations is  , where
, where  ) is the standard state Gibbs free energy difference and
) is the standard state Gibbs free energy difference and  is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol-K). Melting occurs when
is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol-K). Melting occurs when  (i.e.,
(i.e.,  ).
).  . The parameter
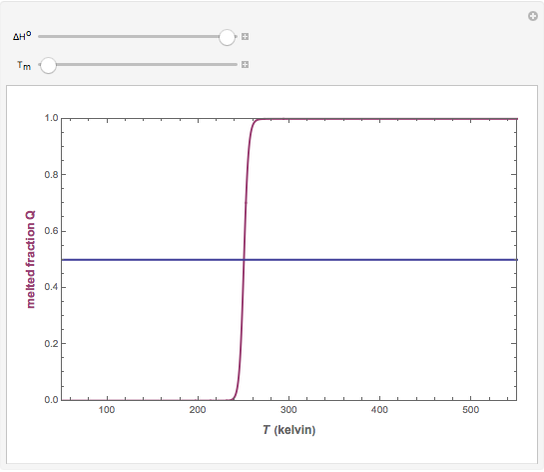
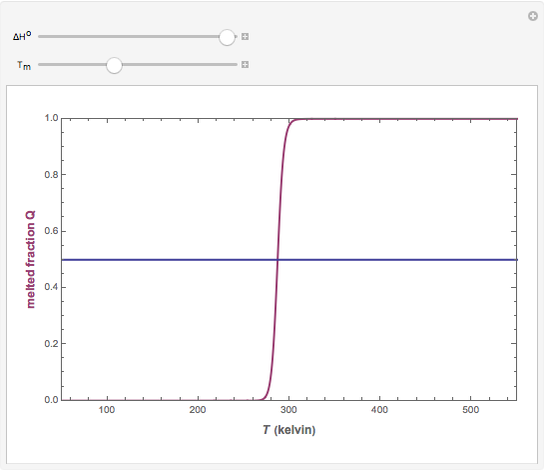
. The parameter  (standard state enthalpy difference) controls the steepness of the transition, but does not affect the location of the point where
(standard state enthalpy difference) controls the steepness of the transition, but does not affect the location of the point where  . The temperature (
. The temperature ( ) at which
) at which  is
is  and
and  .
.
Contributed by: David L. Pincus (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation